Normal Contact Stiffness on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
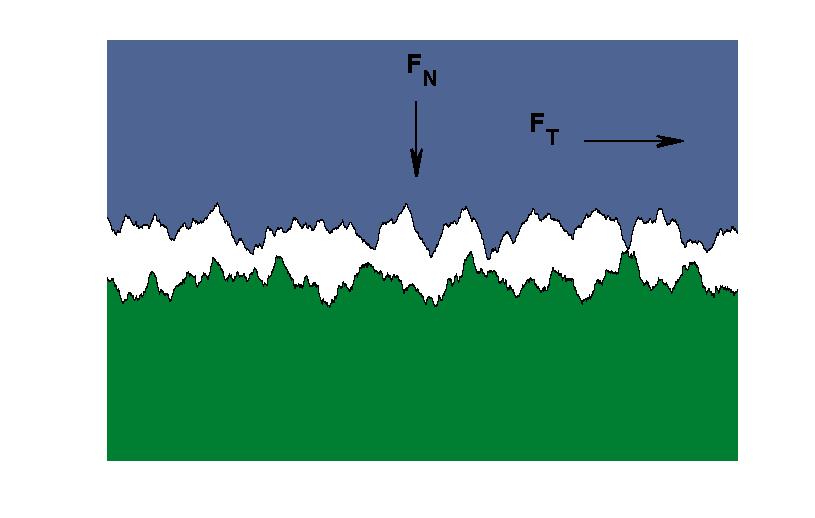 Normal contact stiffness is a physical quantity related to the generalized force displacement behavior of rough surfaces in contact with a
Normal contact stiffness is a physical quantity related to the generalized force displacement behavior of rough surfaces in contact with a
 Normal contact stiffness is a physical quantity related to the generalized force displacement behavior of rough surfaces in contact with a
Normal contact stiffness is a physical quantity related to the generalized force displacement behavior of rough surfaces in contact with a rigid body
In physics, a rigid body, also known as a rigid object, is a solid body in which deformation is zero or negligible, when a deforming pressure or deforming force is applied on it. The distance between any two given points on a rigid body rema ...
or a second similar rough surface. Specifically it is the amount of force per unit displacement required to compress an elastic object in the contact region. Rough surfaces can be considered as consisting of large numbers of asperities
In materials science, asperity, defined as "unevenness of surface, roughness, ruggedness" (from the Latin ''asper''—"rough"), has implications (for example) in physics and seismology. Smooth surfaces, even those polished to a mirror finish, ar ...
. As two solid bodies of the same material approach one another, the asperities interact, and they transition from conditions of non-contact to homogeneous bulk behaviour, with changes in the contact area. The varying values of stiffness and true contact area at an interface during this transition are dependent on the conditions of applied pressure and are of importance for the study of systems involving the physical interactions of multiple bodies including granular matter, electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or a gas). In electrochemical cells, electrodes are essential parts that can consist of a varie ...
contacts, and thermal contact
In heat transfer and thermodynamics, a thermodynamic system
A thermodynamic system is a body of matter and/or radiation separate from its surroundings that can be studied using the laws of thermodynamics.
Thermodynamic systems can be passive ...
s, where the interface-localized structures govern overall system performance by controlling the transmission of force, heat, charge carriers or matter through the interface.
References