|
Chinthe
''Chinthe'' ( (); (); ()) is the Burmese language, Burmese word for 'Asiatic lion, lion'. The wiktionary:leograph, leograph of ''Chinthe'' is a highly stylized lion commonly depicted in Burmese iconography and Myanmar architecture, architecture, especially as a pair of guardians flanking the entrances of Buddhist pagodas and ''kyaung'' (or Buddhist monasteries). Natural lion Contrary to popular belief, the ''Chinthe'' is not a mythical creature but instead an entirely natural lion, although often associated with myths and legends. The Burmese leograph is related to other stylized lions in the Asian region, including the ''sing'' (สิงห์) of Thailand, Cambodia, Laos, and the ''simha'' (සිංහ) of Sri Lanka, where it is featured prominently on the Sri Lankan rupee. It is also related to East Asian leographs, such as the Chinese guardian lions, guardian lions of China, ''komainu'' of Japan, ''shisa'' of Okinawa and Snow Lion of Tibet. Origins The story of why th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myanma Kyat
The kyat ( or ; ; ISO 4217 code MMK) is the currency of Myanmar (Burma). The typical notation for the kyat is "K" (singular) and "Ks." (plural), placed before the numerals followed by "/-". Amounts less than K. 1/- are typically denoted with the number of pyas following "-/" (e.g. -/50 denotes half a kyat). The term ''kyat'' derives from the Myanmar units of measurement, Burmese unit ''kyattha'' (), equal to 16.3 (16.329324593) grams of silver. Current MMK exchange rates From 2001 to 2012, the official exchange rate varied between Ks. 5/75 and Ks. 6/70 per US dollar (Ks. 8/20 to Ks. 7/- per euro). However, the street rate (black market rate), which more accurately took into account the standing of the national economy, has varied from Ks. 750/- to Ks. 1,335/- per USD (Ks. 985/- to Ks. 1,475/- per EUR). The black market exchange rates (USD to MMK) decrease during the peak of the tourist season in Burma (December to January). During ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinthe
''Chinthe'' ( (); (); ()) is the Burmese language, Burmese word for 'Asiatic lion, lion'. The wiktionary:leograph, leograph of ''Chinthe'' is a highly stylized lion commonly depicted in Burmese iconography and Myanmar architecture, architecture, especially as a pair of guardians flanking the entrances of Buddhist pagodas and ''kyaung'' (or Buddhist monasteries). Natural lion Contrary to popular belief, the ''Chinthe'' is not a mythical creature but instead an entirely natural lion, although often associated with myths and legends. The Burmese leograph is related to other stylized lions in the Asian region, including the ''sing'' (สิงห์) of Thailand, Cambodia, Laos, and the ''simha'' (සිංහ) of Sri Lanka, where it is featured prominently on the Sri Lankan rupee. It is also related to East Asian leographs, such as the Chinese guardian lions, guardian lions of China, ''komainu'' of Japan, ''shisa'' of Okinawa and Snow Lion of Tibet. Origins The story of why th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Seal Of Myanmar
The State Seal of the Republic of the Union of Myanmar () is the national emblem used in all official government documents, including publications. As the seal is an official symbol, there are State Seal and regarding appropriate usage of it. The seal's design was partly inspired by that of the Coat of arms of the United Kingdom, and since Myanmar's independence, has changed three times. Description * At the centre of the Seal is the map of the Republic of the Union of Myanmar. The sprigs of ''Eugenia'' containing fourteen leaves each are on either side of the map. * The sprigs of ''Eugenia'' are flanked on each side by an artistic Myanmar lion. The lion on the left side faces towards the left and the lion on the right side faces towards the right * The name of the country in Burmese, , is expressed on the ribbon at the foot of the Seal. The expression is on the scroll which is under the left lion. The expression is under the map. The expression is under the right lion. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Guardian Lions
Chinese guardian lions, or imperial guardian lions, are a traditional Chinese architectural ornament. Typically made of stone, they are also known as stone lions or shishi (). They are known in colloquial English as lion dogs, foo dogs, or fu dogs. The concept, which originated and became popular in Chinese Buddhism, features a pair of Asiatic lions — often one male with a ball that represents the material elements and one female with a cub that represents the element of spirit — that were thought to protect the building from harmful spiritual influences and harmful people that might be a threat. Used in imperial Chinese palaces and tombs, the lions subsequently spread to other parts of Asia including Japan (see komainu), Korea, Mongolia, the Philippines, Tibet, Thailand, Myanmar, Vietnam, Sri Lanka, India, Nepal, Cambodia, Laos, Singapore, and Malaysia. Description Statues of guardian lions have traditionally stood in front of Chinese Imperial palaces, I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burmese Zodiac
The Burmese zodiac ( ) is the traditional Burmese system of astronomy and astrology. While it is still an important component of the Burmese calendar, today, the zodiac is closely identified with Burmese astrology, called ''Baydin'' (). Largely derived from Hindu astronomy and Hindu astrology, Vedic astrology, the Burmese zodiac consists of not only the same 12 signs of the Western zodiac but also 27 lunar mansions of the month and eight weekday signs. Structure Seasons The Burmese zodiac, like the Western zodiac, is divided into 12 signs called ''yathi'' ( ). The Burmese signs are identical to Indian and Western signs as they were derived from Indian and ultimately Western zodiac. Each ''yathi'' is divided into 30 degrees ( ); each degree into 60 minutes ( ); and each minute into 60 seconds ( ).Irwin 1909: 7–8 Lunar mansions The zodiac month consists of 27 days, approximating the mean sidereal month of 27.321661 days. Thus each zodiac day, called ''nekkhat'' ( ), represents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palin (throne)
''Palin'' (; from , or 'sofa') refers to any one of six types of thrones recognized in traditional Burmese scholarship. The ''palin'' is an important symbol of the Burmese monarchy and features prominently in Burmese architecture and Burmese Buddhist iconography. The ''palin'' is featured on the seal of Myanmar's Ministry of Religious Affairs and Culture (Myanmar), Ministry of Religious Affairs and Culture. Types of ''palin'' Traditional Burmese scholarship recognizes six types of thrones, namely: # () – the Buddha's throne # () – Brahma's throne # () – Nat (spirit), nat's throne # () – monarch's throne # () – Buddhist monk's throne # () – judge's throne Usage by Burmese monarchs In pre-colonial times, the (Burmese ''yazapalin'') seated the sovereign and his chief consort. Traditionally, Burmese palaces possessed eight types of thrones, housed in nine palace halls, leading to the Burmese adage, "eight thrones, nine palace halls" (ပလ္လင်ရှ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Komainu
, often called lion-dogs in English, are statue pairs of lion-like creatures, which traditionally guard the entrance or gate of the shrine, or placed in front of or within the ''honden'' (inner sanctum) of Japanese Shinto shrines. Symbolic meaning A twin pair of ''komainu'' (construable as "Korean dog") or two ''shishi'' ("lion")/''karajishi'' ("Chinese lion") are the typical stone-made creatures associated with Gatekeeper, gatekeeping on Shinto shrine grounds. The dog and lion pairs are seen as interchangeable. Meant to ward off evil spirits, modern ''komainu'' statues usually are almost identical, but one has the mouth open, the other closed (however, exceptions exist, where both ''komainu'' have their mouth either open or closedShogakukan Encyclopedia, ''Komainu''), and together they symbolically represent the beginning and the end of all things. The two forms are called for the open mouthed statue symbolically representing the beginning of all things, and for the clos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
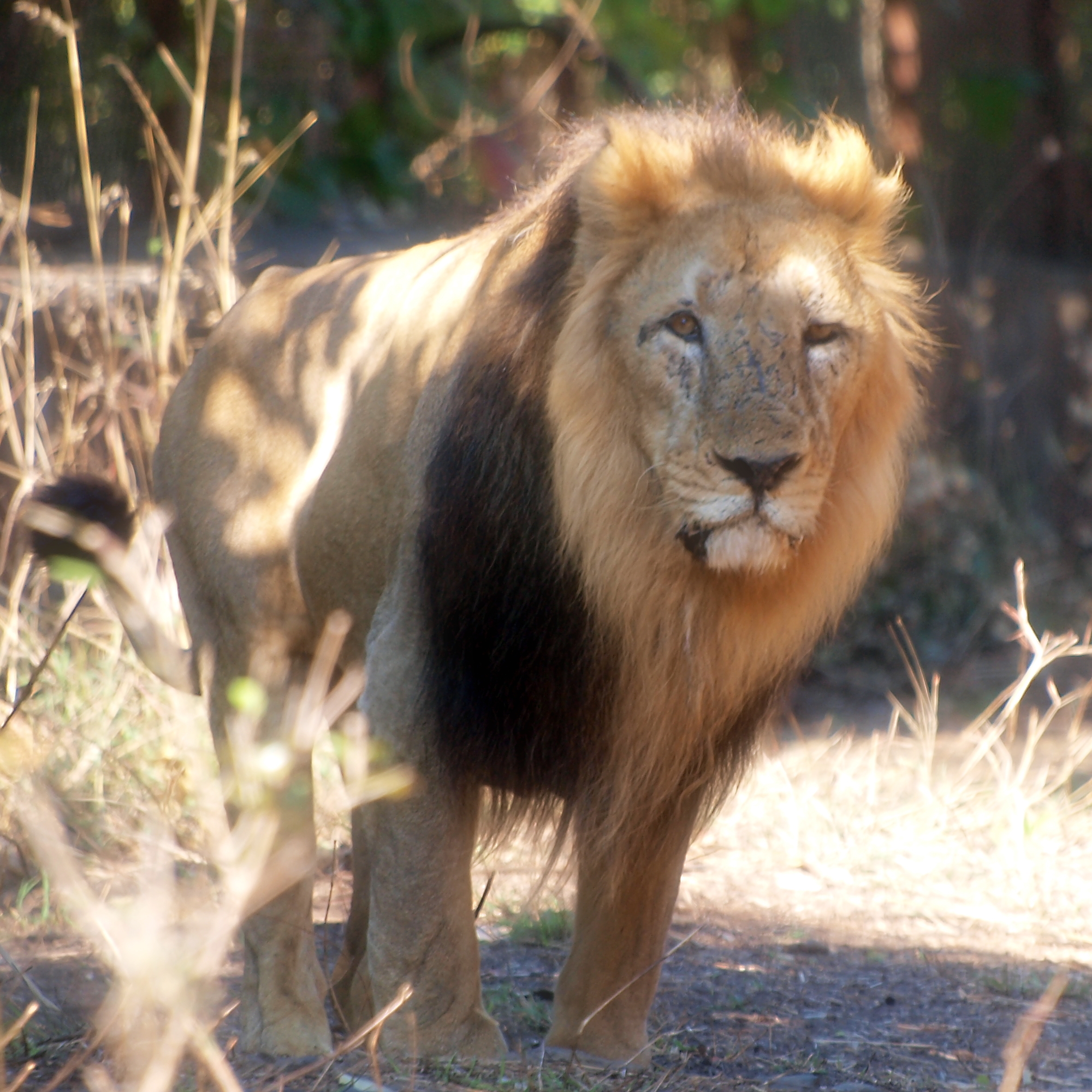
Lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large Felidae, cat of the genus ''Panthera'', native to Sub-Saharan Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body (biology), body; a short, rounded head; round ears; and a dark, hairy tuft at the tip of its tail. It is sexually dimorphic; adult male lions are larger than females and have a prominent mane. It is a social species, forming groups called prides. A lion's pride consists of a few adult males, related females, and cubs. Groups of female lions usually hunt together, preying mostly on medium-sized and large ungulates. The lion is an apex predator, apex and keystone predator. The lion inhabits grasslands, savannahs, and shrublands. It is usually more diurnality, diurnal than other wild cats, but when persecuted, it adapts to being active nocturnality, at night and crepuscular, at twilight. During the Neolithic period, the lion ranged throughout Africa and Eurasia, from Southeast Europe to India, but it has been reduced to fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, Indian peninsula by the Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait. It shares a maritime border with the Maldives in the southwest and India in the northwest. Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte is the legislative capital of Sri Lanka, while the largest city, Colombo, is the administrative and judicial capital which is the nation's political, financial and cultural centre. Kandy is the second-largest urban area and also the capital of the last native kingdom of Sri Lanka. The most spoken language Sinhala language, Sinhala, is spoken by the majority of the population (approximately 17 million). Tamil language, Tamil is also spoken by approximately five million people, making it the second most-spoken language in Sri Lanka. Sri Lanka has a population of appr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinhabahu
Sinhabahu (Sinha = Lion, Bahu = Arm) is a legendary king of ancient India, mentioned in Sri Lankan texts. He was father of Vijaya of Sri Lanka and king of Sinhapura. He was the son of Suppadevi, a Vanga Kingdom princess. According to the Mahavamsa's Legend (the chronicled history of Sri Lanka), Sinhabahu's father was a lion and his mother a princess of Vanga, who was to decide to leave the kingdom alone to 'maghada". She traveled towards mhagada with traders. When the traders arrived at "lata" land a lion appeared and chased them. All the peoples ran away. Lion saw the princess and he immediately liked her. The lion came near the princess but the princess was unafraid because she remembers the predictions about her and a lion. The lion takes her to a cave. There she births two children, a boy named inhabahuand girl named inhaseevali When Sinhabahu is sixteen, he asks his mother why their father is different from them. She reveals their story. He asks, “Why don’t we l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengal
Bengal ( ) is a Historical geography, historical geographical, ethnolinguistic and cultural term referring to a region in the Eastern South Asia, eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. The region of Bengal proper is divided between the modern-day sovereign nation of Bangladesh and the States and union territories of India, Indian states of West Bengal, and Karimganj district of Assam. The ancient Vanga Kingdom is widely regarded as the namesake of the Bengal region. The Bengali calendar dates back to the reign of Shashanka in the 7th century CE. The Pala Empire was founded in Bengal during the 8th century. The Sena dynasty and Deva dynasty ruled between the 11th and 13th centuries. By the 14th century, Bengal was absorbed by Muslim conquests in the Indian subcontinent. An independent Bengal Sultanate was formed and became the eastern frontier of the Islamic world. During this period, Bengal's rule and influence spread to Assam, Arakan, Tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanga Kingdom
Vaṅga was an ancient kingdom and geopolitical division within the Ganges delta in the Indian subcontinent. The kingdom is one of the namesakes of the Bengal region. It was located in eastern and southern Bengal. Vanga features prominently in the epics and tales of ancient India as well as in the history of Sri Lanka. Vanga was probably the centre of the Gangaridai Empire mentioned by numerous Greco-Roman writers. The exact capital of ancient Vanga kingdom could not be identified. After the rule of the Gupta Empire, ancient Bengal was divided into two independent kingdoms – Gauda kingdom, Gauda and Vanga. Kotalipara Upazila, Kotalipara, an ancient fortified city of independent Vanga kingdom, present-day in Gopalganj District, Bangladesh, Gopalganj district of Dhaka division, emerged as the centre of administration of Vanga kings after Gupta kingdom, Gupta period. Vanga was probably the centre of the Gangaridai Empire mentioned by numerous Greco-Roman writers.Indian and Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |