|
Coexist
Coexistence is the property of things existing at the same time and in a proximity close enough to affect each other, without causing harm to one another. The term is often used with respect to people of different persuasions existing together, particularly where there is some history of antipathy or violence between those groups. Coexistence can be observed to a property of all systems in which different aspects capable of interacting with each other exist at the same time. As one source asserts, "even at the molecular level, existence is always already coexistence". Nonliving things can also be characterized as coexisting where multiple kinds of such things exist in the same space, with the term having been used for things as disparate as different kinds of dunes on Mars, and black holes existing in the same region of space as dense nuclear star clusters. Other examples of coexistence include: * Peaceful coexistence, Soviet theory regarding relations between the socialist and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coexistence Theory
Coexistence theory is a framework to understand how competitor traits can maintain species diversity and stave-off competitive exclusion even among similar species living in ecologically similar environments. Coexistence theory explains the stable coexistence of species as an interaction between two opposing forces: fitness differences between species, which should drive the best-adapted species to exclude others within a particular ecological niche, and stabilizing mechanisms, which maintains diversity via niche differentiation. For many species to be stabilized in a community, population growth must be negative density-dependent, i.e. all participating species have a tendency to increase in density as their populations decline. In such communities, any species that becomes rare will experience positive growth, pushing its population to recover and making local extinction unlikely. As the population of one species declines, individuals of that species tend to compete predomi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peaceful Coexistence
Peaceful coexistence () was a theory, developed and applied by the Soviet Union at various points during the Cold War in the context of primarily Marxist–Leninist foreign policy and adopted by Soviet-dependent socialist states, according to which the Socialist Bloc could peacefully coexist with the capitalist bloc (i.e., U.S.-allied states). This was in contrast to the antagonistic contradiction principle that socialism and capitalism could never coexist in peace. The Soviet Union applied it to relations between the western world, particularly NATO countries, and nations of the Warsaw Pact. Debates over differing interpretations of peaceful coexistence were one aspect of the Sino-Soviet split in the 1950s and 1960s. During the 1970s, the People's Republic of China under the leadership of its founder, Mao Zedong, argued that a belligerent attitude should be maintained towards capitalist countries, and so initially rejected the peaceful coexistence theory as essentially Marxist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coexist (U2 Vertigo Tour)
Coexistence is the property of things existing at the same time and in a proximity close enough to affect each other, without causing harm to one another. The term is often used with respect to people of different persuasions existing together, particularly where there is some history of antipathy or violence between those groups. Coexistence can be observed to a property of all systems in which different aspects capable of interacting with each other exist at the same time. As one source asserts, "even at the molecular level, existence is always already coexistence". Nonliving things can also be characterized as coexisting where multiple kinds of such things exist in the same space, with the term having been used for things as disparate as different kinds of dunes on Mars, and black holes existing in the same region of space as dense nuclear star clusters. Other examples of coexistence include: * Peaceful coexistence, Soviet theory regarding relations between the socialist and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperboreae Undae
Hyperboreae Undae (Latin: "Far Northern Waves/Dunes") is one of the largest and densest dune fields of Planum Boreum, the Mars, Martian North Pole. It is named after one of the classical albedo features on Mars. Its name was officially approved by IAU in 1988. It extends from latitude 77.12°N to 82.8°N and from longitude 302.92°E to 316.02°E (43.98°W – 57.08°W). Its centre is at latitude 79.96°N, longitude 49.49°W, and has a diameter of . Hyperboreae Undae is southwest of the Boreum Cavus depression, an arc-like depression at the northeastern boundary of Chasma Boreale. From there, Hyperboreae Undae continues in a southwestern direction through Chasma Boreale, and into the lowlands of Vastitas Borealis. It overlays the eastern part of Hyperboreae Lingua and the region above Escorial (crater), Escorial crater. Hyperboreae Undae is well known for the barchanoid and linear dunes that have formed at its location, although they are seemingly incompatible. Research has been o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peace And Conflict Studies
Peace and conflict studies is a social science field that identifies and analyzes violence, violent and nonviolence, nonviolent behaviors as well as the structural violence, structural mechanisms attending Conflict (process), conflicts (including social conflicts), to understand those processes which lead to a more desirable human condition. A variation on this, Peace and Justice Studies Association, peace studies, is an interdisciplinarity, interdisciplinary effort aiming at the prevention, de-escalation, and solution of conflicts by peaceful means, based on achieving conflict resolution and dispute resolution at the international relations, international and peacebuilding, domestic levels based on win-win game, positive sum, rather than Zero-sum game, negative sum, solutions. In contrast with strategic studies or war studies, which focus on traditionally realism (international relations), realist objectives based on the foreign policy analysis, state or individual unit level of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plurinationalism
Plurinationality, plurinational, or plurinationalism is defined as the coexistence of two or more sealed or preserved national groups within a polity (an organized community or body of peoples). In plurinationalism, the idea of nationality is plural, meaning there are many nationals within an organized community or body of peoples. Derived from this concept, a plurinational state is the existence of multiple political communities and constitutional asymmetry. The usage of plurinationality assists in avoiding the division of societies within a state or country. Furthermore, a plurinational democracy recognizes the multiple demoi (common people or populace)demos thefreedictionary.com within a polity.Keating, Michael [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sociology
Sociology is the scientific study of human society that focuses on society, human social behavior, patterns of Interpersonal ties, social relationships, social interaction, and aspects of culture associated with everyday life. The term sociology was coined in the late 18th century to describe the scientific study of society. Regarded as a part of both the social sciences and humanities, sociology uses various methods of Empirical research, empirical investigation and critical analysis to develop a body of knowledge about social order and social change. Sociological subject matter ranges from Microsociology, micro-level analyses of individual interaction and agency (sociology), agency to Macrosociology, macro-level analyses of social systems and social structure. Applied sociological research may be applied directly to social policy and welfare, whereas Theory, theoretical approaches may focus on the understanding of social processes and phenomenology (sociology), phenomenologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Hole
A black hole is a massive, compact astronomical object so dense that its gravity prevents anything from escaping, even light. Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass will form a black hole. The boundary (topology), boundary of no escape is called the event horizon. A black hole has a great effect on the fate and circumstances of an object crossing it, but has no locally detectable features according to general relativity. In many ways, a black hole acts like an ideal black body, as it reflects no light. Quantum field theory in curved spacetime predicts that event horizons emit Hawking radiation, with thermal radiation, the same spectrum as a black body of a temperature inversely proportional to its mass. This temperature is of the Orders of magnitude (temperature), order of billionths of a kelvin for stellar black holes, making it essentially impossible to observe directly. Objects whose gravitational fields are too strong for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equity (economics)
Economic equity is the construct, concept or idea of ''fairness'' in economics and ''justice'' in the distribution of wealth, resources, and taxation within a society. Equity is closely tied to taxation policies, welfare economics, and the discussions of public finance, influencing how resources are allocated among different segments of the population. Overview According to Peter Corning, there are three distinct categories of substantive fairness (equality, equity, and reciprocity) that must be combined and balanced in order to achieve a truly fair society. But while most of middle-income countries increased inequality in recent years, it is important to note that middle classes and—to a lesser extent—poorer-income groups seem to be getting an increasing share of income in recent years. To some, this advance is still vulnerable and needs to be quickly accelerated in the 21st century Definitions of equity Equity in economics refers to a condition of fairness where the econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Violence
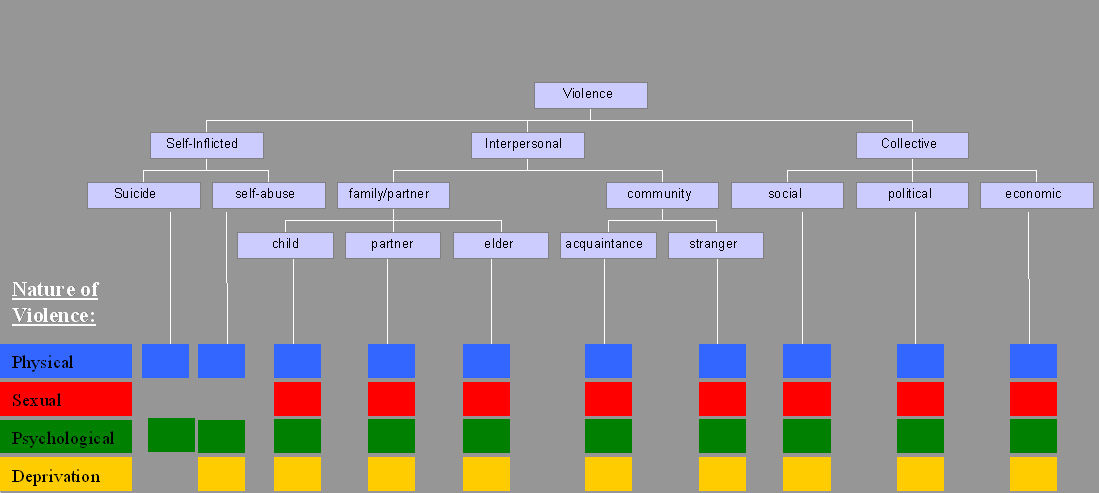
Violence is characterized as the use of physical force by humans to cause harm to other living beings, or property, such as pain, injury, disablement, death, damage and destruction. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines violence as "the intentional use of physical force or power, threatened or actual, against oneself, another person, or against a group or community, which either results in or has a high likelihood of resulting in injury, death, psychological harm, maldevelopment, or deprivation"; it recognizes the need to include violence not resulting in injury or death. Categories The World Health Organization (WHO) divides violence into three broad categories: self-directed, interpersonal, and collective. This categorization differentiates between violence inflicted to and by oneself, by another individual or a small group, and by larger groups such as states. Alternatively, violence can primarily be classified as either instrumental or hostile. Self-in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millet (Ottoman Empire)
In the Ottoman Empire, a ''millet'' (; ) was an independent court of law pertaining to "personal law" under which a confessional community (a group abiding by the laws of Muslim sharia, Christian canon law, or Jewish halakha) was allowed to rule itself under its own laws. Despite frequently being referred to as a "system", before the nineteenth century the organization of what are now retrospectively called millets in the Ottoman Empire was not at all systematic. Rather, non-Muslims were simply given a significant degree of autonomy within their own community, without an overarching structure for the ''millet'' as a whole. The notion of distinct ''millets'' corresponding to different religious communities within the empire would not emerge until the eighteenth century. Subsequently, the ''millet'' system was justified through numerous foundation myths linking it back to the time of Sultan Mehmed the Conqueror (r. 1451–81), although it is now understood that no such system exis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |