|
Dendrite (crystal)
A crystal dendrite is a crystal that develops with a typical multi-branching form, resembling a fractal. The name comes from the Ancient Greek word (), which means "tree", since the crystal's structure resembles that of a tree. These crystals can be synthesised by using a supercooled pure liquid, however they are also quite common in nature. The most common crystals in nature exhibit dendritic growth are snowflakes and frost on windows, but many minerals and metals can also be found in dendritic structures. History Maximum velocity principle The first dendritic patterns were discovered in palaeontology and are often mistaken for fossils because of their appearance. The first theory for the creation of these patterns was published by Nash and Glicksman in 1974, they used a very mathematical method and derived a non-linear integro-differential equation for a classical needle growth. However they only found an inaccurate numerical solution close to the tip of the needle a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendrites01
A dendrite (from Greek δένδρον ''déndron'', "tree") or dendron is a branched cytoplasmic process that extends from a nerve cell that propagates the electrochemical stimulation received from other neural cells to the cell body, or soma, of the neuron from which the dendrites project. Electrical stimulation is transmitted onto dendrites by upstream neurons (usually via their axons) via synapses which are located at various points throughout the dendritic tree. Dendrites play a critical role in integrating these synaptic inputs and in determining the extent to which action potentials are produced by the neuron. Structure and function Dendrites are one of two types of cytoplasmic processes that extrude from the cell body of a neuron, the other type being an axon. Axons can be distinguished from dendrites by several features including shape, length, and function. Dendrites often taper off in shape and are shorter, while axons tend to maintain a constant radius and can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James S
James may refer to: People * James (given name) * James (surname) * James (musician), aka Faruq Mahfuz Anam James, (born 1964), Bollywood musician * James, brother of Jesus * King James (other), various kings named James * Prince James (other) * Saint James (other) Places Canada * James Bay, a large body of water * James, Ontario United Kingdom * James College, a college of the University of York United States * James, Georgia, an unincorporated community * James, Iowa, an unincorporated community * James City, North Carolina * James City County, Virginia ** James City (Virginia Company) ** James City Shire * James City, Pennsylvania * St. James City, Florida Film and television * ''James'' (2005 film), a Bollywood film * ''James'' (2008 film), an Irish short film * ''James'' (2022 film), an Indian Kannada-language film * "James", a television episode of ''Adventure Time'' Music * James (band), a band from Manchester ** ''James'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubic Crystal System
In crystallography, the cubic (or isometric) crystal system is a crystal system where the unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals. There are three main varieties of these crystals: *Primitive cubic (abbreviated ''cP'' and alternatively called simple cubic) *Body-centered cubic (abbreviated ''cI'' or bcc) *Face-centered cubic (abbreviated ''cF'' or fcc) Note: the term fcc is often used in synonym for the ''cubic close-packed'' or ccp structure occurring in metals. However, fcc stands for a face-centered cubic Bravais lattice, which is not necessarily close-packed when a motif is set onto the lattice points. E.g. the diamond and the zincblende lattices are fcc but not close-packed. Each is subdivided into other variants listed below. Although the ''unit cells'' in these crystals are conventionally taken to be cubes, the primitive unit cells often are not. Bravais lattices The three Bravais latices ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Structure
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of ordered arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in a crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from intrinsic nature of constituent particles to form symmetric patterns that repeat along the principal directions of three-dimensional space in matter. The smallest group of particles in a material that constitutes this repeating pattern is the unit cell of the structure. The unit cell completely reflects the symmetry and structure of the entire crystal, which is built up by repetitive translation of the unit cell along its principal axes. The translation vectors define the nodes of the Bravais lattice. The lengths of principal axes/edges, of the unit cell and angles between them are lattice constants, also called ''lattice parameters'' or ''cell parameters''. The symmetry properties of a crystal are described by the concept of space groups. All possible symmetric arrangements of particles in three-dimensional space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parabola
In mathematics, a parabola is a plane curve which is Reflection symmetry, mirror-symmetrical and is approximately U-shaped. It fits several superficially different Mathematics, mathematical descriptions, which can all be proved to define exactly the same curves. One description of a parabola involves a Point (geometry), point (the Focus (geometry), focus) and a Line (geometry), line (the Directrix (conic section), directrix). The focus does not lie on the directrix. The parabola is the locus (mathematics), locus of points in that plane that are equidistant from the directrix and the focus. Another description of a parabola is as a conic section, created from the intersection of a right circular conical surface and a plane (geometry), plane Parallel (geometry), parallel to another plane that is tangential to the conical surface. The graph of a function, graph of a quadratic function y=ax^2+bx+ c (with a\neq 0 ) is a parabola with its axis parallel to the -axis. Conversely, every ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wulff Construction
The Wulff construction is a method to determine the equilibrium shape of a droplet or crystal of fixed volume inside a separate phase (usually its saturated solution or vapor). Energy minimization arguments are used to show that certain crystal planes are preferred over others, giving the crystal its shape. It is of fundamental importance in a number of areas ranging from the shape of nanoparticles and precipitates to nucleation. It also has more applied relevance in areas such as the shapes of active particles in heterogeneous catalysis. Theory In 1878 Josiah Willard Gibbs proposed that a droplet or crystal will arrange itself such that its surface Gibbs free energy is minimized by assuming a shape of low surface energy. He defined the quantity :\Delta G_i= \sum_\gamma_j O_j~ Here \gamma _j represents the surface (Gibbs free) energy per unit area of the jth crystal face and O_j is the area of said face. \Delta G_i represents the difference in energy between a real crystal c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faceted Crystal
Faceted may refer to an object containing a facet. Faceted may also refer to: *Faceted classification, organizational system allowing multiple characteristics or attributes of each item *Faceted search Faceted search augments lexical search with a faceted navigation system, allowing users to narrow results by applying filters based on a faceted classification of the items. It is a parametric search technique. A faceted classification system clas ..., technique for accessing information via faceted classification *Faceted striking platform See also * Facet (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
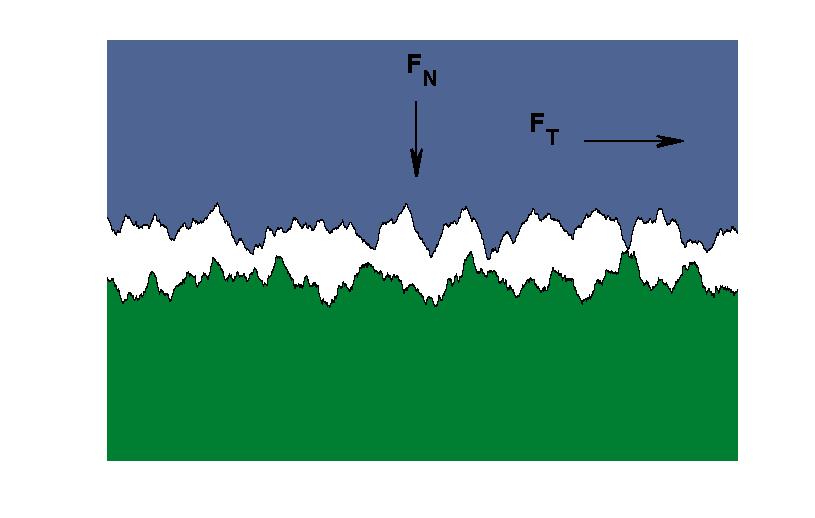
Normal Contact Stiffness
Normal contact stiffness is a physical quantity related to the generalized force displacement behavior of rough surfaces in contact with a rigid body or a second similar rough surface. Specifically it is the amount of force per unit displacement required to compress an elastic object in the contact region. Rough surfaces can be considered as consisting of large numbers of asperities. As two solid bodies of the same material approach one another, the asperities interact, and they transition from conditions of non-contact to homogeneous bulk behaviour, with changes in the contact area. The varying values of stiffness and true contact area at an interface during this transition are dependent on the conditions of applied pressure and are of importance for the study of systems involving the physical interactions of multiple bodies including granular matter, electrode contacts, and thermal contact In heat transfer and thermodynamics, a thermodynamic system A thermodynamic system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gibbs–Thomson Equation
The Gibbs–Thomson effect, in common physics usage, refers to variations in vapor pressure or chemical potential across a curved surface or interface. The existence of a positive interfacial energy will increase the energy required to form small particles with high curvature, and these particles will exhibit an increased vapor pressure. See Ostwald–Freundlich equation. More specifically, the Gibbs–Thomson effect refers to the observation that small crystals that are in equilibrium with their liquid, melt at a lower temperature than large crystals. In cases of confined geometry, such as liquids contained within porous media, this leads to a depression in the freezing point / melting point that is inversely proportional to the pore size, as given by the Gibbs–Thomson equation. Introduction The technique is closely related to using gas adsorption to measure pore sizes, but uses the Gibbs–Thomson equation rather than the Kelvin equation. They are both particular cases of the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interface (matter)
In the physical sciences, an interface is the boundary between two spatial regions occupied by different matter, or by matter in different physical states. The interface between matter and air, or matter and vacuum, is called a surface, and studied in surface science. In thermal equilibrium, the regions in contact are called phases, and the interface is called a phase boundary. An example for an interface out of equilibrium is the grain boundary in polycrystalline matter. The importance of the interface depends on the type of system: the bigger the quotient area/volume, the greater the effect the interface will have. Consequently, interfaces are very important in systems with large interface area-to-volume ratios, such as colloids. Interfaces can be flat or curved. For example, oil droplets in a salad dressing are spherical but the interface between water and air in a glass of water is mostly flat. Surface tension is the physical property which rules interface process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Energy
In surface science, surface energy (also interfacial free energy or surface free energy) quantifies the disruption of intermolecular bonds that occurs when a surface is created. In solid-state physics, surfaces must be intrinsically less energetically favorable than the bulk of the material (that is, the atoms on the surface must have more energy than the atoms in the bulk), otherwise there would be a driving force for surfaces to be created, removing the bulk of the material by sublimation. The surface energy may therefore be defined as the excess energy at the surface of a material compared to the bulk, or it is the work required to build an area of a particular surface. Another way to view the surface energy is to relate it to the work required to cut a bulk sample, creating two surfaces. There is "excess energy" as a result of the now-incomplete, unrealized bonding between the two created surfaces. Cutting a solid body into pieces disrupts its bonds and increases the surfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anisotropy
Anisotropy () is the structural property of non-uniformity in different directions, as opposed to isotropy. An anisotropic object or pattern has properties that differ according to direction of measurement. For example, many materials exhibit very different physical or mechanical properties when measured along different axes, e.g. absorbance, refractive index, conductivity, and tensile strength. An example of anisotropy is light coming through a polarizer. Another is wood, which is easier to split along its grain than across it because of the directional non-uniformity of the grain (the grain is the same in one direction, not all directions). Fields of interest Computer graphics In the field of computer graphics, an anisotropic surface changes in appearance as it rotates about its geometric normal, as is the case with velvet. Anisotropic filtering (AF) is a method of enhancing the image quality of textures on surfaces that are far away and viewed at a shallow angle. Older ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |