|
Deverbal Noun
Deverbal nouns are nouns that are derived from verbs or verb phrases. Formation Hausa Verbal nouns and deverbal nouns are distinct syntactic word classes. Functionally, deverbal nouns operate as autonomous common nouns, while verbal nouns retain verbal characteristics. French There are two connotations of the deverbal nouns: the one formed without any suffix, or any noun descending from a verb. See also * Denominal verb * Gerund * Verbal noun Historically, grammarians have described a verbal noun or gerundial noun as a verb form that functions as a noun. An example of a verbal noun in English is 'sacking' as in the sentence "The ''sacking'' of the city was an epochal event" (wherein ... References Further reading * A Comprehensive Grammar of the English Language. Longman Publication. Page. 1288 (Chapter 17) * Nouns by type {{grammar-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verbal Noun
Historically, grammarians have described a verbal noun or gerundial noun as a verb form that functions as a noun. An example of a verbal noun in English is 'sacking' as in the sentence "The ''sacking'' of the city was an epochal event" (wherein ''sacking'' is a gerund form of the verb ''sack''). A verbal noun, as a type of nonfinite verb form, is a term that some grammarians still use when referring to gerunds, gerundives, supines, and nominal forms of infinitives. In English however, ''verbal noun'' has most frequently been treated as a synonym for ''gerund''. Aside from English, the term ''verbal noun'' may apply to: * the citation form of verbs such as the masdar in Arabic and the verbal noun (''berfenw'') in Welsh * declinable verb forms in Mongolian that can serve as predicates, comparable to participles but with a larger area of syntactic use Types Verbal nouns, whether derived from verbs or constituting an infinitive, behave syntactically as grammatical obj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerund
In linguistics, a gerund ( abbreviated ger) is any of various nonfinite verb forms in various languages; most often, but not exclusively, it is one that functions as a noun. The name is derived from Late Latin ''gerundium,'' meaning "which is to be carried out". In English, the gerund has the properties of both verb and noun, such as being modifiable by an adverb and being able to take a direct object. The term "''-ing'' form" is often used in English to refer to the gerund specifically. Traditional grammar makes a distinction within ''-ing'' forms between present participles and gerunds, a distinction that is not observed in such modern grammars as '' A Comprehensive Grammar of the English Language'' and '' The Cambridge Grammar of the English Language''. Traditional use The Latin gerund, in a restricted set of syntactic contexts, denotes the sense of the verb in isolation after certain prepositions, and in certain uses of the genitive, dative, and ablative cases. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deverbal Noun
Deverbal nouns are nouns that are derived from verbs or verb phrases. Formation Hausa Verbal nouns and deverbal nouns are distinct syntactic word classes. Functionally, deverbal nouns operate as autonomous common nouns, while verbal nouns retain verbal characteristics. French There are two connotations of the deverbal nouns: the one formed without any suffix, or any noun descending from a verb. See also * Denominal verb * Gerund * Verbal noun Historically, grammarians have described a verbal noun or gerundial noun as a verb form that functions as a noun. An example of a verbal noun in English is 'sacking' as in the sentence "The ''sacking'' of the city was an epochal event" (wherein ... References Further reading * A Comprehensive Grammar of the English Language. Longman Publication. Page. 1288 (Chapter 17) * Nouns by type {{grammar-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noun
In grammar, a noun is a word that represents a concrete or abstract thing, like living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, and ideas. A noun may serve as an Object (grammar), object or Subject (grammar), subject within a phrase, clause, or sentence.Example nouns for: * Living creatures (including people, alive, dead, or imaginary): ''mushrooms, dogs, Afro-Caribbeans, rosebushes, Mandela, bacteria, Klingons'', etc. * Physical objects: ''hammers, pencils, Earth, guitars, atoms, stones, boots, shadows'', etc. * Places: ''closets, temples, rivers, Antarctica, houses, Uluru, utopia'', etc. * Actions of individuals or groups: ''swimming, exercises, cough, explosions, flight, electrification, embezzlement'', etc. * Physical qualities: ''colors, lengths, porosity, weights, roundness, symmetry, solidity,'' etc. * Mental or bodily states: ''jealousy, sleep, joy, headache, confusion'', etc. In linguistics, nouns constitute a lexical category (part of speech) defined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verb
A verb is a word that generally conveys an action (''bring'', ''read'', ''walk'', ''run'', ''learn''), an occurrence (''happen'', ''become''), or a state of being (''be'', ''exist'', ''stand''). In the usual description of English, the basic form, with or without the particle ''to'', is the infinitive. In many languages, verbs are inflected (modified in form) to encode tense, aspect, mood, and voice. A verb may also agree with the person, gender or number of some of its arguments, such as its subject, or object. In English, three tenses exist: present, to indicate that an action is being carried out; past, to indicate that an action has been done; and future, to indicate that an action will be done, expressed with the auxiliary verb ''will'' or ''shall''. For example: * Lucy ''will go'' to school. ''(action, future)'' * Barack Obama ''became'' the President of the United States in 2009. ''(occurrence, past)'' * Mike Trout ''is'' a center fielder. ''(state of bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
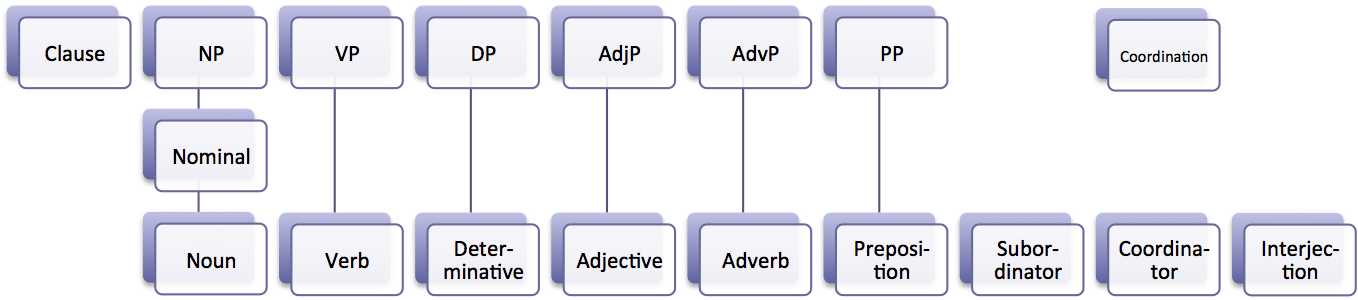
Word Class
In grammar, a part of speech or part-of-speech (abbreviated as POS or PoS, also known as word class or grammatical category) is a category of words (or, more generally, of lexical items) that have similar grammatical properties. Words that are assigned to the same part of speech generally display similar syntactic behavior (they play similar roles within the grammatical structure of sentences), sometimes similar morphological behavior in that they undergo inflection for similar properties and even similar semantic behavior. Commonly listed English parts of speech are noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, preposition, conjunction, interjection, numeral, article, and determiner. Other terms than ''part of speech''—particularly in modern linguistic classifications, which often make more precise distinctions than the traditional scheme does—include word class, lexical class, and lexical category. Some authors restrict the term ''lexical category'' to refer only to a particu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Benjamins Publishing
John Benjamins Publishing Company is an independent academic publisher in social sciences and humanities with its head office in Amsterdam, Netherlands. The company was founded in the 1960s by John and Claire Benjamins and is currently managed by their daughter Seline Benjamins. John Benjamins is especially noted for its publications in language, linguistics, translation studies, political linguistics and literary studies. It publishes books, as well as 80+ academic journals An academic journal (or scholarly journal or scientific journal) is a periodical publication in which scholarship relating to a particular academic discipline is published. They serve as permanent and transparent forums for the dissemination, scr ..., including among others: ''Diachronica'', '' International Journal of Corpus Linguistics'', '' Language Problems and Language Planning'', '' Studies in Language'', '' Lingvisticae Investigationes'', Target, '' Translation, Cognition & Behavior'', ''Journal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denominal Verb
In grammar, denominal verbs are verbs derived from nouns. Many languages have regular morphological indicators to create denominal verbs. English English examples are ''to school'', from ''school'', meaning to instruct; ''to shelve'', from ''shelf'', meaning to put on shelves; and ''to symbolize'', from ''symbol'', meaning to be a symbol for. Some common denominalizing affixes in English are ''-ize/-ise'' (e.g., ''summarize''), ''-ify'' (e.g., ''classify''), ''-ate'' (e.g., ''granulate''), ''en-'' (e.g., ''enslave''), ''be-'' (e.g., ''behead''), and zero or ''-∅'' (e.g., ''school''). A variety of semantic relations are expressed between the base noun X and the derived verb. Although there is no simple relationship between the affix and the semantic relation,Carolyn A. Gottfurcht, ''Denominal Verb Formation in English'', Ph.D. dissertation, Northwestern University, 200full text/ref> there are semantic regularities that can define certain subclasses. Such subclasses include: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerund
In linguistics, a gerund ( abbreviated ger) is any of various nonfinite verb forms in various languages; most often, but not exclusively, it is one that functions as a noun. The name is derived from Late Latin ''gerundium,'' meaning "which is to be carried out". In English, the gerund has the properties of both verb and noun, such as being modifiable by an adverb and being able to take a direct object. The term "''-ing'' form" is often used in English to refer to the gerund specifically. Traditional grammar makes a distinction within ''-ing'' forms between present participles and gerunds, a distinction that is not observed in such modern grammars as '' A Comprehensive Grammar of the English Language'' and '' The Cambridge Grammar of the English Language''. Traditional use The Latin gerund, in a restricted set of syntactic contexts, denotes the sense of the verb in isolation after certain prepositions, and in certain uses of the genitive, dative, and ablative cases. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verbal Noun
Historically, grammarians have described a verbal noun or gerundial noun as a verb form that functions as a noun. An example of a verbal noun in English is 'sacking' as in the sentence "The ''sacking'' of the city was an epochal event" (wherein ''sacking'' is a gerund form of the verb ''sack''). A verbal noun, as a type of nonfinite verb form, is a term that some grammarians still use when referring to gerunds, gerundives, supines, and nominal forms of infinitives. In English however, ''verbal noun'' has most frequently been treated as a synonym for ''gerund''. Aside from English, the term ''verbal noun'' may apply to: * the citation form of verbs such as the masdar in Arabic and the verbal noun (''berfenw'') in Welsh * declinable verb forms in Mongolian that can serve as predicates, comparable to participles but with a larger area of syntactic use Types Verbal nouns, whether derived from verbs or constituting an infinitive, behave syntactically as grammatical obj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |