|
Corn Gluten
Corn gluten meal (CGM) is the principal protein of corn (maize) endosperm consisting mainly of zein and glutelin. It is a byproduct of corn processing that has historically been used as an animal feed. Despite the name, corn gluten does not contain true gluten, which is formed by the interaction of gliadin and glutenin proteins. Production Corn gluten meal is one product of wet-milling corn as well as corn starch, germ oil meal, corn gluten feed, and steep liquor. Corn is steeped in water mixed with sulfur dioxide and ground to separate germ from the endosperm to extract oil. The endosperm goes through screenings to separate starch and proteins from the corn fiber or bran. The remaining starch and proteins are centrifuged to separate the starch from the corn gluten meal. Corn gluten meal as commonly produced contains "71.4% crude protein, 4.1% fat, 0.8% fiber, 1.2% ash, 12.4% starch, 10.1% other carbohydrates". The product is a golden yellow to brown powder with a cereal odor. U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native Americans planted it alongside beans and squashes in the Three Sisters polyculture. The leafy stalk of the plant gives rise to male inflorescences or tassels which produce pollen, and female inflorescences called ears. The ears yield grain, known as kernels or seeds. In modern commercial varieties, these are usually yellow or white; other varieties can be of many colors. Maize relies on humans for its propagation. Since the Columbian exchange, it has become a staple food in many parts of the world, with the total production of maize surpassing that of wheat and rice. Much maize is used for animal feed, whether as grain or as the whole plant, which can either be baled or made into the more palatable silage. Sugar-rich varieties called sw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur Dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless gas with a pungent smell that is responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic activity and is produced as a by-product of metals refining and the burning of Sour gas, sulfur-Sour crude oil, bearing fossil fuels. Sulfur dioxide is somewhat toxic to humans, although only when inhaled in relatively large quantities for a period of several minutes or more. It was known to medieval alchemy, alchemists as "volatile spirit of sulfur". Structure and bonding SO2 is a bent molecule with ''C''2v Point groups in three dimensions, symmetry point group. A valence bond theory approach considering just ''s'' and ''p'' orbitals would describe the bonding in terms of resonance (chemistry), resonance between two resonance structures. The sulfur–oxygen bond has a bond order of 1.5. There is support f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensitization (immunology)
In immunology, the term sensitization is used for the following concepts:Anderson DM, ed. (2003). "Sensitization." ''Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary'', 30th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders, p. 1680. .Brown MJ, ed. (1992). "Sensitization." ''Miller-Keane Encyclopedia & Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health'', 5th ed. Philadelphia; London: Saunders, p. 1352. .Pugh MB, ed. (2000). "Sensitization." ''Stedman's Medical Dictionary'', 27th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, p. 1619. .Tada T, Taniguchi M, Okumura Y, Miyasaka M, eds. (1993). "Sensitization." ''Dictionary of Terms in Immunology'', 3rd ed. Osaka: Saishin-Igakusha, Ltd., p. 510. C3547 (in Japanese). * Immunization by inducing an adaptive response in the immune system. In this sense, sensitization is the term more often in usage for induction of allergic responses.Janeway C, Travers P, Walport M, Shlomchik M, eds. (2001). ''Immunobiology 5: The Immune System in Health and Disease.'' New York: Ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodenticide
Rodenticides are chemicals made and sold for the purpose of killing rodents. While commonly referred to as "rat poison", rodenticides are also used to kill mice, woodchucks, chipmunks, porcupines, nutria, beavers, and voles. Some rodenticides are lethal after one exposure while others require more than one. Rodents are disinclined to gorge on an unknown food (perhaps reflecting an adaptation to their inability to vomit), preferring to sample, wait and observe whether it makes them or other rats sick. This phenomenon of poison shyness is the rationale for poisons that kill only after multiple doses. Besides being directly toxic to the mammals that ingest them, including dogs, cats, and humans, many rodenticides present a secondary poisoning risk to animals that hunt or scavenge the dead corpses of rats. Classes of rodenticides Anticoagulants Anticoagulants are defined as chronic (death occurs one to two weeks after ingestion of the lethal dose, rarely sooner), single-d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolyzed Vegetable Protein
Hydrolyzed vegetable protein (HVP) products are foodstuffs obtained by the hydrolysis of protein, and have a meaty, savory taste similar to broth (bouillon). Regarding the production process, a distinction can be made between acid-hydrolyzed vegetable protein (aHVP), enzymatically produced HVP, and other seasonings, e.g., fermented soy sauce. Hydrolyzed vegetable protein products are particularly used to round off the taste of soups, sauces, meat products, snacks, and other dishes, as well as for the production of ready-to-cook soups and bouillons. History Food technologists have long known that protein hydrolysis produces a meat bouillon-like odor and taste. Hydrolysates have been a part of the human diet for centuries, notably in the form of fermented soy sauce, or Shoyu. Shoyu, traditionally made from wheat and soy protein, has been produced in Japan for over 1,500 years, following its introduction from mainland China. The origins of producing these materials through the ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nutrient Pollution
Nutrient pollution is a form of water pollution caused by too many Nutrient, nutrients entering the water. It is a primary cause of eutrophication of surface waters (lakes, rivers and Coast, coastal waters), in which excess nutrients, usually nitrogen or phosphorus, stimulate algae, algal growth. Sources of nutrient pollution include surface runoff from farms, waste from septic tanks and feedlots, and air pollution, emissions from burning fuels. Raw sewage, which is rich in nutrients, also contributes to the issue when dumped in water bodies. Excess Reactive nitrogen, nitrogen causes environmental problems such as harmful algal blooms, Hypoxia (environmental), hypoxia, acid rain, nitrogen saturation in forests, and climate change. Agricultural production relies heavily on the use of natural and synthetic Fertilizer, fertilizers, which often contain high levels of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. When nitrogen and phosphorus are not fully used by the growing plants, they can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bran
Bran, also known as miller's bran, is the component of a Cereal, cereal grain consisting of the hard layersthe combined aleurone and Fruit anatomy#Pericarp layers, pericarpsurrounding the endosperm. Maize, Corn (maize) bran also includes the pedicel (tip cap). Along with the cereal germ, germ, it is an integral part of whole grains, and is often produced as a byproduct of mill (grinding), milling in the production of refined grains. Bran is highly nutritious, but is difficult to digest due to its high fiber content; its high fat content also reduces its shelf life as the oils/fats are prone to becoming rancid. As such, it is typically removed from whole grain during the Refined grains, refining processe.g. in processing wheat grain into white flour, or refining brown rice into white rice. Bran is present in cereal grain, including rice, maize, corn (maize), wheat, oats, barley, rye, and millet. Bran is not the same as chaff, which is a coarser, scaly material surrounding the gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cereal Germ
The germ of a cereal grain is the part that develops into a plant; it is the seed embryo. Along with bran, germ is often a by-product of the milling that produces refined grain products. Cereal grains and their components, such as wheat germ oil, rice bran oil, and maize bran, may be used as a source from which vegetable oil is extracted, or used directly as a food ingredient. The germ is retained as an integral part of whole-grain foods. Non-whole grain methods of milling are intended to isolate the endosperm, which is ground into flour, with removal of both the husk (bran) and the germ. Removal of bran produces a flour with a white rather than a brown color and eliminates fiber. The germ is rich in polyunsaturated fats (which have a tendency to oxidize and become rancid on storage) and so germ removal improves the storage qualities of flour. Wheat germ Wheat germ or wheatgerm is a concentrated source of several essential nutrients, including vitamin E, folate (foli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steeped
Steeping is the soaking of an organic solid, such as leaves, in a liquid (usually water) to extract flavours or to soften it. The specific process of teas being prepared for drinking by leaving the leaves in heated water to release the flavour and nutrients is known as steeping. Herbal teas may be prepared by decoction, infusion, or maceration (food), maceration. Some solids are soaked to remove an ingredient, such as salt, where the solute is not the desired product. Corn One example is the steeping of corn (or maize), part of the Mill (grinding), milling process. As described by the US Corn Refiners Association, harvested caryopsis, kernels of corn are cleaned and then steeped in water at a temperature of for 30 to 40 hours. In the process their moisture content rises from 15% to 45% and their volume more than doubles. The gluten bonds in the corn are weakened and starch is released. The corn is then ground to break free the cereal germ, germ and other components, and the wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
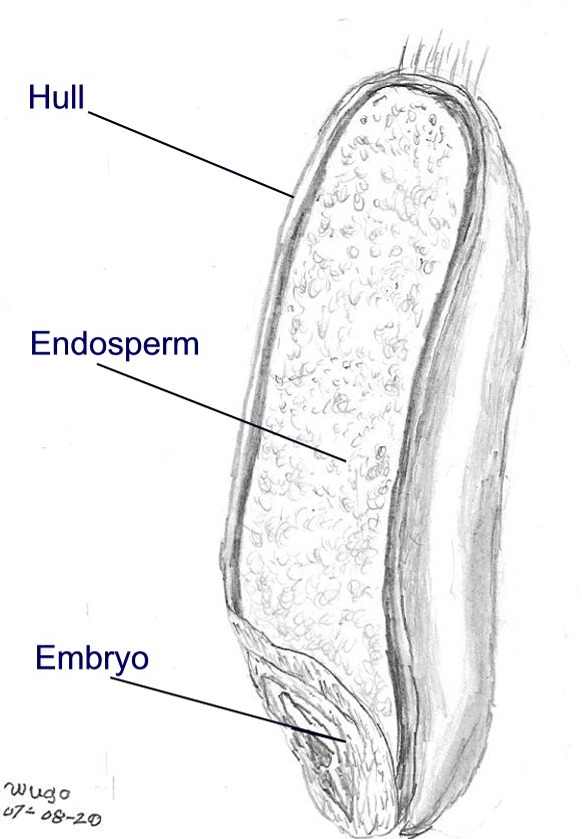
Endosperm
The endosperm is a tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following double fertilization. It is triploid (meaning three chromosome sets per nucleus) in most species, which may be auxin-driven. It surrounds the Embryo#Plant embryos, embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain Vegetable oil, oils and protein. This can make endosperm a source of nutrition in animal diet. For example, wheat endosperm is ground into flour for bread (the rest of the grain is included as well in whole wheat flour), while barley endosperm is the main source of sugars for beer production. Other examples of endosperm that forms the bulk of the edible portion are coconut "meat" and coconut "water", and Maize, corn. Some plants, such as certain orchids, lack endosperm in their seeds. Ancestral flowering plants have seeds with small embryos and abundant endosperm. In some modern flowering plants the embryo occupies most of the seed and the endosperm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corn Starch
Cornflour, cornstarch, maize starch, or corn starch (American English) is the starch derived from corn (maize) grain. The starch is obtained from the endosperm of the seed, kernel. Corn starch is a common food ingredient, often used to thicken sauces or soups, and to make corn syrup and other sugars. Corn starch is versatile, easily modified, and finds many uses in industry such as adhesives, in paper products, as an anti-sticking agent, and textile manufacturing. It has medical uses as well, such as to supply glucose for people with glycogen storage disease. Like many products in dust form, it can be hazardous in large quantities due to its flammable, flammability—see dust explosion. When mixed with a fluid, corn starch can rearrange itself into a non-Newtonian fluid. For example, adding water transforms corn starch into a material commonly known as Non-Newtonian fluid#Oobleck, oobleck while adding oil transforms corn starch into an electrorheological fluid, electrorheolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
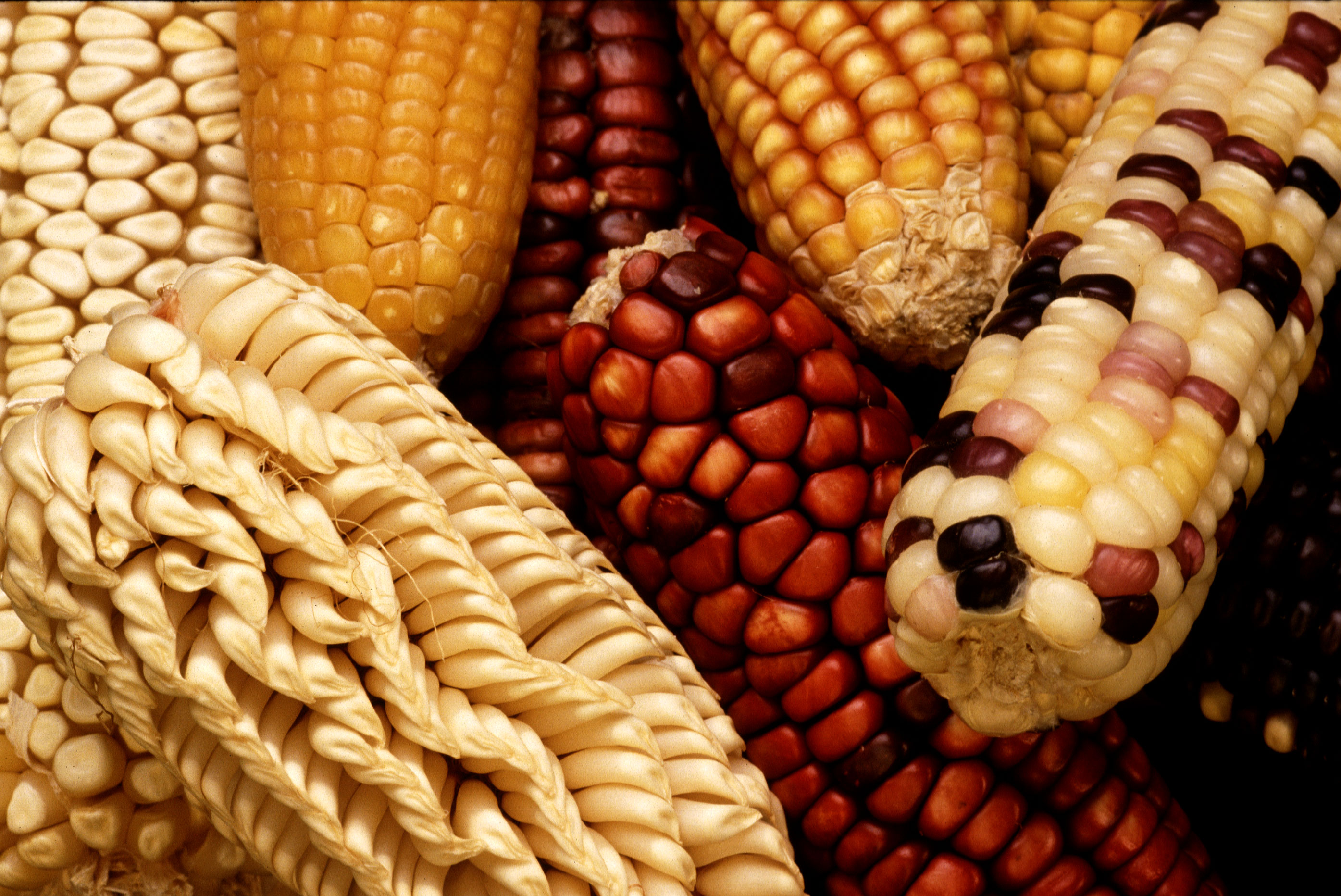
Corn
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout Poaceae, grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples of Mexico, indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native Americans planted it alongside beans and Cucurbita, squashes in the Three Sisters (agriculture), Three Sisters polyculture. The leafy Plant stem, stalk of the plant gives rise to male inflorescences or tassels which produce pollen, and female inflorescences called ear (botany), ears. The ears yield grain, known as Corn kernels, kernels or seeds. In modern commercial varieties, these are usually yellow or white; other varieties can be of many colors. Maize relies on humans for its propagation. Since the Columbian exchange, it has become a staple food in many parts of the world, with the List of most valuable crops and livestock products, total production of maize surpassing that of wheat and rice. Much maize is u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |