|
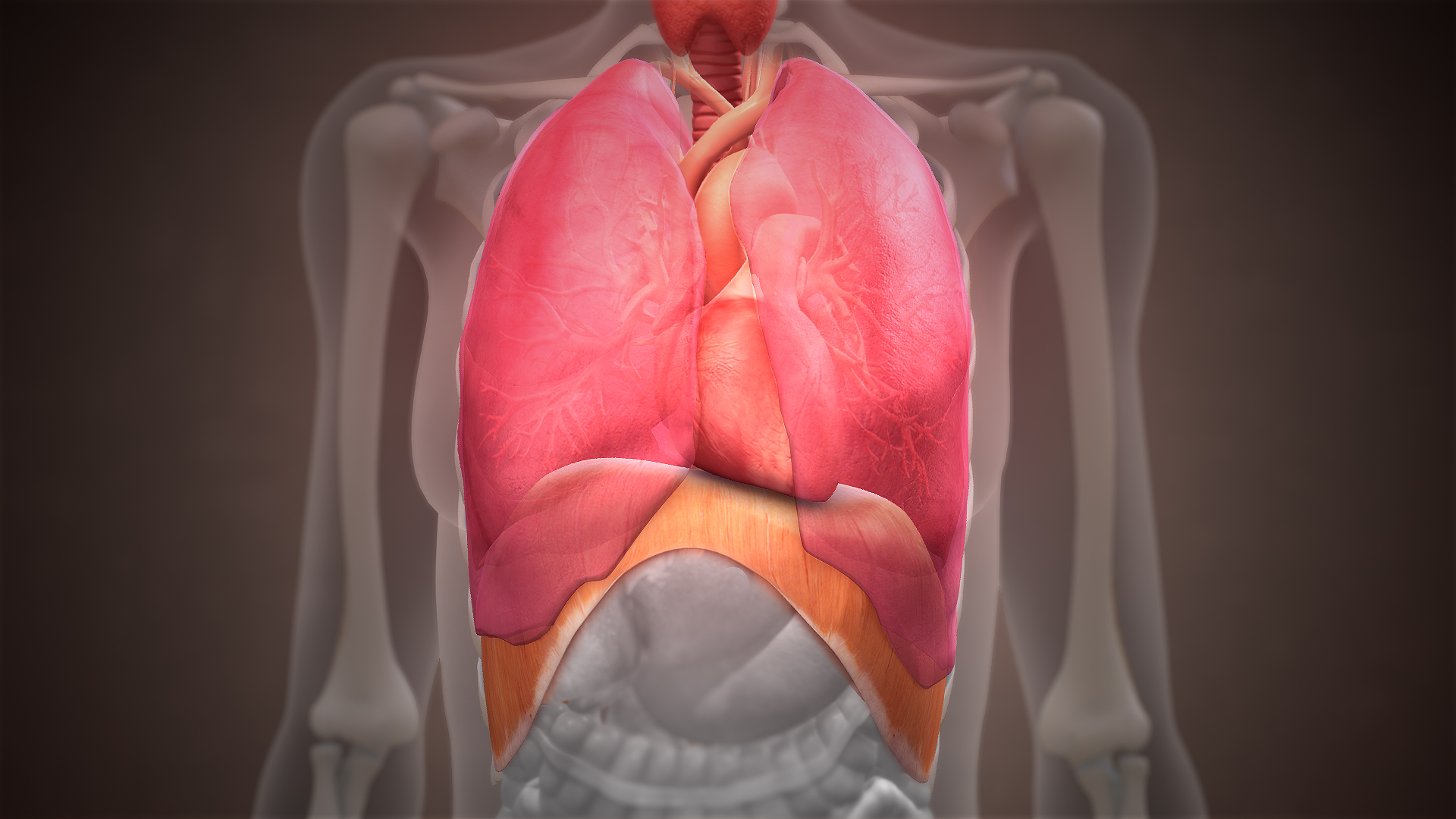
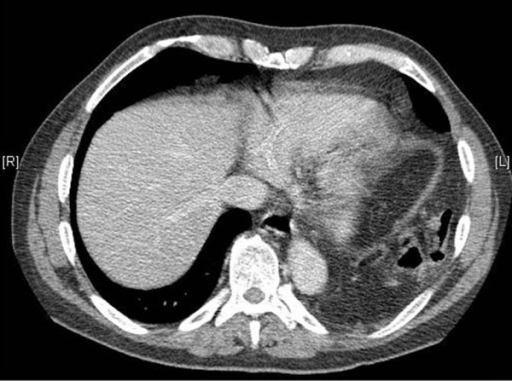
Diaphragmatic Hernia
Diaphragmatic hernia is a defect or hole in the diaphragm that allows the abdominal contents to move into the chest cavity. Treatment is usually surgical. Types * Congenital diaphragmatic hernia ** Morgagni's hernia ** Bochdalek hernia * Hiatal hernia * Iatrogenic diaphragmatic hernia * Traumatic diaphragmatic hernia Signs and symptoms A scaphoid abdomen (sucked inwards) may be the presenting symptom in a newborn. Diagnosis Diagnosis can be made by either CT or X-ray. Treatment Treatment for a diaphragmatic hernia usually involves surgery, with acute injuries often repaired with monofilament permanent sutures. Other animals Peritoneopericardial diaphragmatic hernia is a type of hernia more common in other mammal A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...s. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphragm (anatomy)
The thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm (; ), is a sheet of internal skeletal muscle in humans and other mammals that extends across the bottom of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm is the most important muscle of respiration, and separates the thoracic cavity, containing the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity: as the diaphragm contracts, the volume of the thoracic cavity increases, creating a negative pressure there, which draws air into the lungs. Its high oxygen consumption is noted by the many mitochondria and capillaries present; more than in any other skeletal muscle. The term ''diaphragm'' in anatomy, created by Gerard of Cremona, can refer to other flat structures such as the urogenital diaphragm or Pelvic floor, pelvic diaphragm, but "the diaphragm" generally refers to the thoracic diaphragm. In humans, the diaphragm is slightly asymmetric—its right half is higher up (superior) to the left half, since the large liver rests beneath the right half of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the gut, belly, tummy, midriff, tucky, or stomach) is the front part of the torso between the thorax (chest) and pelvis in humans and in other vertebrates. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal cavity. In arthropods, it is the posterior (anatomy), posterior tagma (biology), tagma of the body; it follows the thorax or cephalothorax. In humans, the abdomen stretches from the thorax at the thoracic diaphragm to the pelvis at the pelvic brim. The pelvic brim stretches from the lumbosacral joint (the intervertebral disc between Lumbar vertebrae, L5 and Vertebra#Sacrum, S1) to the pubic symphysis and is the edge of the pelvic inlet. The space above this inlet and under the thoracic diaphragm is termed the abdominal cavity. The boundary of the abdominal cavity is the abdominal wall in the front and the peritoneal surface at the rear. In vertebrates, the abdomen is a large body cavity enclosed by the abdominal muscles, at the front an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) is a birth defect of the diaphragm. The most common type of CDH is a Bochdalek hernia; other types include Morgagni hernia, diaphragm eventration and central tendon defects of the diaphragm. Malformation of the diaphragm allows the abdominal organs to push into the chest cavity, hindering proper lung formation. CDH is a life-threatening pathology in infants and a major cause of death due to two complications: pulmonary hypoplasia and pulmonary hypertension. Experts disagree on the relative importance of these two conditions, with some focusing on hypoplasia, others on hypertension. Newborns with CDH often have severe respiratory distress which can be life-threatening unless treated appropriately. Classification Bochdalek hernia The Bochdalek hernia, also known as a postero-lateral diaphragmatic hernia, is the most common manifestation of CDH, accounting for more than 95% of cases. In this instance the diaphragm abnormality is char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bochdalek Hernia
Bochdalek hernia is one of two forms of a congenital diaphragmatic hernia, the other form being Morgagni hernia. A Bochdalek hernia is a congenital abnormality in which an opening exists in the infant's diaphragm, allowing normally intra-abdominal organs (particularly the stomach and intestines) to enter into the thoracic cavity. In the majority of people, the affected lung will be deformed, and the resulting lung compression can be life-threatening. Bochdalek hernias occur more commonly on the posterior left side (85%, versus the right side 15%). Bochdalek hernias are rare. This type of hernia was first described in 1754 by McCauley and subsequently studied and named after the Czech pathologist Vincenz Alexander Bochdalek (1801–1883). Signs and symptoms Children In normal Bochdalek hernia cases, the symptoms are often observable simultaneously with the baby's birth. A few of the symptoms of Bochdalek Hernia include difficulty breathing, fast respiration and increased heart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiatal Hernia
A hiatal hernia or hiatus hernia is a type of hernia in which abdominal organs (typically the stomach) slip through the diaphragm into the middle compartment of the chest. This may result in gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR) with symptoms such as a taste of acid in the back of the mouth or heartburn. Other symptoms may include trouble swallowing and chest pains. Complications may include iron deficiency anemia, volvulus, or bowel obstruction. The most common risk factors are obesity and older age. Other risk factors include major trauma, scoliosis, and certain types of surgery. There are two main types: sliding hernia, in which the body of the stomach moves up; and paraesophageal hernia, in which an abdominal organ moves beside the esophagus. The diagnosis may be confirmed with endoscopy or medical imaging. Endoscopy is typically only required when concerning symptoms are present, symptoms are resistant to treatment, or the person i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iatrogenic Diaphragmatic Hernia
Iatrogenesis is the causation of a disease, a harmful complication, or other ill effect by any medical activity, including diagnosis, intervention, error, or negligence."Iatrogenic", ''Merriam-Webster.com'', Merriam-Webster, Inc., accessed 27 Jun 2020. First used in this sense in 1924, the term was introduced to sociology in 1976 by Ivan Illich, alleging that industrialized societies impair quality of life by overmedicalizing life."iatrogenesis" ''A Dictionary of Sociology'', . updated 31 May 2020. Iatrogenesis may thus include mental suffering via medical beliefs or a practitioner's statements. Some iatrogeni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traumatic Diaphragmatic Hernia
Diaphragmatic rupture (also called diaphragmatic injury or tear) is a tear of the diaphragm, the muscle across the bottom of the ribcage that plays a crucial role in breathing. Most commonly, acquired diaphragmatic tears result from physical trauma. Diaphragmatic rupture can result from blunt or penetrating trauma and occurs in about 0.5% of all people with trauma. Diagnostic techniques include X-ray, computed tomography, and surgical techniques such as an explorative surgery. Diagnosis is often difficult because signs may not show up on X-ray, or signs that do show up appear similar to other conditions. Signs and symptoms include chest and abdominal pain, difficulty breathing, and decreased lung sounds. When a tear is discovered, surgery is needed to repair it. Injuries to the diaphragm are usually accompanied by other injuries, and they indicate that more severe injury may have occurred. The outcome often depends more on associated injuries than on the diaphragmatic injury i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scaphoid Abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the gut, belly, tummy, midriff, tucky, or stomach) is the front part of the torso between the thorax (chest) and pelvis in humans and in other vertebrates. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal cavity. In arthropods, it is the posterior tagma of the body; it follows the thorax or cephalothorax. In humans, the abdomen stretches from the thorax at the thoracic diaphragm to the pelvis at the pelvic brim. The pelvic brim stretches from the lumbosacral joint (the intervertebral disc between L5 and S1) to the pubic symphysis and is the edge of the pelvic inlet. The space above this inlet and under the thoracic diaphragm is termed the abdominal cavity. The boundary of the abdominal cavity is the abdominal wall in the front and the peritoneal surface at the rear. In vertebrates, the abdomen is a large body cavity enclosed by the abdominal muscles, at the front and to the sides, and by part of the vertebral column at the back. Low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphragm Hernia2
Diaphragm may refer to: Anatomy * Thoracic diaphragm, a thin sheet of muscle between the thorax and the abdomen * Pelvic diaphragm or pelvic floor, a pelvic structure * Urogenital diaphragm or triangular ligament, a pelvic structure Other * Diaphragm (optics), a stop in the light path of a lens, having an aperture that regulates the amount of light that passes * Diaphragm (acoustics), a thin, semi-rigid membrane that vibrates to produce or transmit sound waves * Diaphragm (birth control), a small rubber dome placed in the vagina to wall off the cervix, thus preventing sperm from entering * Diaphragm (mechanical device), a sheet of a semi-flexible material anchored at its periphery * Diaphragm (structural system), a structural engineering system used to resist lateral loads See also * Diaphragm arch * Diaphragm pump * Diaphragm seal, a membrane that seals an enclosure * Diaphragm shutter, a type of leaf shutter consisting of a number of thin blades in a camera * Diaphragm valv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute (medicine)
In medicine, describing a disease as acute denotation, denotes that it is of recent wikt:onset#Noun, onset; it occasionally denotes a short wikt:duration#Noun, duration. The quantification (science), quantification of how much time constitutes "short" and "recent" varies by disease and by context, but the core denotation of "acute" is always qualitative property, qualitatively in contrast with "chronic condition, chronic", which denotes long-lasting disease (for example, in acute leukaemia and chronic leukaemia). In the context of the mass noun "acute disease", it refers to the acute phase (that is, a short course) of any disease entity. For example, in an article on ulcerative enteritis in poultry, the author says, "in acute disease there may be increased mortality rate, mortality without any obvious medical sign, signs", referring to the acute form or phase of ulcerative enteritis. Meaning variations A mild stubbed toe is an acute injury. Similarly, many acute upper respirator ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
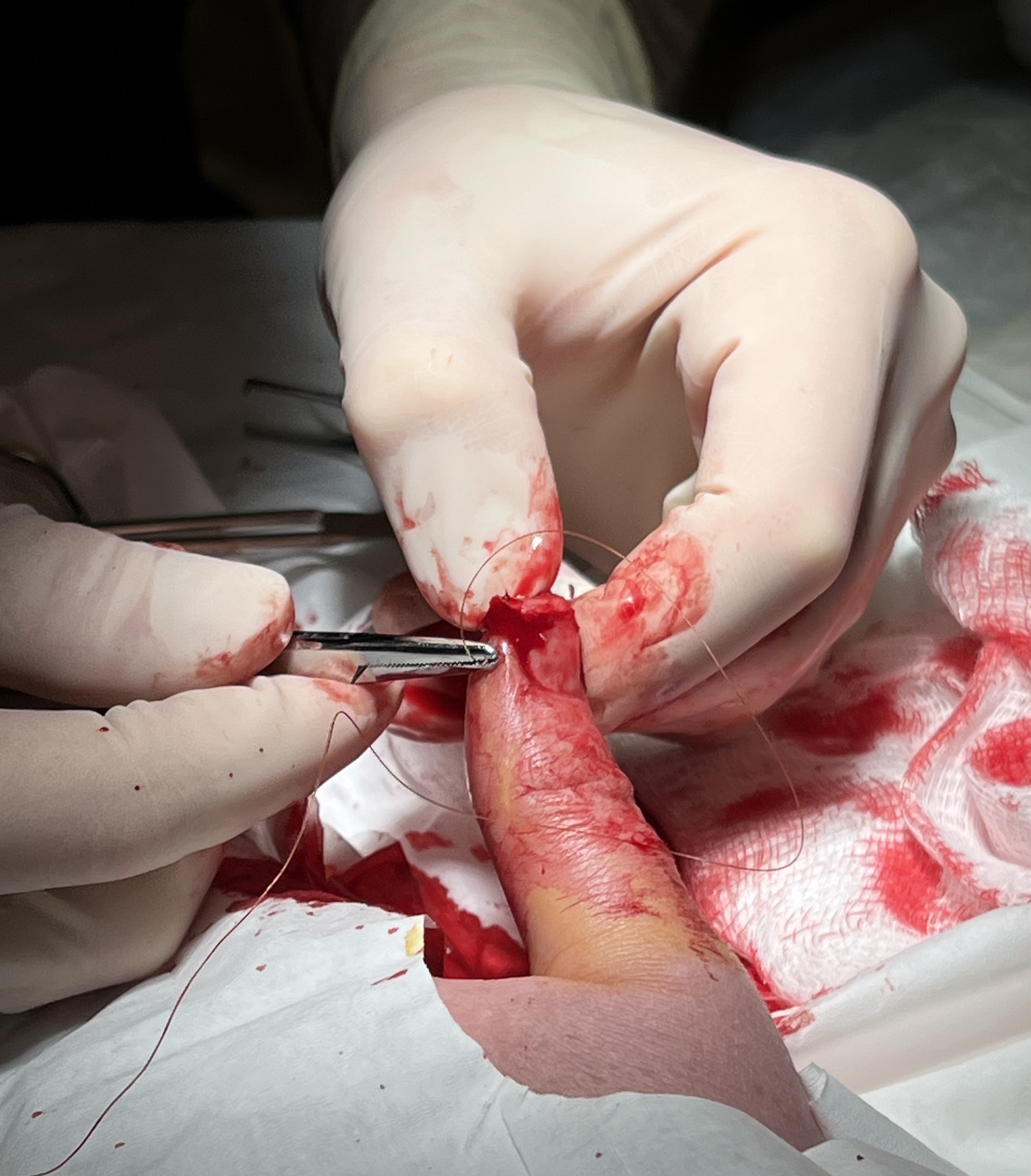
Surgical Suture
A surgical suture, also known as a stitch or stitches, is a medical device used to hold Tissue (biology), body tissues together and approximate wound edges after an injury or surgery. Application generally involves using a Sewing needle, needle with an attached length of thread (yarn), thread. There are numerous types of suture which differ by needle shape and size as well as thread material and characteristics. Selection of surgical suture should be determined by the characteristics and location of the wound or the specific body tissues being approximated. In selecting the needle, thread, and suturing technique to use for a specific patient, a medical care provider must consider the tensile strength of the specific suture thread needed to efficiently hold the tissues together depending on the mechanical and shear forces acting on the wound as well as the thickness of the tissue being approximated. One must also consider the elasticity of the thread and ability to adapt to differe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |