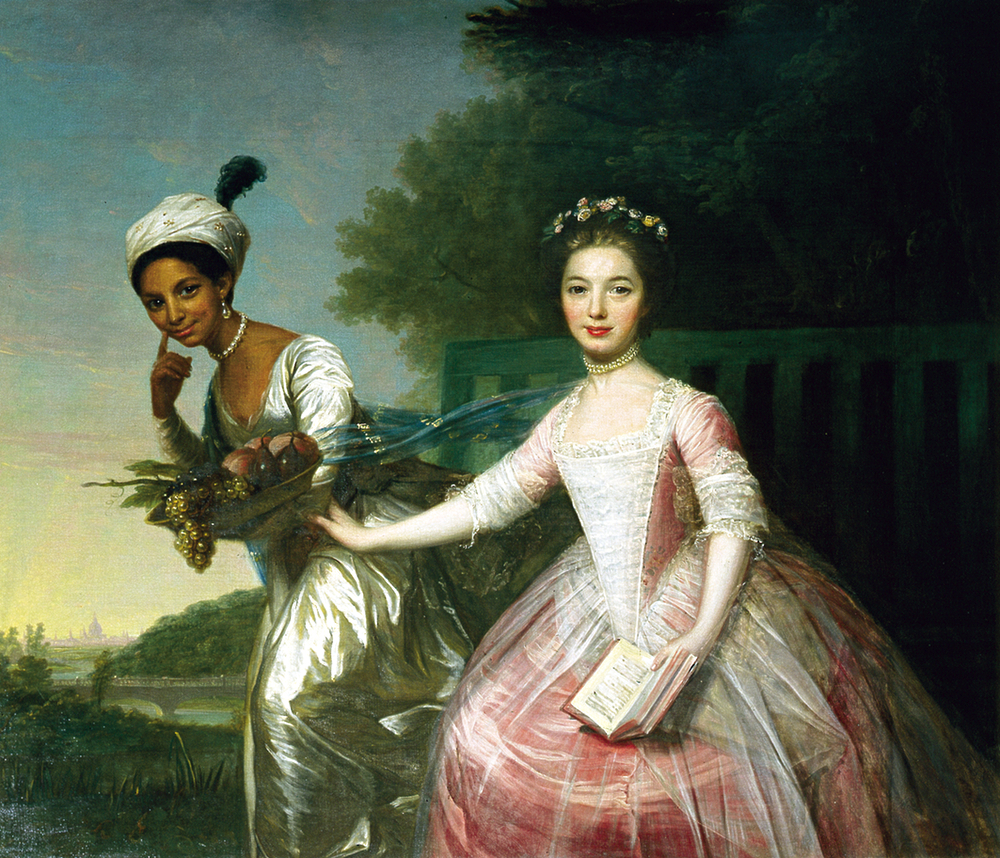|
Coade Stone
Coade stone or ''Lithodipyra'' or ''Lithodipra'' () is stoneware that was often described as an artificial stone in the late 18th and early 19th centuries. It was used for moulding neoclassical architecture, neoclassical statues, architectural decorations and garden ornaments of the highest quality that remain virtually weatherproof today. Coade stone features were produced Royal Warrant of Appointment (United Kingdom), by appointment to George III of the United Kingdom, George III and the George IV of the United Kingdom, Prince Regent for St George's Chapel, Windsor; Royal Pavilion, The Royal Pavilion, Brighton; Carlton House, London; the Royal Naval College, Greenwich; and refurbishment of Buckingham Palace in the 1820s. Coade stone was prized by the most important architects such as: John Nash (architect), John Nash-Buckingham Palace; Sir John Soane-Bank of England; Robert Adam-Kenwood House; and James Wyatt-Radcliffe Observatory. The product (originally known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eleanor Coade
Eleanor Coade (3 or 24 June 1733 – 18 November 1821) was a British businesswoman known for manufacturing Neoclassical statues, architectural decorations and garden ornaments made of ''Lithodipyra'' (Coade stone) for over 50 years from 1769 until her death. She should not be confused or conflated with her mother, also named Eleanor. ''Lithodipyra'' ("stone fired twice") was a high-quality, durable moulded weather-resistant, stoneware; statues and decorative features from this still look almost new today. Coade did not invent 'artificial stone', as various inferior quality precursors had been both patented and manufactured over the previous forty years, but she probably perfected both the formulation and the firing process. She combined high-quality manufacturing and artistic taste, together with entrepreneurial, business and marketing skills, to create the overwhelmingly successful stone products of her age. She produced stoneware for St George's Chapel, Windsor; The Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
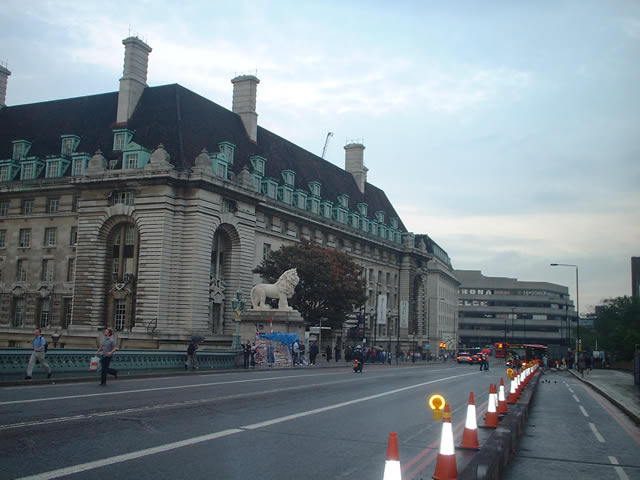
South Bank Lion (5809599144) (cropped)
The ''South Bank Lion'' is an 1837 sculpture in Central London. Since 1966 it has stood next to County Hall, on the South Bank of the River Thames. It is a significant depiction of a lion, along with the four that surround Nelson's Column in Trafalgar Square just across the river. The statue is about long and high, and weighs about . It was cast in 1837, the year of Queen Victoria's accession, of Coade stone, one of the earliest types of artificial stone. The material is very resistant to weathering, and the fine details of the lion's modelling still remain clear after decades of exposure to the corrosive effects of London's severe air pollution, the infamous pea soup fog, prior to the passage of the Clean Air Act 1956. The statue was made in separate parts and cramped together on an iron frame. It was formerly known as the Red Lion, as it was painted that colour between 1951 and 1966. History The lion was originally mounted on the parapet of James Goding's Lion Brewery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Nash (architect)
John Nash (18 January 1752 – 13 May 1835) was an English architect of the Georgian and Regency eras. He was responsible for the design, in the neoclassical and picturesque styles, of many important areas of London. His designs were financed by the Prince Regent and by the era's most successful property developer, James Burton. Nash also collaborated extensively with Burton's son, Decimus Burton. Nash's best-known solo designs are the Royal Pavilion, Brighton; Marble Arch; and Buckingham Palace. His best-known collaboration with James Burton is Regent Street and his best-known collaborations with Decimus Burton are Regent's Park and its terraces and Carlton House Terrace. The majority of his buildings, including those that the Burtons did not contribute to, were built by James Burton's company. Background and early career Nash was born in 1752, probably in Lambeth, south London. His father was a millwright also called John (1714–1772). From 1766 or 1767, Nash ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Gentleman's Magazine
''The Gentleman's Magazine'' was a monthly magazine founded in London, England, by Edward Cave in January 1731. It ran uninterrupted for almost 200 years, until 1907, ceasing publication altogether in 1922. It was the first to use the term ''magazine'' (from the French language, French ''magazine'', meaning "storehouse") for a periodical. Samuel Johnson's first regular employment as a writer was with ''The Gentleman's Magazine''. History The original complete title was ''The Gentleman's Magazine: or, Trader's monthly intelligencer''. Cave's innovation was to create a monthly digest of news and commentary on any topic the educated public might be interested in, from commodity prices to Latin poetry. It carried original content from a stable of regular contributors, as well as extensive quotations and extracts from other periodicals and books. Cave, who edited ''The Gentleman's Magazine'' under the pen name "Sylvanus Urban", was the first to use the term ''magazine'' (meaning "st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poor Rate
In England and Wales the poor rate was a tax on property levied in each parish, which was used to provide poor relief. It was collected under both the Old Poor Law and the New Poor Law. It was absorbed into "general rate" local taxation in the 1920s, and has continuity with the currently existing Council Tax. Introduction The Poor Relief Act 1601 consolidated earlier poor relief legislation and introduced a system of rating property. The introduction of the poor rate required the authorities, known as a vestry, in each parish to meet once a year to set the poor rate and to appoint an overseer of the poor to collect the rate. The justices of the peace at the quarter sessions had a role in checking the accounts of the poor rate. Reform The system of rating was subject to reform, such as excluding property outside of the parish in which a rate was paid. Because the poor rate was collected and spent locally within a single parish the notion of settlement was confirmed by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burton Upon Trent Town Hall
Burton upon Trent Town Hall is a municipal building in King Edward Place, Burton upon Trent, Staffordshire, England. It is a Grade II listed building. History The building In the mid 19th century local council meetings were held in the old Town Hall in the Market Square: this was a building which was commissioned by the lord of the manor, Henry Paget, 1st Earl of Uxbridge (second creation), Lord Paget. It had been designed in the Classical architecture, classical style, possibly by James Wyatt, and completed in 1772. The current building, which was designed by Reginald Churchill in a Victorian architecture, Victorian Gothic style, was commissioned by Michael Thomas Bass for use as the St Paul's, Burton upon Trent, St Paul's Institute and the Liberal Club and completed in 1878. Bass' son, Michael Bass, 1st Baron Burton, Michael Arthur Bass, donated the building to the town in 1891 and it was extended, by the inclusion of purpose-built municipal offices, a council chamber, a con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hatfield Peverel Priory
Hatfield Peverel Priory (also known as Hatfield Priory) was a Benedictine priory in Essex, England, founded as a secular college before 1087 and converted into priory as a cell of St Albans by William Peverel ''ante'' 1100. It is in the English Heritage Register of Parks and Gardens of Special Historic Interest in England and is located on the south side of the village of Hatfield Peverel, about 5 miles north-east of Chelmsford. At the Dissolution of the Monasteries, a timber-frame structure dominated the property. According to tradition the priory was founded by the Saxon Ingelrica, wife of Ranulph Peverel and reputed to be the mistress of William the Conqueror, to atone for her sins. The parish church, St Andrew's (Church of England) is the surviving fragment of the Norman priory church nave. The property was acquired by the Wright family when John Wright, a coachmaker, first landed his family in Essex in 1764. The current house, in a park designed by Richard Woods (landscape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rupert Gunnis
Rupert Forbes Gunnis (11 March 1899 – 31 July 1965) was an English collector and historian of British sculpture. He is best known for his ''Dictionary of British Sculptors 1660–1851'', which "revolutionized the study of British sculpture, providing the foundation for all later studies on the subject".Tim Knox‘Gunnis, Rupert Forbes (1899–1965)’ ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, 2004 , accessed 17 Oct 2010 Life Born in Cadogan Square, London, Gunnis was educated at Eton College. In 1923 he entered the Colonial Service, serving as private secretary to the Governor of Uganda (1923–1926) and then the Governor of Cyprus, Sir Ronald Storrs (November 1926 – June 1932). From 1932 to 1935 he worked as Inspector of Antiquities for the Cyprus Museum. Although Gunnis was a government official he acquired and sold antiquities illegally. In 1936 he was appointed as a member of the Antiquities Advisory board, and published his important book ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alison Kelly (art Historian)
Avery Alison Kelly, FSA, (17 October 1913 – 15 August 2016) was an English art historian who was an authority on Coade stone and Wedgwood pottery. During the Second World War she designed camouflage for the home front and later she lectured in London on the fine arts and wrote several books on Wedgwood. Early life Avery Alison Kelly was born into a Quaker family in Liverpool on 17 October 1913, the only child of Sir Robert Kelly, the professor of surgery at the University of Liverpool and his wife Averill Edith Irma. Her father collected furniture and glass, and was an accomplished photographer, all areas reflected in Alison's later interests. Plarr's Lives of the Fellows Online, Royal College of Surgeons. Retrieved 29 October 2016. She was educated at [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radcliffe Observatory
Radcliffe Observatory was the astronomical observatory of the University of Oxford from 1773 until 1934, when the Radcliffe Trustees sold it and built a new observatory in Pretoria, South Africa. It is a Grade I listed building. Today, the building forms part of Green Templeton College of the University of Oxford. History The observatory was founded and named after the physician John Radcliffe (1650–1714) by the Radcliffe Trustees. It was built on the suggestion of the astronomer Thomas Hornsby, who was occupying the Savilian Chair of Astronomy, following his observation of the notable transit of Venus across the sun's disc in 1769 from a room in the nearby Radcliffe Infirmary. The observatory building, at a site on Woodstock Road, commenced to designs by Henry Keene in 1772 and was completed in 1794 to the designs of James Wyatt. It has a prominent octagonal tower based on the Tower of the Winds in Athens, topped with a statue by John Bacon of Atlas holding up the Wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Wyatt
James Wyatt (3 August 1746 – 4 September 1813) was an English architect, a rival of Robert Adam in the Neoclassicism, neoclassical and neo-Gothic styles. He was elected to the Royal Academy of Arts in 1785 and was its president from 1805 to 1806. Early life Wyatt was born on 3 August 1746 at Weeford, near Lichfield, Staffordshire, England. Early classical career Wyatt spent six years in Italy, 1762–68, in company with Richard Bagot of Staffordshire, who was Secretary to Charles Compton, 7th Earl of Northampton's embassy to the Venetian Republic. In Venice, Wyatt studied with Antonio Visentini (1688–1782) as an architectural draughtsman and painter. In Rome he made measured drawings of the dome of St. Peter's Basilica, "being under the necessity of lying on his back on a ladder slung horizontally, without cradle or side-rail, over a frightful void of 300 feet". Back in England, his selection as architect of the proposed Pantheon (London), Pantheon or "Winter Ranelegh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenwood House
Kenwood House (also known as the Iveagh Bequest) is a stately home in Hampstead, London, on the northern boundary of Hampstead Heath. The present house, built in the late 17th century, was remodelled in the 18th century for William Murray, 1st Earl of Mansfield by Scottish architect Robert Adam, serving as a residence for the Earls of Mansfield until the 20th century. The house and part of the grounds were bought from the 6th Earl of Mansfield in 1925 by Edward Guinness, 1st Earl of Iveagh, and donated to the nation in 1927. The entire estate came under ownership of the London County Council and was open to the public by the end of the 1920s. It remains a popular local tourist attraction. Location The house is at the north edge of Hampstead Heath, to the south of Hampstead Lane (the B519). It is in the London Borough of Camden, just south of its boundary with the London Borough of Haringey. History Early history The original house on the property was presumed to have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |