|
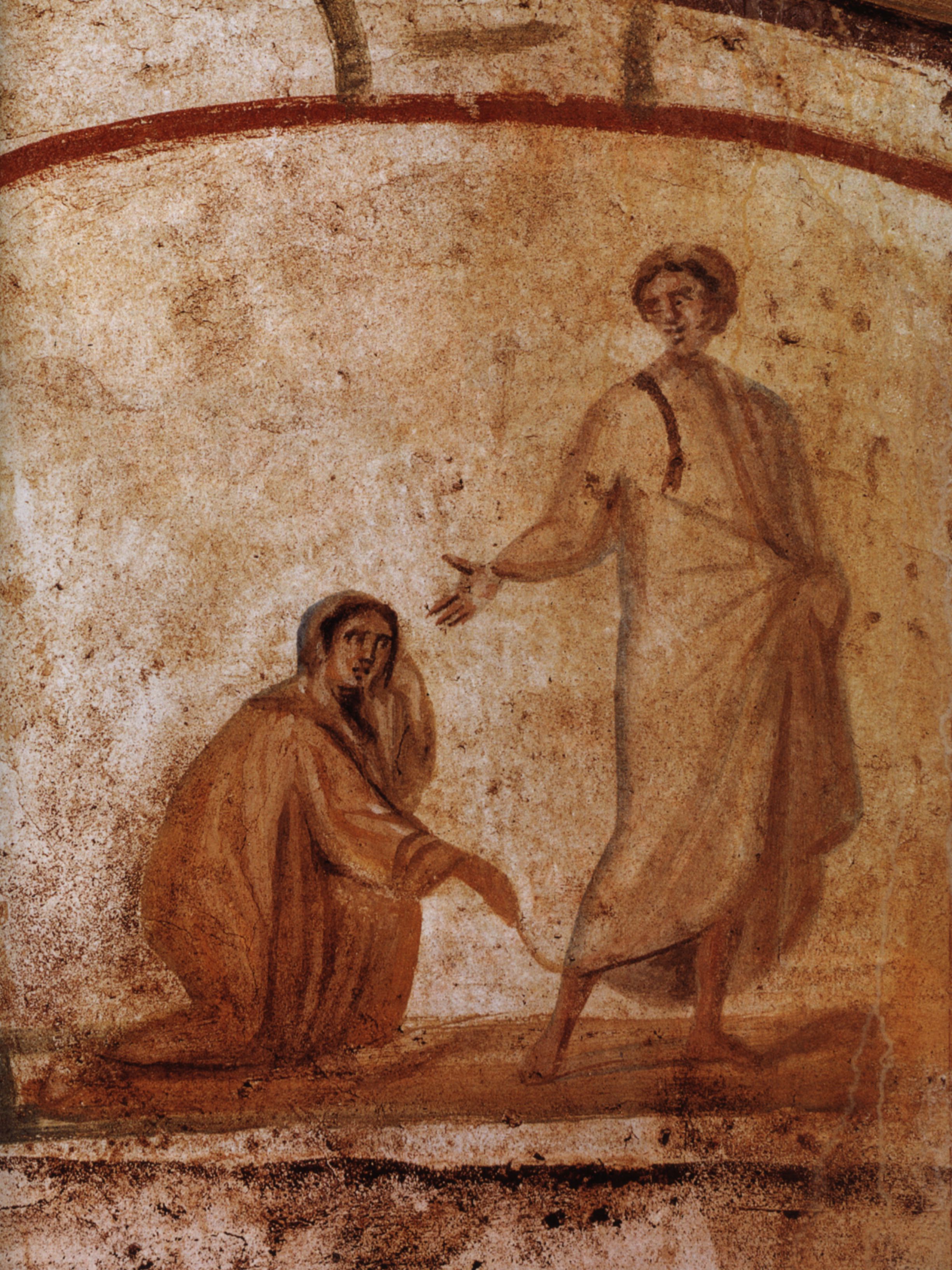
Cure Of A Bleeding Woman
Jesus healing the bleeding woman (or "woman with an issue of blood" and other variants) is one of the miracles of Jesus recorded in the synoptic gospels. __TOC__ Context In the Gospel accounts, this miracle immediately follows the exorcism at Gerasa and is combined with the miracle of the raising of Jairus's daughter. The narrative interrupts the story of Jairus's daughter, a stylistic element which scholars call an intercalated or sandwich narrative. Narrative comparison There are several differences between the accounts given by Mark, Matthew and Luke. Mark The incident occurred while Jesus was traveling to Jairus's house, amid a large crowd, according to Mark: The woman's condition, which is not clear in terms of a modern medical diagnosis, is translated as an 'issue of blood' in the King James Version and a 'flux of blood' in the Wycliffe Bible and some other versions. In scholarly language she is often referred to by the original New Testament Greek term as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Healing Of A Bleeding Women Marcellinus-Peter-Catacomb
With physical trauma or disease suffered by an organism, healing involves the repairing of damaged tissue (biology), tissue(s), organ (anatomy), organs and the biological system as a whole and resumption of (normal) functioning. Medicine includes the process by which the Cell (biology), cells in the Human body, body regenerate and repair to reduce the size of a damaged or necrosis, necrotic area and replace it with new living tissue. The replacement can happen in two ways: by ''regeneration'' in which the necrotic cells are replaced by new cells that form "like" tissue as was originally there; or by ''repair'' in which injured tissue is replaced with scar, scar tissue. Most Organ (anatomy), organs will heal using a mixture of both mechanisms. Within surgery, healing is more often referred to as recovery, and postoperative recovery has historically been viewed simply as restitution of function and readiness for discharge. More recently, it has been described as an energy‐requirin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
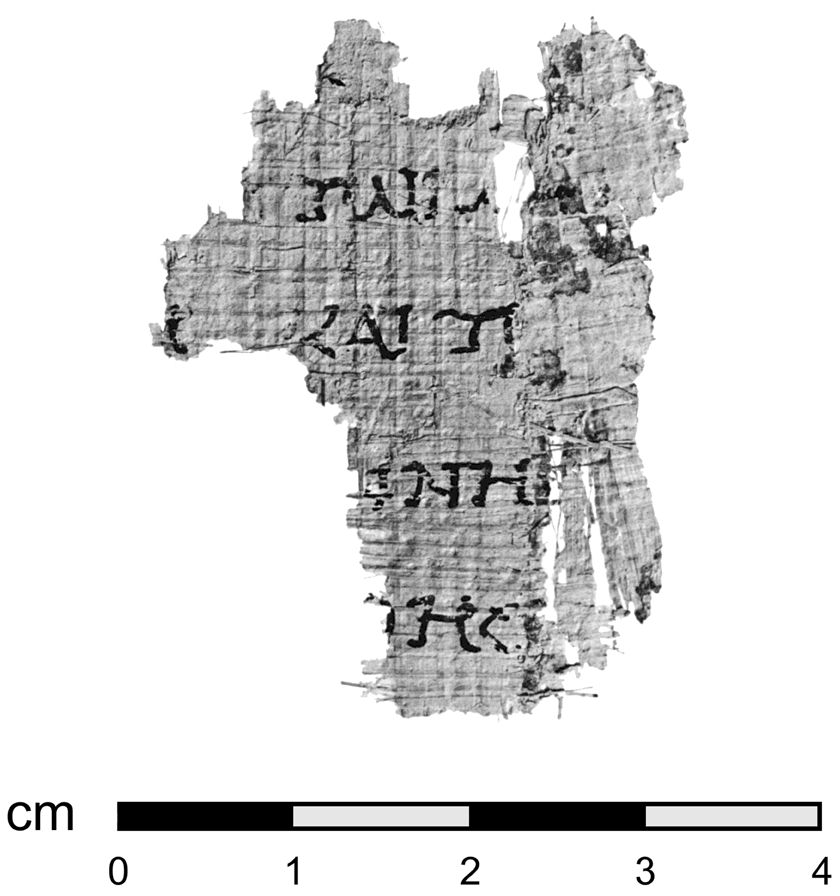
Mark 6
Mark 6 is the sixth chapter of the Gospel of Mark in the New Testament of the Christianity, Christian Bible. In this chapter, Jesus goes to Nazareth and experiences rejection by his own family. He then sends his Apostles in the New Testament, Apostles in pairs to various cities in the region, where they might also face rejection. Finally, Jesus goes back to the Sea of Galilee and performs some of his most famous miracles, including the Feeding of The 5000, feeding of the 5,000 and Jesus walking on water, walking on water. This chapter also gives an account of the Beheading of St John the Baptist, murder of John the Baptist. Text The original text was written in Koine Greek. Chapters and verses of the Bible, This chapter is divided into 56 verses. Textual witnesses Some early biblical manuscript#New Testament manuscripts, manuscripts containing the text of this chapter are: *Codex Vaticanus (325–350; complete) *Codex Sinaiticus (330–360; complete) *Codex Bezae (~400; complete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloids (such as arsenic or silicon). These additions produce a range of alloys some of which are harder than copper alone or have other useful properties, such as strength, ductility, or machinability. The archaeological period during which bronze was the hardest metal in widespread use is known as the Bronze Age. The beginning of the Bronze Age in western Eurasia is conventionally dated to the mid-4th millennium BCE (~3500 BCE), and to the early 2nd millennium BCE in China; elsewhere it gradually spread across regions. The Bronze Age was followed by the Iron Age, which started about 1300 BCE and reaching most of Eurasia by about 500 BCE, although bronze continued to be much more widely used than it is in modern times. Because historica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine I
Constantine I (27 February 27222 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was a Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337 and the first Roman emperor to convert to Christianity. He played a Constantine the Great and Christianity, pivotal role in elevating the status of Christianity in Rome, Edict of Milan, decriminalising Christian practice and ceasing Persecution of Christians in the Roman Empire, Christian persecution. This was a turning point in the Historiography of the Christianization of the Roman Empire, Christianisation of the Roman Empire. He founded the city of Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) and made it the capital of the Empire, which it remained for over a millennium. Born in Naissus, a city located in the Roman province, province of Moesia Superior (now Niš, Serbia), Constantine was the son of Flavius Constantius, a Roman army officer from Moesia Superior, who would become one of the four emperors of the Tetrarchy. His mother, Helena, mother of Constantin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eusebius
Eusebius of Caesarea (30 May AD 339), also known as Eusebius Pamphilius, was a historian of Christianity, exegete, and Christian polemicist from the Roman province of Syria Palaestina. In about AD 314 he became the bishop of Caesarea Maritima. Together with Pamphilus, Eusebius was a scholar of the biblical canon and is regarded as one of the most learned Christians during late antiquity. He wrote the ''Demonstrations of the Gospel'', '' Preparations for the Gospel'' and ''On Discrepancies between the Gospels'', studies of the biblical text. His work '' Onomasticon'' is an early geographical lexicon of places in the Holy Land mentioned in the Bible. As "Father of Church History" (not to be confused with the title of Church Father), he produced the ''Ecclesiastical History'', ''On the Life of Pamphilus'', the ''Chronicle'' and ''On the Martyrs''. He also produced a biographical work on Constantine the Great, the first Christian Roman emperor, who was ''Augustus'' between A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HADRIANUS RIC II 938-789065
Hadrianus may refer to: People * Hadrian (76–138), Roman emperor * Gaius Fabius Hadrianus, Roman colonial administrator & politician * Pope Adrian (other) (any of the listed popes) * Hadrianus Junius Hadrianus Junius (1511–1575), also known as Adriaen de Jonghe, was a Dutch physician, classical scholar, translator, lexicographer, antiquarian, historiographer, emblematist, school rector, and Latin poet. He is not to be confused with several ... (1511–1575), also known as Adriaen de Jonghe Other * 7446 Hadrianus, an asteroid * ''Hadrianus'' (turtle), an extinct genus of tortoise *The origin of the Emperor family, Hadria Picena or Hatria the modern Atri in Abruzzo region, Italy See also * {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relics
In religion, a relic is an object or article of religious significance from the past. It usually consists of the physical remains or personal effects of a saint or other person preserved for the purpose of veneration as a tangible memorial. Relics are an important aspect of some forms of Buddhism, Christianity, Islam, shamanism, and many other religions. ''Relic'' derives from the Latin ''reliquiae'', meaning "remains", and a form of the Latin verb ''relinquere'', to "leave behind, or abandon". A reliquary is a shrine that houses one or more religious relics. In classical antiquity In ancient Greece, a city or sanctuary might claim to possess, without necessarily displaying, the remains of a venerated hero as a part of a hero cult. Other venerable objects associated with the hero were more likely to be on display in sanctuaries, such as spears, shields, or other weaponry; chariots, ships or figureheads; furniture such as chairs or tripods; and clothing. The sanctuary of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John McEvilly
John McEvilly (1818–1902) was an Irish Roman Catholic Church clergyman who served as the Archbishop of Tuam from 1881 to 1902. He was born on 15 April 1818 in Louisburgh, a small town near Westport, County Mayo, Ireland., ''The Episcopal Succession in England, Scotland and Ireland, volume 2'', p. 233. He entered the Seminary of Tuam in January 1833, then was sent to Maynooth College in September 1833, where among his contemporaries was the future Archbishop of Armagh Joseph Dixon. In 1842, McEvilly was ordained a priest of the Archdiocese of Tuam. On 9 January 1857, he was appointed the Bishop of Galway by the Holy See and was consecrated on 22 March 1857 by the Most Reverend John MacHale, Archbishop of Tuam., ''Handbook of British Chronology'', p. 430. While as Bishop of Galway, McEvilly was appointed the Apostolic Administrator of Kilmacduagh and Kilfenora in September 1866 and appointed Coadjutor Archbishop of Tuam on 11 January 1878. On the death of Archbishop MacH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venerable Bede
Bede (; ; 672/326 May 735), also known as Saint Bede, Bede of Jarrow, the Venerable Bede, and Bede the Venerable (), was an English monk, author and scholar. He was one of the most known writers during the Early Middle Ages, and his most famous work, ''Ecclesiastical History of the English People'', gained him the title "The Father of History of England, English History". He served at the monastery of St Peter and its companion monastery of St Paul in the Kingdom of Northumbria of the Angles (tribe), Angles. Born on lands belonging to the twin monastery of Monkwearmouth–Jarrow Abbey, Monkwearmouth–Jarrow in present-day Tyne and Wear, England, Bede was sent to Monkwearmouth at the age of seven and later joined Abbot Ceolfrith at Jarrow. Both of them survived a plague that struck in 686 and killed the majority of the population there. While Bede spent most of his life in the monastery, he travelled to several abbeys and monasteries across the British Isles, even visiting t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornelius A Lapide
Cornelius Cornelii a Lapide (''né'' Cornelis Cornelissen van den Steen; 28 December 1567 – 12 March 1637) was a Flemish Catholic priest. He was a Jesuit and exegete of Sacred Scripture. Life Lapide was born in Bocholt, Belgium. He studied humanities and philosophy at the Jesuit colleges in Maastricht and Cologne, first theology for half a year at the University of Douai and afterwards for four years at the Old University of Leuven; he entered the Society of Jesus on 11 June 1592 and, after a novitiate of two years and another year of theology, was ordained a Catholic priest on 24 December 1595. After teaching philosophy for half a year, he was made a professor of Sacred Scripture at Leuven in 1596 and professor of Hebrew in 1597. During his professorship at Leuven, he spent his holidays preaching and administering the Sacraments, especially at the pilgrimage of Scherpenheuvel (Montaigu). In 1616, Lapide was called to Rome in the same capacity, where, on 3 November, he assum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tzitzit
''Tzitzit'' ( ''ṣīṣīṯ'', ; plural ''ṣīṣiyyōṯ'', Ashkenazi Hebrew, Ashkenazi: '; and Samaritan Hebrew, Samaritan: ') are specially knotted ritual Fringe (trim), fringes, or tassels, worn in antiquity by Israelites and today by observant Jews and Samaritans. are usually attached to the four corners of the ''tallit gadol'' (prayer shawl), usually referred to simply as a or ; and ''tallit katan'' (everyday undershirt). Through synecdoche, a may be referred to as . Etymology The word may derive from the semitic root, Hebrew root [n-ts-h]. shares this root with the Hebrew for 'lock of hair'. For example, in the Book of Ezekiel an angel grabs the prophet "by the of [his] head;" he could be said to be "dragged by his hair." A popular etymological interpretation of derives from another word which shares this root. ( 'budding flower') may once have referred to floral ornamentation on clothing. One can hear distinct similarities with contemporaneous Akkadian lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabbinic Judaism
Rabbinic Judaism (), also called Rabbinism, Rabbinicism, Rabbanite Judaism, or Talmudic Judaism, is rooted in the many forms of Judaism that coexisted and together formed Second Temple Judaism in the land of Israel, giving birth to classical rabbinic Judaism, which flourished from the 1st century CE to the final redaction of the Babylonian Talmud in c. 600. Mainly developing after the destruction of the Jerusalem Temple (70 CE), it eventually became the normative form of Judaism. Rabbinic Judaism has been an orthodox form of Judaism since the 6th century CE, after the codification of the Babylonian Talmud. It has its roots in the Pharisaic school of Second Temple Judaism and is based on the belief that Moses at Mount Sinai received both the Written Torah (''Torah she-be-Khetav'') and the Oral Torah (''Torah she-be-al Peh'') from God. The Oral Torah explains the Written Torah, and it was the rabbis claimed that it was them who possessed this memorized and orally transmitte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |