|
Complex Conjugate Representation
In mathematics, if is a group and is a representation of it over the complex vector space , then the complex conjugate representation is defined over the complex conjugate vector space as follows: : is the conjugate of for all in . is also a representation, as one may check explicitly. If is a real Lie algebra and is a representation of it over the vector space , then the conjugate representation is defined over the conjugate vector space as follows: : is the conjugate of for all in .This is the mathematicians' convention. Physicists use a different convention where the Lie bracket of two real vectors is an imaginary vector. In the physicist's convention, insert a minus in the definition. is also a representation, as one may check explicitly. If two real Lie algebras have the same complexification, and we have a complex representation of the complexified Lie algebra, their conjugate representations are still going to be different. See spinor for some examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group (mathematics)
In mathematics, a group is a Set (mathematics), set with an Binary operation, operation that combines any two elements of the set to produce a third element within the same set and the following conditions must hold: the operation is Associative property, associative, it has an identity element, and every element of the set has an inverse element. For example, the integers with the addition, addition operation form a group. The concept of a group was elaborated for handling, in a unified way, many mathematical structures such as numbers, geometric shapes and polynomial roots. Because the concept of groups is ubiquitous in numerous areas both within and outside mathematics, some authors consider it as a central organizing principle of contemporary mathematics. In geometry, groups arise naturally in the study of symmetries and geometric transformations: The symmetries of an object form a group, called the symmetry group of the object, and the transformations of a given type form a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Representation Theory
Representation theory is a branch of mathematics that studies abstract algebra, abstract algebraic structures by ''representing'' their element (set theory), elements as linear transformations of vector spaces, and studies Module (mathematics), modules over these abstract algebraic structures. In essence, a representation makes an abstract algebraic object more concrete by describing its elements by matrix (mathematics), matrices and their algebraic operations (for example, matrix addition, matrix multiplication). The algebraic objects amenable to such a description include group (mathematics), groups, associative algebras and Lie algebras. The most prominent of these (and historically the first) is the group representation, representation theory of groups, in which elements of a group are represented by invertible matrices such that the group operation is matrix multiplication. Representation theory is a useful method because it reduces problems in abstract algebra to problems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Number
In mathematics, a complex number is an element of a number system that extends the real numbers with a specific element denoted , called the imaginary unit and satisfying the equation i^= -1; every complex number can be expressed in the form a + bi, where and are real numbers. Because no real number satisfies the above equation, was called an imaginary number by René Descartes. For the complex number is called the , and is called the . The set of complex numbers is denoted by either of the symbols \mathbb C or . Despite the historical nomenclature, "imaginary" complex numbers have a mathematical existence as firm as that of the real numbers, and they are fundamental tools in the scientific description of the natural world. Complex numbers allow solutions to all polynomial equations, even those that have no solutions in real numbers. More precisely, the fundamental theorem of algebra asserts that every non-constant polynomial equation with real or complex coefficie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector Space
In mathematics and physics, a vector space (also called a linear space) is a set (mathematics), set whose elements, often called vector (mathematics and physics), ''vectors'', can be added together and multiplied ("scaled") by numbers called scalar (mathematics), ''scalars''. The operations of vector addition and scalar multiplication must satisfy certain requirements, called ''vector axioms''. Real vector spaces and complex vector spaces are kinds of vector spaces based on different kinds of scalars: real numbers and complex numbers. Scalars can also be, more generally, elements of any field (mathematics), field. Vector spaces generalize Euclidean vectors, which allow modeling of Physical quantity, physical quantities (such as forces and velocity) that have not only a Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude, but also a Orientation (geometry), direction. The concept of vector spaces is fundamental for linear algebra, together with the concept of matrix (mathematics), matrices, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Conjugate Vector Space
In mathematics, the complex conjugate of a complex vector space V\, is a complex vector space \overline V that has the same elements and additive group structure as V, but whose scalar multiplication involves conjugation of the scalars. In other words, the scalar multiplication of \overline V satisfies \alpha\,*\, v = where * is the scalar multiplication of \overline and \cdot is the scalar multiplication of V. The letter v stands for a vector in V, \alpha is a complex number, and \overline denotes the complex conjugate of \alpha. More concretely, the complex conjugate vector space is the same underlying vector space (same set of points, same vector addition and real scalar multiplication) with the conjugate linear complex structure J (different multiplication by i). Motivation If V and W are complex vector spaces, a function f : V \to W is antilinear if f(v + w) = f(v) + f(w) \quad \text \quad f(\alpha v) = \overline \, f(v) With the use of the conjugate vector space \overline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Number
In mathematics, a real number is a number that can be used to measure a continuous one- dimensional quantity such as a duration or temperature. Here, ''continuous'' means that pairs of values can have arbitrarily small differences. Every real number can be almost uniquely represented by an infinite decimal expansion. The real numbers are fundamental in calculus (and in many other branches of mathematics), in particular by their role in the classical definitions of limits, continuity and derivatives. The set of real numbers, sometimes called "the reals", is traditionally denoted by a bold , often using blackboard bold, . The adjective ''real'', used in the 17th century by René Descartes, distinguishes real numbers from imaginary numbers such as the square roots of . The real numbers include the rational numbers, such as the integer and the fraction . The rest of the real numbers are called irrational numbers. Some irrational numbers (as well as all the rationals) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lie Algebra
In mathematics, a Lie algebra (pronounced ) is a vector space \mathfrak g together with an operation called the Lie bracket, an alternating bilinear map \mathfrak g \times \mathfrak g \rightarrow \mathfrak g, that satisfies the Jacobi identity. In other words, a Lie algebra is an algebra over a field for which the multiplication operation (called the Lie bracket) is alternating and satisfies the Jacobi identity. The Lie bracket of two vectors x and y is denoted ,y/math>. A Lie algebra is typically a non-associative algebra. However, every associative algebra gives rise to a Lie algebra, consisting of the same vector space with the commutator Lie bracket, ,y= xy - yx . Lie algebras are closely related to Lie groups, which are groups that are also smooth manifolds: every Lie group gives rise to a Lie algebra, which is the tangent space at the identity. (In this case, the Lie bracket measures the failure of commutativity for the Lie group.) Conversely, to any finite-di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lie Bracket Of Vector Fields
In the mathematical field of differential topology, the Lie bracket of vector fields, also known as the Jacobi–Lie bracket or the commutator of vector fields, is an operator that assigns to any two vector fields X and Y on a smooth manifold M a third vector field denoted ,Y/math>. Conceptually, the Lie bracket ,Y/math> is the derivative of Y along the flow generated by X, and is sometimes denoted ''\mathcal_X Y'' ("Lie derivative of Y along X"). This generalizes to the Lie derivative of any tensor field along the flow generated by X. The Lie bracket is an R- bilinear operation and turns the set of all smooth vector fields on the manifold M into an (infinite-dimensional) Lie algebra. The Lie bracket plays an important role in differential geometry and differential topology, for instance in the Frobenius integrability theorem, and is also fundamental in the geometric theory of nonlinear control systems. V. I. Arnold refers to this as the "fisherman derivative", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complexification
In mathematics, the complexification of a vector space over the field of real numbers (a "real vector space") yields a vector space over the complex number field, obtained by formally extending the scaling of vectors by real numbers to include their scaling ("multiplication") by complex numbers. Any basis for (a space over the real numbers) may also serve as a basis for over the complex numbers. Formal definition Let V be a real vector space. The of is defined by taking the tensor product of V with the complex numbers (thought of as a 2-dimensional vector space over the reals): :V^ = V\otimes_ \Complex\,. The subscript, \R, on the tensor product indicates that the tensor product is taken over the real numbers (since V is a real vector space this is the only sensible option anyway, so the subscript can safely be omitted). As it stands, V^ is only a real vector space. However, we can make V^ into a complex vector space by defining complex multiplication as follows: :\alp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
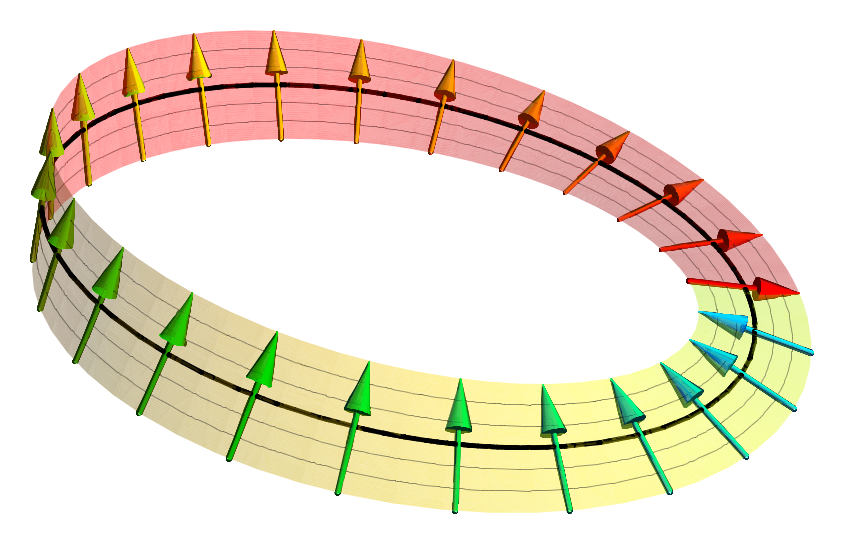
Spinor
In geometry and physics, spinors (pronounced "spinner" IPA ) are elements of a complex numbers, complex vector space that can be associated with Euclidean space. A spinor transforms linearly when the Euclidean space is subjected to a slight (infinitesimal transformation, infinitesimal) rotation, but unlike Euclidean vector, geometric vectors and tensors, a spinor transforms to its negative when the space rotates through 360° (see picture). It takes a rotation of 720° for a spinor to go back to its original state. This property characterizes spinors: spinors can be viewed as the "square roots" of vectors (although this is inaccurate and may be misleading; they are better viewed as "square roots" of Section (fiber bundle), sections of vector bundles – in the case of the exterior algebra bundle of the cotangent bundle, they thus become "square roots" of differential forms). It is also possible to associate a substantially similar notion of spinor to Minkowski space, in which cas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |