|
Consumer Debt
In economics, consumer debt is the amount owed by consumers (as opposed to amounts owed by businesses or governments). It includes debts incurred on purchase of goods that are consumable and/or do not appreciate. In macroeconomic terms, it is debt which is used to fund consumption rather than investment. The most common forms of consumer debt are credit card debt, payday loans, student loans and other consumer finance, which are often at higher interest rates than long-term secured loans, such as mortgages. Long-term consumer debt is often considered fiscally suboptimal. While some consumer items such as automobiles may be marketed as having high levels of utility that justify incurring short-term debt, most consumer goods are not. For example, incurring high-interest consumer debt through buying a big-screen television "now", rather than saving for it, cannot usually be financially justified by the subjective benefits of having the television early. In many countries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumer And Government Debt As A % Of GDP
A consumer is a person or a group who intends to order, or use purchased goods, products, or services primarily for personal, social, family, household and similar needs, who is not directly related to entrepreneurial or business activities. The term most commonly refers to a person who purchases goods and services for personal use. Rights "Consumers, by definition, include us all", said President John F. Kennedy, offering his definition to the United States Congress on March 15, 1962. This speech became the basis for the creation of World Consumer Rights Day, now celebrated on March 15. In his speech, John Fitzgerald Kennedy outlined the integral responsibility to consumers from their respective governments to help exercise consumers' rights, including: *The right to safety: To be protected against the marketing of goods that are hazardous to health or life. *The right to be informed: To be protected against fraudulent, deceitful, or grossly misleading information, advertisin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumer Leverage Ratio
The consumer leverage ratio (CLR) is the ratio of total household debt to disposable personal income. In the United States these are reported, respectively, by the Federal Reserve (as the household debt service ratio (DSR)) and the Bureau of Economic Analysis of the US Department of Commerce. \mbox = The concept has been used to quantify the amount of debt an average consumer has, relative to their disposable income. In essence, the consumer leverage ratio demonstrates how many years it would take an average consumer to pay off their debt if their entire annual disposable income went toward it. Overview The concept, popularized by William Jarvis and Dr. Ian C MacMillan in a series of articles in the Harvard Business Review, is being used in economic analysis and reporting, having been compared to other relevant economic indicators since the 1970s. The consumer leverage ratio in the US was increasing in the years before the 2008 financial crisis, peaking at 1.29x in 2007 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debt
Debt is an obligation that requires one party, the debtor, to pay money Loan, borrowed or otherwise withheld from another party, the creditor. Debt may be owed by a sovereign state or country, local government, company, or an individual. Commercial debt is generally subject to contractual terms regarding the amount and timing of repayments of #Principal, principal and interest. Loans, bond (finance), bonds, notes, and Mortgage loan, mortgages are all types of debt. In financial accounting, debt is a type of financial transaction, as distinct from equity (finance), equity. The term can also be used metaphorically to cover morality, moral obligations and other interactions not based on a monetary value. For example, in Western cultures, a person who has been helped by a second person is sometimes said to owe a "debt of gratitude" to the second person. Etymology The English term "debt" was first used in the late 13th century and comes by way of Old French from the Latin verb ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Consumer Law Center
The National Consumer Law Center (NCLC) is an American nonprofit organization headquartered in Boston, Massachusetts Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Maine to its east, Connecticut and Rhode ..., specializing in consumer issues on behalf of low-income people. Legal services, government, and private attorneys, as well as community organizations, work with the center to advocate for state and federal consumer reform. NCLC was founded in 1969 out of the Boston College School of Law. Areas of work On February 26, 2019, the NCLC testified before the U.S. House of Representatives Committee on Financial Services regarding “Who’s Keeping Score? Holding Credit Bureaus Accountable and Repairing a Broken System”. Publications NCLC publishes treatises on consumer law and practice manuals aimed at attorneys. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
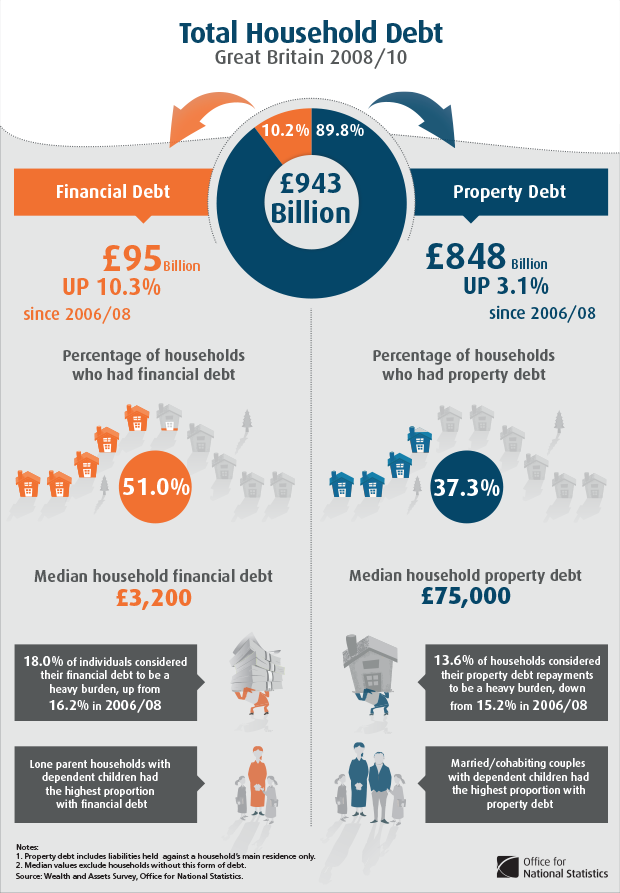
Household Debt
Household debt is the combined debt of all people in a household, including consumer debt and mortgage loans. A significant rise in the level of this debt coincides historically with many severe economic crises and was a cause of the U.S. and subsequent euro area crisis. Several economists have argued that lowering this debt is essential to economic recovery in the U.S. and selected Eurozone countries. Overview Household debt can be defined in several ways, based on what types of debt are included. Common debt types include home mortgages, home equity loans, auto loans, student loans, and credit cards. Household debt can also be measured across an economy, to measure how indebted households are relative to various measures of income (e.g., pre-tax and disposable income) or relative to the size of the economy (GDP). The burden of debt can also be measured in terms of the amount of interest it generates relative to the income of the borrower. For example, the U.S. Federal Reser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumer Credit Risk
:''The following article is based on UK market; other countries may differ.'' Consumer credit risk (also retail credit risk) is the risk of loss due to a consumer's failure or inability to repay ( default) on a consumer credit product, such as a mortgage, unsecured personal loan, credit card, overdraft etc. (the latter two options being forms of unsecured banking credit). Consumer credit risk management Most companies involved in lending to consumers have departments dedicated to the measurement, prediction and control of losses due to credit risk. This field is loosely referred to consumer/retail credit risk management, however, the word ''management'' is commonly dropped. Scorecards A common method for predicting credit risk is through the credit scorecard. The scorecard is a statistically based model for attributing a number (''score'') to a customer (or an account) which indicates the predicted probability that the customer will exhibit a certain behaviour. In calculating t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumerism
Consumerism is a socio-cultural and economic phenomenon that is typical of industrialized societies. It is characterized by the continuous acquisition of goods and services in ever-increasing quantities. In contemporary consumer society, the purchase and the consumption of products have evolved beyond the mere satisfaction of basic human needs, Stearns, Peter (2006). ''Consumerism in World History''. 2nd ed. Routledge. p. vii–viii. transforming into an activity that is not only economic but also cultural, social, and even identity-forming. It emerged in Western Europe and the United States during the Industrial Revolution and became widespread around the 20th century. In economics, consumerism refers to policies that emphasize consumption. It is the consideration that the free choice of consumers should strongly inform the choice by manufacturers of what is produced and how, and therefore influence the economic organization of a society. Consumerism has been criticized b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Channel Islands
The Channel Islands are an archipelago in the English Channel, off the French coast of Normandy. They are divided into two Crown Dependencies: the Jersey, Bailiwick of Jersey, which is the largest of the islands; and the Bailiwick of Guernsey, consisting of Guernsey, Alderney, Sark, Herm and some smaller islands. Historically, they are the remnants of the Duchy of Normandy. Although they are not part of the United Kingdom, the UK is responsible for the defence and international relations of the islands as it is for the other Crown Dependency, the Isle of Man, and the British Overseas Territories. The Crown Dependencies are neither members of the Commonwealth of Nations, nor part of the European Union. They have a total population of about , and the bailiwicks' Capital city, capitals, Saint Helier and Saint Peter Port, have populations of 33,500 and 18,207 respectively. "Channel Islands" is a geographical term, not a political unit. The two bailiwicks have been administered sepa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debt-to-GDP Ratio
In economics, the debt-to-GDP ratio is the ratio of a country's accumulation of government debt (measured in units of currency) to its gross domestic product (GDP) (measured in units of currency per year). A low debt-to-GDP ratio indicates that an economy produces goods and services sufficient to pay back debts without incurring further debt. Geopolitical and economic considerations – including interest rates, war, recessions, and other variables – influence the borrowing practices of a nation and the choice to incur further debt. It should not be confused with a deficit-to-GDP ratio, which, for countries running budget deficits, measures a country's annual net fiscal loss in a given year ( government budget balance, or the net change in debt per annum) as a percentage share of that country's GDP; for countries running budget surpluses, a ''surplus-to-GDP ratio'' measures a country's annual net fiscal ''gain'' as a share of that country's GDP. Particularly in macroeconomics, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debt Service Ratio
In economics and government finance, a country’s debt service ratio is the ratio of its debt service payments (principal + interest) to its export earnings.Glossary of Statistical TermsDebt service ratio OECD, Sep 25, 2001. A country's international finances are healthier when this ratio is low. For most countries the ratio is between 0 and 20%. In contrast to the debt service coverage ratio, which is calculated as income divided by debt, this ratio is inverse and calculated as debt service divided by country's income from international trade International trade is the exchange of capital, goods, and services across international borders or territories because there is a need or want of goods or services. (See: World economy.) In most countries, such trade represents a significan ..., i.e., exports. References {{macroeconomics-stub Macroeconomic indicators Financial ratios ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Reserve System
The Federal Reserve System (often shortened to the Federal Reserve, or simply the Fed) is the central banking system of the United States. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, after a series of financial panics (particularly the panic of 1907) led to the desire for central control of the monetary system in order to alleviate financial crises. Although an instrument of the U.S. government, the Federal Reserve System considers itself "an independent central bank because its monetary policy decisions do not have to be approved by the president or by anyone else in the executive or legislative branches of government, it does not receive funding appropriated by Congress, and the terms of the members of the board of governors span multiple presidential and congressional terms." Over the years, events such as the Great Depression in the 1930s and the Great Recession during the 2000s have led to the expansion of the roles and responsibi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
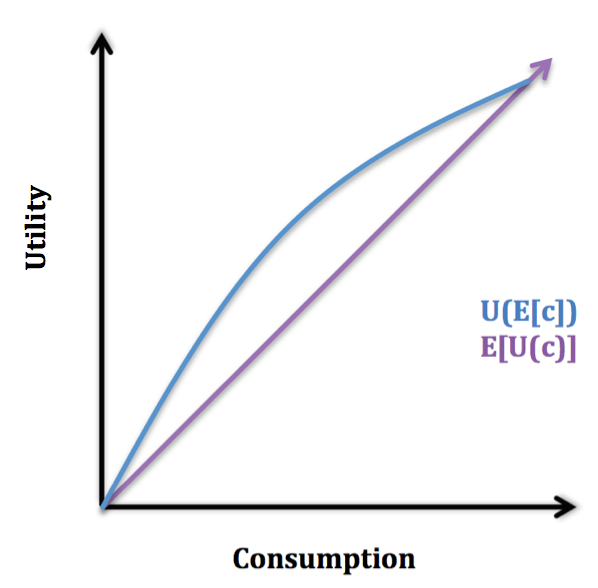
Consumption Smoothing
Consumption smoothing is an economic concept for the practice of optimizing a person's standard of living through an appropriate balance between savings and consumption over time. An optimal consumption rate should be relatively similar at each stage of a person's life rather than fluctuate wildly. Luxurious consumption at an old age does not compensate for an impoverished existence at other stages in one's life. Since income tends to be hump-shaped across an individual's life, economic theory suggests that individuals should on average have low or negative savings rate at early stages in their life, high in middle age, and negative during retirement. Although many popular books on personal finance advocate that individuals should at all stages of their careers set aside money in savings, economist James Choi states that this deviates from the advice of economists. Expected utility model The graph below illustrates the expected utility model, in which U(c) is increasing in and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |