|
Dermatocranium
The dermatocranium is the portion of the cranium that is composed of dermal bone, as opposed to the endocranium and splanchnocranium, which are composed of endochondral bone. The dermatocranium comprises the skull roof, the facial skeleton (usually excluding the dentary In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla). The jawbone ...), and—in fishes—the opercular bones. References Human anatomy Vertebrate anatomy {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skull Roof
The skull roof or the roofing bones of the skull are a set of bones covering the brain, eyes and nostrils in bony fishes, including land-living vertebrates. The bones are derived from dermal bone and are part of the dermatocranium. In comparative anatomy, the term is applied to the whole dermatocranium. Romer, A.S. & T.S. Parsons. 1977. ''The Vertebrate Body.'' 5th ed. Saunders, Philadelphia. (6th ed. 1985) In general anatomy, the roofing bones may refer specifically to the bones that form above and alongside the brain and neurocranium (i.e., excluding the marginal upper jaw bones such as the maxilla and premaxilla). In human anatomy, the skull roof often refers specifically to the skullcap. Origin Early armoured fish (such as jawless ostracoderms and jawed placoderms) did not have a skull in the common understanding of the word, but instead had a cartilaginous endocranium that was partially open from above. The loose cartilage was topped by dermal bones forming armo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Facial Skeleton
The facial skeleton comprises the ''facial bones'' that may attach to build a portion of the skull. The remainder of the skull is the neurocranium. In human anatomy and development, the facial skeleton is sometimes called the ''membranous viscerocranium'', which comprises the mandible and dermatocranial elements that are not part of the braincase. Structure In the human skull, the facial skeleton consists of fourteen bones in the face: * Inferior turbinal (2) * Lacrimal bones (2) * Mandible * Maxilla (2) * Nasal bones (2) * Palatine bones (2) * Vomer * Zygomatic bones (2) Variations Elements of the ''cartilaginous viscerocranium'' (i.e., splanchnocranial elements), such as the hyoid bone, are sometimes considered part of the facial skeleton. The ethmoid bone (or a part of it) and also the sphenoid bone are sometimes included, but otherwise considered part of the neurocranium. Because the maxillary bones are fused, they are often collectively listed as only one bone. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cranium
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate. In the human, the skull comprises two prominent parts: the neurocranium and the facial skeleton, which evolved from the first pharyngeal arch. The skull forms the frontmost portion of the axial skeleton and is a product of cephalization and vesicular enlargement of the brain, with several special senses structures such as the eyes, ears, nose, tongue and, in fish, specialized tactile organs such as barbels near the mouth. The skull is composed of three types of bone: cranial bones, facial bones and ossicles, which is made up of a number of fused flat and irregular bones. The cranial bones are joined at firm fibrous junctions called sutures and contains many foramina, fossae, processes, and sinuses. In zoology, the openings in the skull are called fenestrae, the most p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermal Bone
A dermal bone or investing bone or membrane bone is a bony structure derived from intramembranous ossification forming components of the vertebrate skeleton, including much of the skull, jaws, gill covers, shoulder girdle, fin rays ( lepidotrichia), and the shells of turtles and armadillos. In contrast to endochondral bone, dermal bone does not form from cartilage that then calcifies, and it is often ornamented. Dermal bone is formed within the dermis and grows by accretion only – the outer portion of the bone is deposited by osteoblasts. The function of some dermal bone is conserved throughout vertebrates, although there is variation in shape and in the number of bones in the skull roof and postcranial structures. In bony fish, dermal bone is found in the fin rays and scales. A special example of dermal bone is the clavicle The clavicle, collarbone, or keybone is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately long that serves as a strut between the scapula, shoulder b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocranium
The endocranium in comparative anatomy is a part of the skull base in vertebrates and it represents the basal, inner part of the cranium. The term is also applied to the outer layer of the dura mater in human anatomy. Structure Structurally, the endocranium consists of a boxlike shape, open at the top. The posterior margin exhibits the '' foramen magnum'', an opening for the spinal cord. The floor of the endocranium has several paired openings for the cranial nerves, and the anterior margin holds a spongy construction, allowing for the external nasal nerves to pass through. Romer, A.S. & T.S. Parsons. 1977. ''The Vertebrate Body.'' 5th ed. Saunders, Philadelphia. (6th ed. 1985) All bones of the structure derive from the cranial neural crest during fetal development. Endocranial elements in humans In humans and other mammals, the endocranium forms during fetal development as a cartilaginous neurocranium, that ossifies from several centers. Several of these bones merge, and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splanchnocranium
The splanchnocranium (or visceral skeleton) is the portion of the cranium that is derived from pharyngeal arches. ''Splanchno'' indicates to the gut because the face forms around the mouth, which is an end of the gut. The splanchnocranium consists of cartilage and endochondral bone. In mammals, the splanchnocranium comprises the three ear ossicles (i.e., incus, malleus, and stapes), as well as the alisphenoid, the Temporal styloid process, styloid process, the hyoid apparatus, and the thyroid cartilage. In other tetrapods, such as amphibians and reptiles, homologous bones to those of mammals, such as the quadrate bone, quadrate, articular, columella (auditory system), columella, and entoglossus are part of the splanchnocranium. See also * Dermatocranium * Endocranium * Neurocranium References Human anatomy Vertebrate anatomy {{anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endochondral Bone
Endochondral ossification is one of the two essential pathways by which bone tissue is produced during fetal development and bone repair of the mammalian skeletal system, the other pathway being intramembranous ossification. Both endochondral and intramembranous processes initiate from a precursor mesenchymal tissue, but their transformations into bone are different. In intramembranous ossification, mesenchymal tissue is directly converted into bone. On the other hand, endochondral ossification starts with mesenchymal tissue turning into an intermediate cartilage stage, which is eventually substituted by bone. Endochondral ossification is responsible for development of most bones including long and short bones, the bones of the axial (ribs and vertebrae) and the appendicular skeleton (e.g. upper and lower limbs), the bones of the skull base (including the ethmoid and sphenoid bones) and the medial end of the clavicle. In addition, endochondral ossification is not exclusive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentary
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla). The jawbone is the skull's only movable, posable bone, sharing joints with the cranium's temporal bones. The mandible hosts the lower teeth (their depth delineated by the alveolar process). Many muscles attach to the bone, which also hosts nerves (some connecting to the teeth) and blood vessels. Amongst other functions, the jawbone is essential for chewing food. Owing to the Neolithic advent of agriculture (), human jaws evolved to be smaller. Although it is the strongest bone of the facial skeleton, the mandible tends to deform in old age; it is also subject to fracturing. Surgery allows for the removal of jawbone fragments (or its entirety) as well as regenerative methods. Additionally, the bone is of great forensic significance. Structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
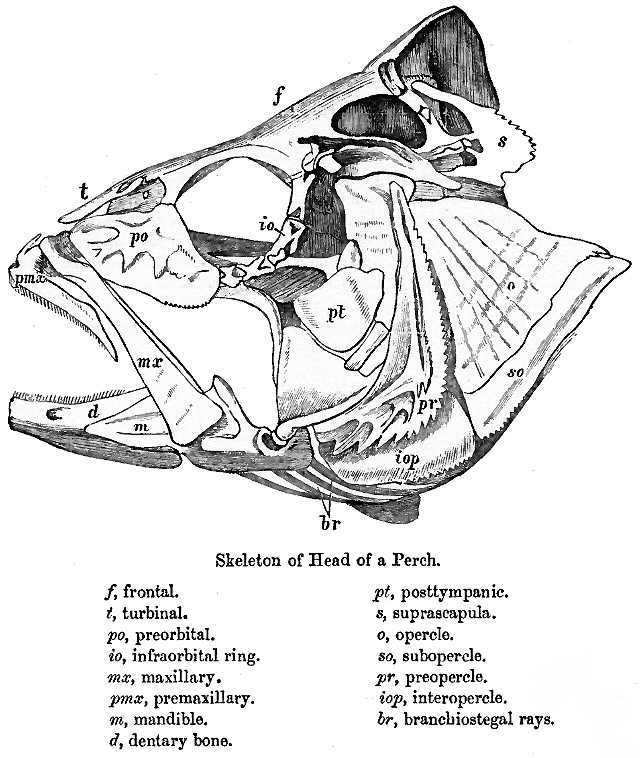
Operculum (fish)
The operculum is a series of bones found in bony fish and chimaeras that serves as a facial support structure and a protective covering for the gills; it is also used for respiration and feeding. Anatomy The opercular series contains four bone segments known as the preoperculum, suboperculum, interoperculum and operculum. The preoperculum is a crescent-shaped structure that has a series of ridges directed posterodorsally to the organism’s canal pores. The preoperculum can be located through an exposed condyle that is present immediately under its ventral margin; it also borders the operculum, suboperculum, and interoperculum posteriorly. The suboperculum is rectangular in shape in most bony fish and is located ventral to the preoperculum and operculum components. It is the thinnest bone segment out of the opercular series and is located directly above the gills. The interoperculum is triangular shaped and borders the suboperculum posterodorsally and the preoperculum anterodo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Anatomy
Human anatomy (gr. ἀνατομία, "dissection", from ἀνά, "up", and τέμνειν, "cut") is primarily the scientific study of the morphology of the human body. Anatomy is subdivided into gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy. Gross anatomy (also called macroscopic anatomy, topographical anatomy, regional anatomy, or anthropotomy) is the study of anatomical structures that can be seen by the naked eye. Microscopic anatomy is the study of minute anatomical structures assisted with microscopes, which includes histology (the study of the organization of tissues), and cytology (the study of cells). Anatomy, human physiology (the study of function), and biochemistry (the study of the chemistry of living structures) are complementary basic medical sciences that are generally together (or in tandem) to students studying medical sciences. In some of its facets human anatomy is closely related to embryology, comparative anatomy and comparative embryology, through common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |