|
Diacylglycerols
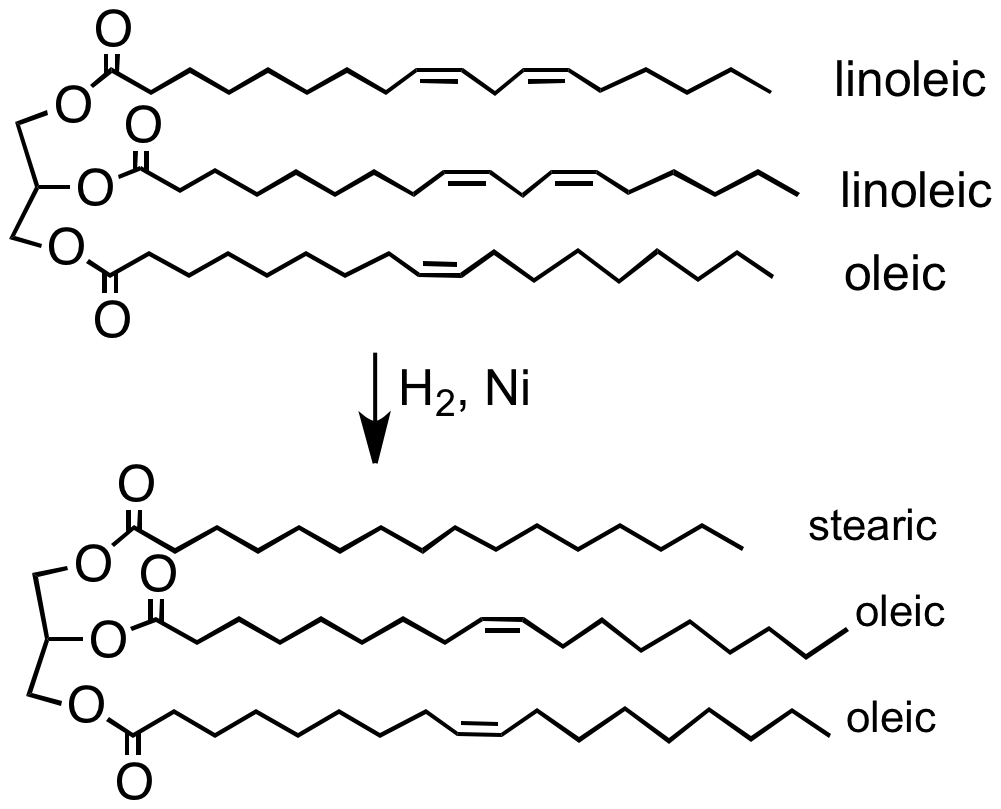
A diglyceride, or diacylglycerol (DAG), is a glyceride consisting of two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkages. Two possible forms exist, 1,2-diacylglycerols and 1,3-diacylglycerols. Diglycerides are natural components of food fats, though minor in comparison to triglycerides. DAGs can act as surfactants and are commonly used as emulsifiers in processed foods. DAG-enriched oil (particularly 1,3-DAG) has been investigated extensively as a fat substitute due to its ability to suppress the accumulation of body fat; with total annual sales of approximately USD 200 million in Japan since its introduction in the late 1990s till 2009. Production Diglycerides are a minor component of many seed oils and are normally present at ~1–6%; or in the case of cottonseed oil as much as 10%. Industrial production is primarily achieved by a glycerolysis reaction between triglycerides and glycerol. The raw materials for this may be either vegetable oil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycerolysis
In organic chemistry glycerolysis refers to any process in which chemical bonds are broken via a reaction with glycerol. The term refers almost exclusively to the transesterification reaction of glycerol with triglycerides (fats/oils) to form mixtures of monoglycerides and diglycerides. These find a variety of uses; as food emulsifiers (e.g. E471), 'low fat' cooking oils (e.g. diacylglycerol oil) and surfactants (such as monolaurin). The transesterification process gives a complex mixture of products, however not all of these are of equivalent use. This has led to the development of optimized processes able to produce better defined products; in particular by using enzymes, reactions in supercritical carbon dioxide and flow chemistry. The production of diglycerides (often called diacylglycerols or DAGs) have been investigated extensively due to their use in foods, with total annual sales of approximately US$200 million in Japan since its introduction in the late 1990s until 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diacylglycerol Oil
Diacylglycerol oil (DAG oil) is a cooking oil in which the ratio of triglycerides, also known as Triacylglycerols (TAGs), to diacylglycerols (DAGs) is shifted to contain mostly DAG, unlike conventional cooking oils, which are rich in TAGs. Vegetable DAG oil, for example, contains 80% DAG and is used as a 1:1 replacement for liquid vegetable oils in all applications. How it works DAGs and TAGs are natural components in all vegetable oils. Through an enzymatic process, the DAG content of a combination of soy and canola oils is significantly increased. Unlike TAG, which is stored as body fat, DAG is immediately burned as energy. With DAG-rich oil containing more than 80% DAG, less of the oil is stored as body fat than with traditional oils, which are rich in TAG. Excess calories consumed by the body are converted into fat and stored, regardless if it is consumed as DAG or TAG. Study According to a 2007 study, Diacylglycerol (DAG) oil is present with vegetable oil. A study in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
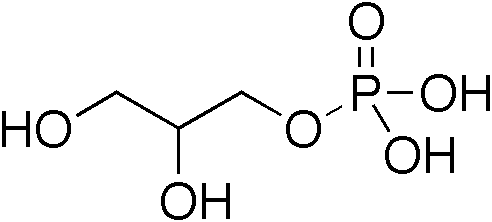
Glyceride
Glycerides, also known as acylglycerols, are esters formed from glycerol and fatty acids, and are generally very hydrophobic. Glycerol has three hydroxyl functional groups, which can be esterified with one, two, or three fatty acids to form mono-, di-, and triglycerides. These structures vary in their fatty acid alkyl groups as they can contain different carbon numbers, different degrees of unsaturation, and different configurations and positions of olefins. Vegetable oils and animal fats contain mostly triglycerides, but are broken down by natural enzymes (lipases) into mono and diglycerides and free fatty acids and glycerol. Soaps are formed from the reaction of glycerides with sodium hydroxide. The product of the reaction is glycerol and salts of fatty acids. Fatty acids in the soap emulsify the oils in dirt, enabling the removal of oily dirt with water. Partial glycerides are esters of glycerol with fatty acids, where not all the hydroxyl groups are esterified. Since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emulsion
An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally Miscibility, immiscible (unmixable or unblendable) owing to liquid-liquid phase separation. Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloids. Although the terms ''colloid'' and ''emulsion'' are sometimes used interchangeably, ''emulsion'' should be used when both phases, dispersed and continuous, are liquids. In an emulsion, one liquid (the dispersed phase (matter), phase) is dispersion (chemistry), dispersed in the other (the continuous phase). Examples of emulsions include vinaigrettes, homogenized milk, liquid biomolecular condensates, and some cutting fluids for metal working. Two liquids can form different types of emulsions. As an example, oil and water can form, first, an oil-in-water emulsion, in which the oil is the dispersed phase, and water is the continuous phase. Second, they can form a water-in-oil emulsion, in which water is the dispersed phase and oil is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phospholipase C
Phospholipase C (PLC) is a class of membrane-associated enzymes that cleave phospholipids just before the phosphate group (see figure). It is most commonly taken to be synonymous with the human forms of this enzyme, which play an important role in eukaryotic cell physiology, in particular signal transduction pathways. Phospholipase C's role in signal transduction is its cleavage of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) into diacyl glycerol (DAG) and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3), which serve as second messengers. Activators of each PLC vary, but typically include heterotrimeric G protein subunits, protein tyrosine kinases, small G proteins, Ca2+, and phospholipids. There are thirteen kinds of mammalian phospholipase C that are classified into six isotypes (β, γ, δ, ε, ζ, η) according to structure. Each PLC has unique and overlapping controls over expression and subcellular distribution. However, PLC is not limited to mammals, and is present in bacteria a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate or PtdIns(4,5)''P''2, also known simply as PIP2 or PI(4,5)P2, is a minor phospholipid component of cell membranes. PtdIns(4,5)''P''2 is enriched at the plasma membrane where it is a substrate for a number of important signaling proteins. PIP2 also forms lipid clusters that sort proteins. PIP2 is formed primarily by the type I phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinases from PI(4)P. In metazoans, PIP2 can also be formed by type II phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate 4-kinases from PI(5)P. The fatty acids of PIP2 are variable in different species and tissues, but the most common fatty acids are stearic in position 1 and arachidonic in 2. Signaling pathways PIP2 is a part of many cellular signaling pathways, including PIP2 cycle, PI3K signalling, and PI5P metabolism. Recently, it has been found in the nucleus with unknown function. Functions Cytoskeleton dynamics near membranes PIP2 regulates the organization, polymerization, and bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of Biomolecule, biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification. Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water. Types Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid Signaling
Lipid signaling, broadly defined, refers to any biological cell signaling event involving a lipid messenger that binds a protein target, such as a receptor (biochemistry), receptor, kinase or phosphatase, which in turn mediate the effects of these lipids on specific cellular responses. Lipid signaling is thought to be qualitatively different from other classical signaling paradigms (such as monoamine neurotransmission) because lipids can freely molecular diffusion, diffuse through Cell membrane, membranes (''see osmosis''). One consequence of this is that lipid messengers cannot be stored in Vesicle (biology), vesicles prior to release and so are often biosynthesis, biosynthesized "on demand" at their intended site of action. As such, many lipid signaling molecules cannot circulate freely in solution but, rather, exist bound to special carrier proteins in serous fluid, serum. Sphingolipid second messengers Ceramide Ceramide (Cer) can be generated by the breakdown of sphingom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
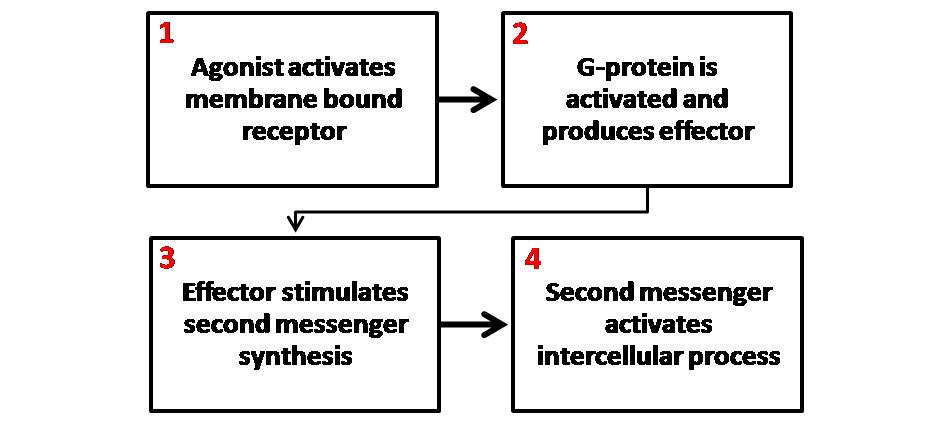
Second Messenger
Second messengers are intracellular signaling molecules released by the cell in response to exposure to extracellular signaling molecules—the first messengers. (Intercellular signals, a non-local form of cell signaling, encompassing both first messengers and second messengers, are classified as autocrine, juxtacrine, paracrine, and endocrine depending on the range of the signal.) Second messengers trigger physiological changes at cellular level such as proliferation, differentiation, migration, survival, apoptosis and depolarization. They are one of the triggers of intracellular signal transduction cascades. Examples of second messenger molecules include cyclic AMP, cyclic GMP, inositol triphosphate, diacylglycerol, and calcium. First messengers are extracellular factors, often hormones or neurotransmitters, such as epinephrine, growth hormone, and serotonin. Because peptide hormones and neurotransmitters typically are biochemically hydrophilic molecules, these first mess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PIP2 Cleavage To IP3 And DAG
Pip, PIP, Pips, PIPS, and similar, may refer to: Common meanings * Pip, colloquial name for the star(s) worn on military uniform as part of rank badge, as in the British Army officer rank insignia or with many Commonwealth police agencies * The seed of some fruits * Pip (counting), a small but easily countable item, such as the dots on dice or symbols on playing cards * Pip, a dot on a domino tile, refer Glossary of domino terms Arts, entertainment and media * "Pip" (''South Park''), a 2000 episode of ''South Park'' * The Pips, the backing singers in the musical group Gladys Knight & the Pips * Providence Initiative for Psychogeographic Studies, an art group * PiP Animation Services, a Canadian animation studio * The Pip, the nickname of a clandestine radio station of Russian origin * BBC Pips or ''The Pips'', a timing signal broadcast by the BBC Finance and management * Percentage in point, a currency exchange rate fluctuation * Performance improvement plan, a management t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pringles
Pringles is an American brand of stackable potato-based chips invented by Procter & Gamble (P&G) in 1968 and marketed as "Pringle's Newfangled Potato Chips". It is technically considered an Extruded food, extruded snack because of the manufacturing process. The brand was sold in 2012 to Kellanova, but in 2024 Kellanova, Kellogg's parent company agreed to be purchased by Mars Inc. Pringles were sold in more than 140 countries. In 2012, Pringles were the fourth most popular snack brand after Lay's, Doritos, and Cheetos (all manufactured by Frito-Lay), with 2.2% market share globally. History In 1956, Procter & Gamble assigned a task to food chemistry, chemist Fredric J. Baur (1918–2008): to develop a new kind of potato chip to address consumer complaints about broken, greasy, and stale chips, as well as air in the bags. Baur spent two years developing saddle-shaped chips from fried dough, and selected a tubular can as the chips' container. The saddle-shape of Pringles ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margarine
Margarine (, also , ) is a Spread (food), spread used for flavoring, baking, and cooking. It is most often used as a substitute for butter. Although originally made from animal fats, most margarine consumed today is made from vegetable oil. The spread was originally named ''oleomargarine'' from Latin for ''oleum'' (olive oil) and Greek language, Greek ''margarite'' ("pearl", indicating luster). The name was later shortened to ''margarine'', or sometimes ''oleo'' (particularly in the Deep South). Margarine consists of a water-in-fat emulsion, with tiny droplets of water dispersed uniformly throughout a fat phase (chemistry), phase in a stable solid form. While butter is made by concentrating the butterfat of milk through centrifugation, modern margarine is made through a more intensive processing of refined vegetable oil and water. Per US federal regulation, products must have a minimum fat content of 80% (with a maximum of 16% water) to be labeled as such in the United States, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |