|
Cylindrocyclophanes
Cylindrocyclophanes are a class of cyclophane, a group of aromatic hydrocarbons composed of two benzene rings attached in a unique structure. Cylindrocyclophanes were the first cyclophanes found in nature, isolated from a species of cyanobacteria, and have proven to be an interesting group of compounds to study due to their unusual molecular structure and intriguing biological possibilities, especially its cytotoxicity to some cancer cell lines. Origin Before the cylindrocyclophanes, the cyclophanes had all been produced synthetically. However, when a culture of the cyanobacteria ''Cylindrospermum lichenforme'' was being evaluated for antitumor activity, the extract was analyzed for new compounds, and a ,7paracyclophane was discovered. The structure of the cyclophane was determined and cylindrocyclophane A was named. A related class of compounds, the nostocyclophanes, were discovered during the same study but from another species of cyanobacteria, the ''Nostoc linckia''. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclophane
In organic chemistry, a cyclophane is a hydrocarbon consisting of an aromatic unit (typically a benzene ring) and a chain that forms a bridge between two non-adjacent positions of the aromatic ring. More complex derivatives with multiple aromatic units and bridges forming cagelike structures are also known. Cyclophanes are well-studied examples of strained organic compounds. Cyclophanes Structures Paracyclophanes adopt the boat conformation normally observed in cyclohexanes. Smaller value of n lead to greater distortions. X-ray crystallography on ' aracyclophane' shows that the aromatic bridgehead carbon atom makes an angle of 20.5° with the plane. The benzyl carbons deviate by another 20.2°. The carbon-to-carbon bond length alternation has increased from 0 for benzene to 39 pm. Despite their distorted structures, cyclophanes retain their aromaticity, as determined by UV-vis spectroscopy. Reactivity With regards to their reactivity, cyclophanes often exhibit diene-lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danheiser Benzannulation
The Danheiser benzannulation is a chemical reaction used in organic chemistry to generate highly substituted phenols in a single step. It is named after Rick L. Danheiser who developed the reaction. Annulation An annulation is defined as a transformation of one or more acyclic precursors resulting in the fusion of a new ring via two newly generated bonds. These strategies can be used to create aromatic systems from acyclic precursors in a single step, with many substituents already in place. Danheiser, R L., Brisbois, R G. James, J. Kowalczyk, Miller, R. F. “An Annulation Method for the Synthesis of Highly Substituted Polycyclic Aromatic and Heteroaromatic Compounds.” J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 3093-3100. A common synthetic annulation reaction is the Robinson annulation. It is a useful reactions for forming six-membered rings and generating polycyclic compounds. It is the combination of the Michael Addition and the Aldol Condensation reaction. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
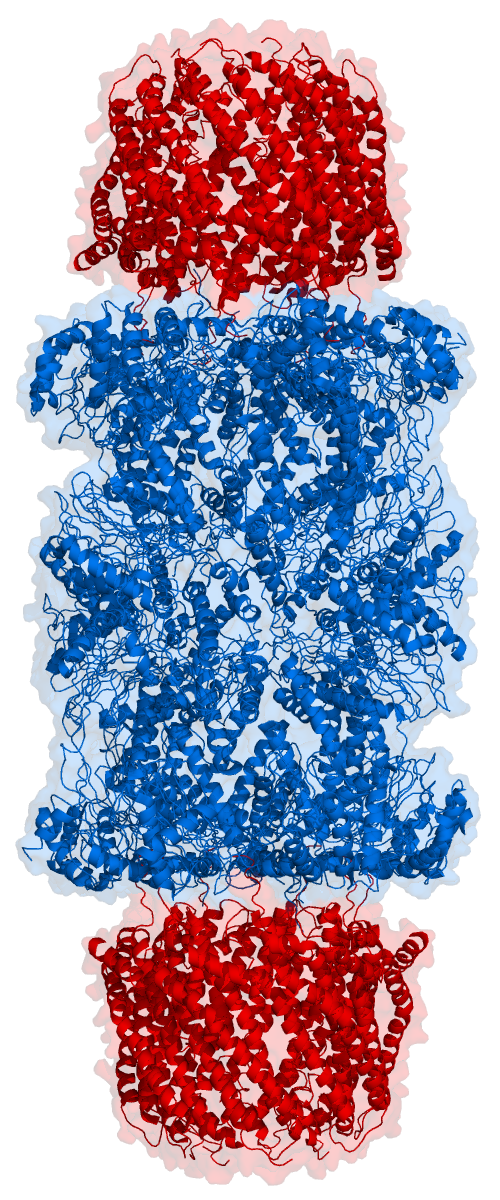
Proteasome
Proteasomes are protein complexes which degrade unneeded or damaged proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions are called proteases. Proteasomes are part of a major mechanism by which cells regulate the concentration of particular proteins and degrade misfolded proteins. Proteins are tagged for degradation with a small protein called ubiquitin. The tagging reaction is catalyzed by enzymes called ubiquitin ligases. Once a protein is tagged with a single ubiquitin molecule, this is a signal to other ligases to attach additional ubiquitin molecules. The result is a ''polyubiquitin chain'' that is bound by the proteasome, allowing it to degrade the tagged protein. The degradation process yields peptides of about seven to eight amino acids long, which can then be further degraded into shorter amino acid sequences and used in synthesizing new proteins. Proteasomes are found inside all eukaryotes and archaea, and in some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olefin Metathesis
Olefin metathesis is an organic reaction that entails the redistribution of fragments of alkenes (olefins) by the scission and regeneration of carbon-carbon double bonds. Because of the relative simplicity of olefin metathesis, it often creates fewer undesired by-products and hazardous wastes than alternative organic reactions. For their elucidation of the reaction mechanism and their discovery of a variety of highly active catalysts, Yves Chauvin, Robert H. Grubbs, and Richard R. Schrock were collectively awarded the 2005 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Catalysts The reaction requires metal catalysts. Most commercially important processes employ heterogeneous catalysts. The heterogeneous catalysts are often prepared by in-situ activation of a metal halides (MClx) using organoaluminium or organotin compounds, e.g. combining MClx–EtAlCl2. A typical catalyst support is alumina. Commercial catalysts are often based on molybdenum and ruthenium. Well-defined organometallic comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resorcinol
Resorcinol (or resorcin) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(OH)2. It is one of three isomeric benzenediols, the 1,3-isomer (or '' meta''-isomer). Resorcinol crystallizes from benzene as colorless needles that are readily soluble in water, alcohol, and ether, but insoluble in chloroform and carbon disulfide. Production Resorcinol is produced in several steps from benzene, starting with dialkylation with propylene to give 1,3-diisopropylbenzene. Oxidation and Hock rearrangement of this disubstituted arene gives acetone and resorcinol. Resorcinol is an expensive chemical, produced in only a very few locations around the world (to date only four commercial plants are known to be operative: in the United States, Germany,China and Japan), and as such it is the determining factor in the cost of PRF adhesives. Many additional routes exist for resorcinol. It was formerly produced by disulfonation of benzene followed by hydrolysis of the 1,3-disulfonate. This method ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kowalski Ester Homologation
The Kowalski ester homologation is a chemical reaction for the homologation of esters. This reaction was designed as a safer alternative to the Arndt–Eistert synthesis, avoiding the need for diazomethane. The Kowalski reaction is named after its inventor, Conrad J. Kowalski. Reaction mechanism The mechanism is disputed. Variations By changing the reagent in the second step of the reaction, the Kowalski ester homologation can also be used for the preparation of silyl ynol ether In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again b ...s. See also * Curtius rearrangement References {{Reflist Rearrangement reactions Carbon-carbon bond forming reactions Name reactions Homologation reactions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes ( morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses between 50 and 70 billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For an average human child between eight and fourteen years old, approximately twenty to thirty billion cells die per day. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the digits undergo apoptosis. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis produces cell fragments called apopt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Products
A natural product is a natural compound or substance produced by a living organism—that is, found in nature. In the broadest sense, natural products include any substance produced by life. Natural products can also be prepared by chemical synthesis (both semisynthesis and total synthesis) and have played a central role in the development of the field of organic chemistry by providing challenging synthetic targets. The term natural product has also been extended for commercial purposes to refer to cosmetics, dietary supplements, and foods produced from natural sources without added artificial ingredients. Within the field of organic chemistry, the definition of natural products is usually restricted to organic compounds isolated from natural sources that are produced by the pathways of primary or secondary metabolism. Within the field of medicinal chemistry, the definition is often further restricted to secondary metabolites. Secondary metabolites (or specialized metabol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteasome
Proteasomes are protein complexes which degrade unneeded or damaged proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions are called proteases. Proteasomes are part of a major mechanism by which cells regulate the concentration of particular proteins and degrade misfolded proteins. Proteins are tagged for degradation with a small protein called ubiquitin. The tagging reaction is catalyzed by enzymes called ubiquitin ligases. Once a protein is tagged with a single ubiquitin molecule, this is a signal to other ligases to attach additional ubiquitin molecules. The result is a ''polyubiquitin chain'' that is bound by the proteasome, allowing it to degrade the tagged protein. The degradation process yields peptides of about seven to eight amino acids long, which can then be further degraded into shorter amino acid sequences and used in synthesizing new proteins. Proteasomes are found inside all eukaryotes and archaea, and in some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aromatic Hydrocarbons
Aromatic compounds, also known as "mono- and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons", are organic compounds containing one or more aromatic rings. The parent member of aromatic compounds is benzene. The word "aromatic" originates from the past grouping of molecules based on smell, before their general chemical properties are understood. The current definition of aromatic compounds does not have any relation with their smell. Heteroarenes are closely related, since at least one carbon atom of CH group is replaced by one of the heteroatoms oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur. Examples of non-benzene compounds with aromatic properties are furan, a heterocyclic compound with a five-membered ring that includes a single oxygen atom, and pyridine, a heterocyclic compound with a six-membered ring containing one nitrogen atom. Hydrocarbons without an aromatic ring are called aliphatic. Benzene ring model Benzene, C6H6, is the least complex aromatic hydrocarbon, and it was the first one named as such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |