|
Cyclostratigraphy
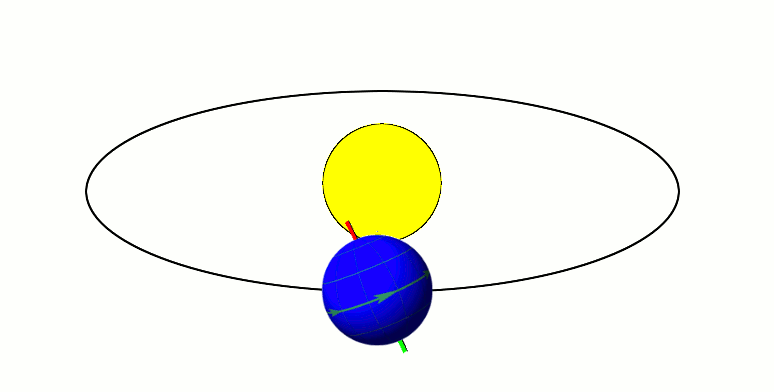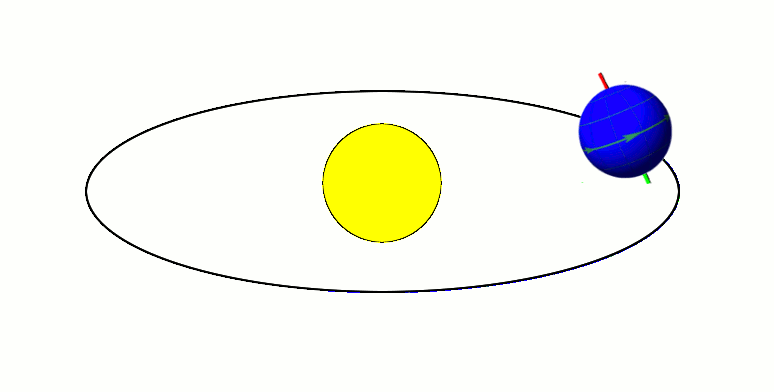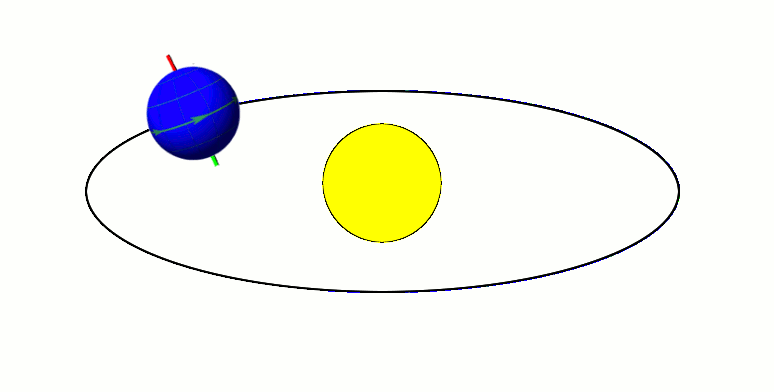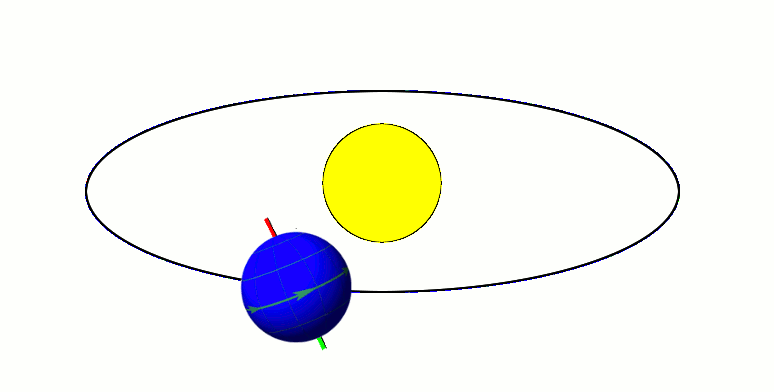
Cyclostratigraphy is a subdiscipline of stratigraphy that studies astronomically forced climate cycles within sedimentary successions. Orbital changes Astronomical cycles (also known as Milankovitch cycles) are variations of the Earth's orbit around the Sun due to the gravitational interaction with other masses within the Solar System. Due to this cyclicity, solar irradiation differs through time on different hemispheres and seasonality is affected. These insolation variations have influence on Earth's climate and on the deposition of sedimentary rocks. The main orbital cycles are precession with main periods of 19 and 23 kyr, obliquity with main periods of 41 kyr, and 1.2 Myr, and eccentricity with main periods of around 100 kyr, 405 kyr, and 2.4 Myr. Precession influences how much insolation each hemisphere receives. Obliquity controls the intensity of the seasons. Eccentricity influences how much insolation the Earth receives altogether. Varied insolation directly infl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Deposits
Cycle, cycles, or cyclic may refer to: Anthropology and social sciences * Cyclic history, a theory of history * Cyclical theory, a theory of American political history associated with Arthur Schlesinger, Sr. * Social cycle, various cycles in social sciences ** Business cycle, the downward and upward movement of gross domestic product (GDP) around its ostensible, long-term growth trend Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Cycle'' (2008 film), a Malayalam film * ''Cycle'' (2017 film), a Marathi film Literature * ''Cycle'' (magazine), an American motorcycling enthusiast magazine * Literary cycle, a group of stories focused on common figures Music Musical terminology * Cycle (music), a set of musical pieces that belong together ** Cyclic form, a technique of construction involving multiple sections or movements ** Interval cycle, a collection of pitch classes generated from a sequence of the same interval class ** Song cycle, individually complete songs design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obliquity
In astronomy, axial tilt, also known as obliquity, is the angle between an object's rotational axis and its orbital axis, which is the line perpendicular to its orbital plane; equivalently, it is the angle between its equatorial plane and orbital plane. It differs from orbital inclination. At an obliquity of 0 degrees, the two axes point in the same direction; that is, the rotational axis is perpendicular to the orbital plane. The rotational axis of Earth, for example, is the imaginary line that passes through both the North Pole and South Pole, whereas the Earth's orbital axis is the line perpendicular to the imaginary plane through which the Earth moves as it revolves around the Sun; the Earth's obliquity or axial tilt is the angle between these two lines. Over the course of an orbital period, the obliquity usually does not change considerably, and the orientation of the axis remains the same relative to the background of stars. This causes one pole to be pointed more to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratigraphy
Stratigraphy is a branch of geology concerned with the study of rock layers (strata) and layering (stratification). It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks. Stratigraphy has three related subfields: lithostratigraphy (lithologic stratigraphy), biostratigraphy (biologic stratigraphy), and chronostratigraphy (stratigraphy by age). Historical development Catholic priest Nicholas Steno established the theoretical basis for stratigraphy when he introduced the law of superposition, the principle of original horizontality and the principle of lateral continuity in a 1669 work on the fossilization of organic remains in layers of sediment. The first practical large-scale application of stratigraphy was by William Smith in the 1790s and early 19th century. Known as the "Father of English geology", Smith recognized the significance of strata or rock layering and the importance of fossil markers for correlating strata; he created the first geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Sediments
Cyclic sediments (also called rhythmic sediments) are sequences of sedimentary rocks that are characterised by repetitive patterns of different rock types (strata) or facies within the sequence. Processes that generate sedimentary cyclicity can be either autocyclic or allocyclic, and can result in piles of sedimentary cycles hundreds or even thousands of metres thick. The study of sequence stratigraphy was developed from controversies over the causes of cyclic sedimentation. Processes leading to cyclic sedimentation Cyclic sedimentation occurs when the depositional environments change repeatedly. Changes in the environment of deposition influence the type and amount of sediments that are deposited, producing different sedimentary rock types. At least one rock type, which is regarded as the starting point, must be repeated. Based on the processes that generate the cyclic deposits, two types of sedimentary cyclic successions can be distinguished. Allocycles Allocycles are sedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argon–argon Dating
Argon–argon (or 40Ar/39Ar) dating is a radiometric dating method invented to supersede Potassium-argon dating, potassiumargon (K/Ar) dating in accuracy. The older method required splitting samples into two for separate potassium and argon measurements, while the newer method requires only one rock fragment or mineral grain and uses a single measurement of isotopes of argon, argon isotopes. 40Ar/39Ar dating relies on neutron irradiation from a nuclear reactor to convert a stable form of potassium (39K) into the radioactive 39Ar. As long as a standard of known age is co-irradiated with unknown samples, it is possible to use a single measurement of argon isotopes to calculate the 40K/40Ar* ratio, and thus to calculate the age of the unknown sample. 40Ar* refers to the radiogenic 40Ar, i.e. the 40Ar produced from radioactive decay of 40K. 40Ar* does not include atmospheric argon adsorbed to the surface or inherited through diffusion and its calculated value is derived from measuring t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleoclimatology
Paleoclimatology ( British spelling, palaeoclimatology) is the scientific study of climates predating the invention of meteorological instruments, when no direct measurement data were available. As instrumental records only span a tiny part of Earth's history, the reconstruction of ancient climate is important to understand natural variation and the evolution of the current climate. Paleoclimatology uses a variety of proxy methods from Earth and life sciences to obtain data previously preserved within rocks, sediments, boreholes, ice sheets, tree rings, corals, shells, and microfossils. Combined with techniques to date the proxies, the paleoclimate records are used to determine the past states of Earth's atmosphere. The scientific field of paleoclimatology came to maturity in the 20th century. Notable periods studied by paleoclimatologists include the frequent glaciations that Earth has undergone, rapid cooling events like the Younger Dryas, and the rapid warming du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiometric Dating
Radiometric dating, radioactive dating or radioisotope dating is a technique which is used to Chronological dating, date materials such as Rock (geology), rocks or carbon, in which trace radioactive impurity, impurities were selectively incorporated when they were formed. The method compares the abundance of a naturally occurring Radionuclide, radioactive isotope within the material to the abundance of its Radioactive decay, decay products, which form at a known constant rate of decay. Radiometric dating of minerals and rocks was pioneered by Ernest Rutherford (1906) and Bertram Boltwood (1907). Radiometric dating is now the principal source of information about the Absolute dating, absolute age of rocks and other Geology, geological features, including the age of Paleontology, fossilized life forms or the age of Earth itself, and can also be used to date a wide range of natural and Artifact (archaeology), man-made materials. Together with stratigraphy, stratigraphic principles, ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Eccentricity
In astrodynamics, the orbital eccentricity of an astronomical object is a dimensionless parameter that determines the amount by which its orbit around another body deviates from a perfect circle. A value of 0 is a circular orbit, values between 0 and 1 form an elliptic orbit, 1 is a parabolic escape orbit (or capture orbit), and greater than 1 is a hyperbola. The term derives its name from the parameters of conic sections, as every Kepler orbit is a conic section. It is normally used for the isolated two-body problem, but extensions exist for objects following a rosette orbit through the Galaxy. Definition In a two-body problem with inverse-square-law force, every orbit is a Kepler orbit. The eccentricity of this Kepler orbit is a non-negative number that defines its shape. The eccentricity may take the following values: * Circular orbit: * Elliptic orbit: * Parabolic trajectory: * Hyperbolic trajectory: The eccentricity is given by e = \sqrt where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precession
Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotational axis of a rotating body. In an appropriate reference frame it can be defined as a change in the first Euler angle, whereas the third Euler angle defines the rotation itself. In other words, if the axis of rotation of a body is itself rotating about a second axis, that body is said to be precessing about the second axis. A motion in which the second Euler angle changes is called '' nutation''. In physics, there are two types of precession: torque-free and torque-induced. In astronomy, ''precession'' refers to any of several slow changes in an astronomical body's rotational or orbital parameters. An important example is the steady change in the orientation of the axis of rotation of the Earth, known as the precession of the equinoxes. Torque-free or torque neglected Torque-free precession implies that no external moment (torque) is applied to the body. In torque-free precession, the angular momentum is a constant, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Irradiance
Solar irradiance is the power per unit area (surface power density) received from the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation in the wavelength range of the measuring instrument. Solar irradiance is measured in watts per square metre (W/m2) in SI units. Solar irradiance is often integrated over a given time period in order to report the radiant energy emitted into the surrounding environment (joule per square metre, J/m2) during that time period. This integrated solar irradiance is called solar irradiation, solar radiation, solar exposure, solar insolation, or insolation. Irradiance may be measured in space or at the Earth's surface after atmospheric absorption and scattering. Irradiance in space is a function of distance from the Sun, the solar cycle, and cross-cycle changes.Michael Boxwell, ''Solar Electricity Handbook: A Simple, Practical Guide to Solar Energy'' (2012), pp. 41–42. Irradiance on the Earth's surface additionally depends on the tilt of the measuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar System" and "solar system" structures in theinaming guidelines document. The name is commonly rendered in lower case ('solar system'), as, for example, in the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' an''Merriam-Webster's 11th Collegiate Dictionary''. is the gravitationally bound Planetary system, system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it. It Formation and evolution of the Solar System, formed about 4.6 billion years ago when a dense region of a molecular cloud collapsed, forming the Sun and a protoplanetary disc. The Sun is a typical star that maintains a hydrostatic equilibrium, balanced equilibrium by the thermonuclear fusion, fusion of hydrogen into helium at its stellar core, core, releasing this energy from its outer photosphere. As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |