|
Di-tert-butyl Chromate
Di-''tert''-butyl chromate is an alkoxide with the formula CrO2(OC(CH3)3)2. It forms red crystals at temperatures below −5 °C, above which it melts to give a red oil. The complex, which is diamagnetic, is of fundamental interest as a model for the intermediates in oxidations of alcohols by chromium(VI). This complex is stable because as a t-butyl groups lack beta-hydrogens. This complex and its analogues have tetrahedral geometry at chromium, as established by X-ray crystallography of its analogues. Preparation It can be prepared from Tert-Butyl alcohol and Chromium Trioxide or Chromyl Chloride Applications It is used as a precursor to chromium-based catalysts, such as the Phillips catalyst, which are employed for the polymerization of ethylene. Safety Like other forms of hexavalent chromium, di-''tert''-butyl chromate is classified as a potential carcinogen by the United States National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health The National Institute for O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkoxide
In chemistry, an alkoxide is the conjugate base of an alcohol and therefore consists of an organic group bonded to a negatively charged oxygen atom. They are written as , where R is the organyl substituent. Alkoxides are strong bases and, when R is not bulky, good nucleophiles and good ligands. Alkoxides, although generally not stable in protic solvents such as water, occur widely as intermediates in various reactions, including the Williamson ether synthesis.excerpt Transition metal alkoxides are widely used for coatings and as catalysts. Enolates are unsaturated alkoxides derived by deprotonation of a bond adjacent to a ketone or aldehyde. The nucleophilic center for simple alkoxides is located on the oxygen, whereas the nucleophilic site on enolates is delocalized onto both carbon and oxygen sites. Ynolates are also unsaturated alkoxides derived from acetylenic alcohols. Phenoxides are close relatives of the alkoxides, in which the alkyl group is replaced by a phe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science of determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to Diffraction, diffract in specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of the X-ray diffraction, a crystallography, crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal and the positions of the atoms, as well as their chemical bonds, crystallographic disorder, and other information. X-ray crystallography has been fundamental in the development of many scientific fields. In its first decades of use, this method determined the size of atoms, the lengths and types of chemical bonds, and the atomic-scale differences between various materials, especially minerals and alloys. The method has also revealed the structure and function of many biological molecules, including vitamins, drugs, proteins and nucleic acids such as DNA. X-ray crystall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tert-Butyl Alcohol
''tert''-Butyl alcohol is the simplest tertiary alcohol, with a formula of (CH3)3COH (sometimes represented as ''t''-BuOH). Its isomers are 1-butanol, isobutanol, and butan-2-ol. ''tert''-Butyl alcohol is a colorless solid, which melts near room temperature and has a camphor-like odor. It is miscible with water, ethanol and diethyl ether. Natural occurrence ''tert''-Butyl alcohol has been identified in beer and chickpeas. It is also found in cassava, which is used as a fermentation ingredient in certain alcoholic beverages. Preparation ''tert''-Butyl alcohol is derived commercially from isobutane as a coproduct of propylene oxide production. It can also be produced by the catalytic hydration of isobutylene, or by a Grignard reaction between acetone and methylmagnesium chloride. Purification cannot be performed by simple distillation due to formation of an azeotrope with water, although initial drying of the solvent containing large amounts of water is performed by addin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromyl Chloride
Chromyl chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula CrO2Cl2. It is a reddish brown compound that is a volatile liquid at room temperature, which is unusual for transition metal compounds. It is the dichloride of chromic acid. Preparation Chromyl chloride can be prepared by the reaction of potassium chromate or potassium dichromate with hydrogen chloride in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid, followed by distillation. :K2Cr2O7 + 6 HCl → 2 CrO2Cl2 + 2 KCl + 3 H2O The sulfuric acid serves as a dehydration agent. It can also be prepared directly by exposing chromium trioxide to anhydrous hydrogen chloride gas. :CrO3 + 2 HCl ⇌ CrO2Cl2 + H2O Usage Test for the presence of chlorides The chromyl chloride test involves heating a sample suspected to contain chlorides with potassium dichromate and concentrated sulfuric acid. If a chloride is present then chromyl chloride forms which is indicated by the evolution of red smoke. No similar compound is formed in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phillips Catalyst
The Phillips catalyst, or the Phillips supported chromium catalyst, is the catalyst used to produce approximately half of the world's polyethylene. A heterogeneous catalyst, it consists of a chromium oxide supported on silica gel. Polyethylene, the most-produced synthetic polymer, is produced industrially by the polymerization of ethylene: :n C2H4 → (C2H4)n Although exergonic (i.e., thermodynamically favorable), the reaction requires catalysts. Three main catalysts are employed commercially: the Phillips catalyst, Ziegler–Natta catalysts (based on titanium trichloride), and, for specialty polymers, metallocene-based catalysts. Preparation and mechanism of action The Phillips catalyst is prepared by impregnating high surface area silica gel with chromium trioxide or related chromium compounds. The solid precatalyst is then calcined in air to give the active catalyst. Only a fraction of the chromium is catalytically active, a fact that interferes with elucidation of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon–carbon bond, carbon–carbon double bonds). Ethylene is widely used in the chemical industry, and its worldwide production (over 150 million tonnes in 2016) exceeds that of any other organic compound. Much of this production goes toward creating polyethylene, which is a widely used plastic containing polymer chains of ethylene units in various chain lengths. Production greenhouse gas emissions, emits greenhouse gases, including methane from feedstock production and carbon dioxide from any non-sustainable energy used. Ethylene is also an important natural plant hormone and is used in agriculture to induce ripening of fruits. The hydrate of ethylene is ethanol. Structure and properties This hydrocarbon has four hydrogen atoms bound to a pair of carbon atoms that are con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexavalent Chromium
Hexavalent chromium (chromium(VI), Cr(VI), chromium 6) is any chemical compound that contains the element chromium in the +6 oxidation state (thus hexavalent). It has been identified as carcinogenic, which is of concern since approximately of hexavalent chromium were produced in 1985. Hexavalent chromium compounds can be carcinogens ( IARC Group 1), especially if airborne and inhaled where they can cause lung cancer. Occurrence and uses Hexavalent chromium occurs only rarely in nature, an exception being crocoite (PbCrO4). It is however produced on a large scale industrially. Virtually all chromium ore is processed via the formation of hexavalent chromium, specifically the salt sodium dichromate. Sodium chromate is converted into other hexavalent chromium compounds such as chromium trioxide and various salts of chromate and dichromate. Industrial uses of hexavalent chromium compounds include chromate pigments in dyes, paints, inks, and plastics; chromates added as anti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Institute For Occupational Safety And Health
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH, ) is the List of United States federal agencies, United States federal agency responsible for conducting research and making recommendations for the prevention of work-related occupational injury, injury, occupational disease, illness, disability, and occupational fatality, death. Its functions include gathering information, conducting scientific research both in the laboratory and in the field, and translating the knowledge gained into products and services.About NIOSH National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. Among NIOSH's programs are determination of recommended exposure limits for toxic chemicals and other hazards, field research such as the Health Hazard Evaluation Program, epidemiology and health surveillance programs such as the National Firefighter Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
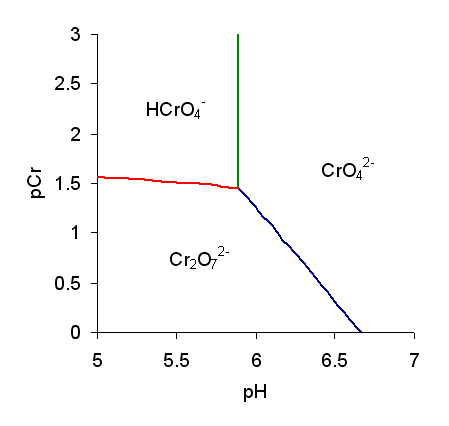
Chromates
Chromate salts contain the chromate anion, . Dichromate salts contain the dichromate anion, . They are oxyanions of chromium in the +6 oxidation state and are moderately strong oxidizing agents. In an aqueous solution, chromate and dichromate ions can be interconvertible. Chemical properties Potassium-chromate-sample.jpg, Potassium chromate Potassium-dichromate-sample.jpg, Potassium dichromate Chromates react with hydrogen peroxide, giving products in which peroxide, , replaces one or more oxygen atoms. In acid solution the unstable blue peroxo complex Chromium(VI) oxide peroxide, , is formed; it is an uncharged covalent molecule, which may be extracted into ether. Addition of pyridine results in the formation of the more stable complex . Acid–base properties In aqueous solution, chromate and dichromate anions exist in a chemical equilibrium. : The predominance diagram shows that the position of the equilibrium depends on both pH and the analytical concentration o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |