|
Daminozide
Daminozide, also known as aminozide, Alar, Kylar, SADH, B-995, B-nine, and DMASA, is an organic compound which acts as a plant growth regulator. It was produced in the U.S. by the Uniroyal Chemical Company, Inc., (now integrated into the Chemtura Corporation), which registered daminozide for use on fruits intended for human consumption in 1963. It was primarily used on apples until 1989, when the manufacturer voluntarily withdrew it after the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency proposed banning it based on concerns about cancer risks to consumers. In addition to apples and ornamental plants, Uniroyal also registered daminozide for use on cherries, peaches, pears, Concord grapes, tomato transplants, and peanut vines. When used on fruit trees, daminozide affects flower bud initiation, fruit maturity, fruit firmness and coloring, preharvest drop and market quality of fruit at time of harvest and during storage. When consumed by mammals, daminozide is catabolised into succinic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octopine
Octopine is a derivative of the amino acids arginine and alanine. It was the first member of the class of chemical compounds known as opines to be discovered. Octopine gets its name from '' Octopus octopodia'' from which it was first isolated in 1927. Octopine has been isolated from the muscle tissue of invertebrates such as octopus, '' Pecten maximus'' and '' Sipunculus nudus'' where it functions as an analog of lactic acid. Plants may also produce this compound after infection by '' Agrobacterium tumefaciens'' and transfer of the octopine synthesis gene from the bacterium to the plant. Octopine is formed by reductive condensation of pyruvic acid Pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH) is the simplest of the keto acids, alpha-keto acids, with a carboxylic acid and a ketone functional group. Pyruvate, the conjugate acid, conjugate base, CH3COCOO−, is an metabolic intermediate, intermediate in several m ... and arginine through the action of the NADH-dependent enzyme octopine de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three Evolution of mammalian auditory ossicles, middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles and birds, from which their ancestors Genetic divergence, diverged in the Carboniferous Period over 300 million years ago. Around 6,640 Neontology#Extant taxon, extant species of mammals have been described and divided into 27 Order (biology), orders. The study of mammals is called mammalogy. The largest orders of mammals, by number of species, are the rodents, bats, and eulipotyphlans (including hedgehogs, Mole (animal), moles and shrews). The next three are the primates (including humans, monkeys and lemurs), the Artiodactyl, even-toed ungulates (including pigs, camels, and whales), and the Carnivora (including Felidae, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unsymmetrical Dimethylhydrazine
Unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine (abbreviated as UDMH; also known as 1,1-dimethylhydrazine, heptyl or Geptil) is a chemical compound with the formula H2NN(CH3)2 that is primarily used as a rocket propellant. At room temperature, UDMH is a colorless liquid, with a sharp, fishy, ammonia-like smell typical of organic amines. Samples turn yellowish on exposure to air and absorb oxygen and carbon dioxide. It is miscible with water, ethanol, and kerosene. At concentrations between 2.5% and 95% in air, its vapors are flammable. It is not sensitive to shock. Symmetrical dimethylhydrazine (1,2-dimethylhydrazine) also exists, but it is not as useful. UDMH can be oxidized in air to form many different substances, including toxic ones. Synthesis In 1875, UDMH was first prepared by Emil Fischer, who discovered and named the class of hydrazines, by reducing N-Nitrosodimethylamine with zinc in boiling acetic acid. Fischer's student Edward Renouf later studied UDMH more extensively as part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants (angiosperms) that is formed from the ovary after flowering. Fruits are the means by which angiosperms disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particular have long propagated using the movements of humans and other animals in a symbiotic relationship that is the means for seed dispersal for the one group and nutrition for the other; humans, and many other animals, have become dependent on fruits as a source of food. Consequently, fruits account for a substantial fraction of the world's agricultural output, and some (such as the apple and the pomegranate) have acquired extensive cultural and symbolic meanings. In common language and culinary usage, ''fruit'' normally means the seed-associated fleshy structures (or produce) of plants that typically are sweet (or sour) and edible in the raw state, such as apples, bananas, grapes, lemons, oranges, and strawberries. In botanical usage, the term ''fruit'' als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical
A chemical substance is a unique form of matter with constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Chemical substances may take the form of a single element or chemical compounds. If two or more chemical substances can be combined without reacting, they may form a chemical mixture. If a mixture is separated to isolate one chemical substance to a desired degree, the resulting substance is said to be chemically pure. Chemical substances can exist in several different physical states or phases (e.g. solids, liquids, gases, or plasma) without changing their chemical composition. Substances transition between these phases of matter in response to changes in temperature or pressure. Some chemical substances can be combined or converted into new substances by means of chemical reactions. Chemicals that do not possess this ability are said to be inert. Pure water is an example of a chemical substance, with a constant composition of two hydrogen atoms bonded to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a simple pnictogen hydride, and is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odour. Hydrazine is highly hazardous unless handled in solution as, for example, hydrazine hydrate (). Hydrazine is mainly used as a foaming agent in preparing Polymeric foam, polymer foams, but applications also include its uses as a precursor (chemistry), precursor to pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals, as well as a long-term storable propellant for in-outer space, space spacecraft propulsion. Additionally, hydrazine is used in various rocket propellant, rocket fuels and to prepare the gas precursors used in airbags. Hydrazine is used within both nuclear and conventional electrical power plant steam cycles as an oxygen scavenger to control concentrations of dissolved oxygen in an effort to reduce corrosion. , approximately 120,000 tons of hydrazine hydrate (corresponding to a 64% solution of hydrazine in water by weight) we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 appear in the genetic code of life. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups ( alpha- , beta- , gamma- amino acids, etc.); other categories relate to polarity, ionization, and side-chain group type ( aliphatic, acyclic, aromatic, polar, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino-acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life on Earth and its emergence. Amino acids are formally named by the IUPAC- IUBMB Joint Commi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrazide
Hydrazides in organic chemistry are a class of organic compounds with the formula where R is acyl (), sulfonyl (), phosphoryl (), phosphonyl () and similar groups (chalcogen analogs are included, for example sulfur analogs called thiohydrazides), (subscription required) and R' are any groups (typically hydrogen or organyl). Unlike hydrazine and alkylhydrazines, hydrazides are nonbasic owing to the inductive influence of the acyl, sulfonyl, or phosphoryl substituent. Sulfonyl hydrazides A common sulfonyl hydrazide is ''p''-toluenesulfonyl hydrazide, a white air-stable solid. They are also widely used as organic reagents. Toluenesulfonyl hydrazide is used to generate toluenesulfonyl hydrazones. When derived from ketones, these hydrazones participate in the Shapiro reaction and the Eschenmoser–Tanabe fragmentation. 2,4,6-Triisopropylbenzenesulfonylhydrazide is a useful source of diimide. Acyl hydrazides Acylhydrazines are derivatives of carboxylic acids, although the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
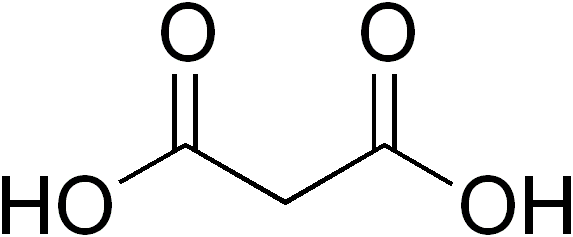
Dicarboxylic Acid
In organic chemistry, a dicarboxylic acid is an organic compound containing two carboxyl groups (). The general molecular formula for dicarboxylic acids can be written as , where R can be aliphatic or aromatic.Boy Cornils, Peter Lappe "Dicarboxylic Acids, Aliphatic" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2014, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. In general, dicarboxylic acids show similar chemical behavior and reactivity to monocarboxylic acids. Dicarboxylic acids are usually colorless solids. A wide variety of dicarboxylic acids are used in industry. Adipic acid, for example, is a precursor to certain kinds of nylon. A wide variety of dicarboxylic acids are found in nature. Aspartic acid and glutamic acid are two amino acids found in all life. Succinic and fumaric acids are essential for metabolism. A large inventory of derivatives are known including many mono- and diesters, amides, etc. Partial list of saturated dicarboxylic acids Some common or illustrative examples : ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Export–Import Bank Of The United States
The Export–Import Bank of the United States (EXIM) is the official export credit agency (ECA) of the United States federal government. Operating as a wholly owned federal government corporation, the bank "assists in financing and facilitating U.S. Foreign trade of the United States, exports of goods and services", particularly when private sector lenders are unable or unwilling to provide financing. Its current chairman and president, Reta Jo Lewis, was confirmed by the Senate on February 9, 2022. The Export–Import Bank was established in 1934 as the Export-Import Bank of Washington by an executive order of President Franklin D. Roosevelt. Its stated goal was "to aid in financing and to facilitate exports and imports and the exchange of commodities between the United States and other Nations or the agencies or nationals thereof." The bank's first transaction was a $3.8 million loan to Cuba in 1935 for the purchase of U.S. silver ingots. In 1945, it was made an Independent age ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinogen
A carcinogen () is any agent that promotes the development of cancer. Carcinogens can include synthetic chemicals, naturally occurring substances, physical agents such as ionizing and non-ionizing radiation, and biologic agents such as viruses and bacteria. Most carcinogens act by creating mutations in DNA that disrupt a cell's normal processes for regulating growth, leading to uncontrolled cellular proliferation. This occurs when the cell's DNA repair processes fail to identify DNA damage allowing the defect to be passed down to daughter cells. The damage accumulates over time. This is typically a multi-step process during which the regulatory mechanisms within the cell are gradually dismantled allowing for unchecked cellular division. The specific mechanisms for carcinogenic activity is unique to each agent and cell type. Carcinogens can be broadly categorized, however, as activation-dependent and activation-independent which relate to the agent's ability to engage dir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1,1-dimethylhydrazine
Unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine (abbreviated as UDMH; also known as 1,1-dimethylhydrazine, heptyl or Geptil) is a chemical compound with the formula H2NN(CH3)2 that is primarily used as a rocket propellant. At room temperature, UDMH is a colorless liquid, with a sharp, fishy, ammonia-like smell typical of organic amines. Samples turn yellowish on exposure to air and absorb oxygen and carbon dioxide. It is Miscibility, miscible with water, ethanol, and kerosene. At concentrations between 2.5% and 95% in air, its vapors are flammable. It is not sensitive to shock. Symmetrical dimethylhydrazine (1,2-dimethylhydrazine) also exists, but it is not as useful. UDMH can be oxidized in air to form many different substances, including toxic ones. Synthesis In 1875, UDMH was first prepared by Emil Fischer, who discovered and named the class of hydrazines, by reducing N-Nitrosodimethylamine with zinc in boiling acetic acid. Fischer's student Edward Renouf (chemist), Edward Renouf later st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |