|
Chanter
The chanter is the part of the bagpipe upon which the player creates the melody. It consists of a number of finger-holes, and in its simpler forms looks similar to a recorder. On more elaborate bagpipes, such as the Northumbrian bagpipes or the Uilleann pipes, it also may have a number of keys, to increase the instrument's range and/or the number of keys (in the modal sense) it can play in. Like the rest of the bagpipe, they are often decorated with a variety of substances, including metal (silver/nickel/gold/brass), bone, ivory, or plastic mountings. Cylindrical vs. conical bore Chanters come in two main types, parallel and non-parallel bored (although there is no clear dividing line between the two). This refers to the shape of the internal bore of the chanter. On the Great Highland Bagpipe, the internal bore is conical: it is this that gives the chanter its exceptional volume. The Northumbrian pipes, on the other hand, have a parallel bore, giving them a much s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uilleann Pipes
The uilleann pipes ( or , ), also known as Union pipes and sometimes called Irish pipes, are the characteristic national bagpipe of Ireland. Their current name is a partial translation of the Irish language terms (literally, "pipes of the elbow"), from their method of inflation. There is no historical record of the name or use of the term ''uilleann pipes'' before the 20th century. It was an invention of W. H. Grattan Flood, Grattan Flood and the name stuck. People mistook the term 'union' to refer to the Acts of Union 1800, 1800 Act of Union; however, this is incorrect as Breandán Breathnach points out that a poem published in 1796 uses the term 'union'. The bag of the uilleann pipes is inflated by means of a small set of bellows strapped around the waist and the right arm (in the case of a right-handed player; in the case of a left-handed player the location and orientation of all components are reversed). The bellows not only relieve the player from the effort needed t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Practice Chanter
A bagpipe practice chanter is a double-reed woodwind instrument, principally used as an adjunct to the Great Highland bagpipe. As its name implies, the practice chanter serves as a practice instrument: firstly for learning to finger the different melody notes of bagpipe music, and (after a player masters the bagpipes) to practice new music. Design and construction The practice chanter is essentially a long, thin piece of wood or plastic (in two parts) with a small-diameter hole bored lengthwise through the centre. Air is directed into and through this borehole and passes through a reed, the vibration of which causes the sound. On the lower portion of the chanter, holes are bored into the instrument at right angles to the central borehole. These holes are then covered or uncovered to produce the melody. Practice chanters can be made out of various materials and come in various sizes: short chanters are designed for the smaller hands of a child; regular chanters (as shown in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bagpipe
Bagpipes are a woodwind instrument using enclosed reeds fed from a constant reservoir of air in the form of a bag. The Great Highland bagpipes are well known, but people have played bagpipes for centuries throughout large parts of Europe, Northern Africa, Western Asia, around the Persian Gulf and northern parts of South Asia. The term ''bagpipe'' is equally correct in the singular or the plural, though pipers usually refer to the bagpipes as "the pipes", "a set of pipes" or "a stand of pipes". Bagpipes are part of the aerophone group because to play the instrument you must blow air into it to produce a sound. Construction A set of bagpipes minimally consists of an air supply, a bag, a chanter, and usually at least one drone. Many bagpipes have more than one drone (and, sometimes, more than one chanter) in various combinations, held in place in stocks—sockets that fasten the various pipes to the bag. Air supply The most common method of supplying air to the bag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northumbrian Smallpipes
The Northumbrian smallpipes (also known as the Northumbrian pipes) are bellows-blown bagpipes from Northeastern England, where they have been an important factor in the local musical culture for more than 250 years. The family of the Duke of Northumberland have had an official piper for over 250 years. The Northumbrian Pipers' Society was founded in 1928, to encourage the playing of the instrument and its music; Although there were so few players at times during the last century that some feared the tradition would die out, there are many players and makers of the instrument nowadays, and the Society has played a large role in this revival. In more recent times the Mayor of Gateshead and the Lord Mayor of Newcastle upon Tyne, Newcastle have both established a tradition of appointing official Northumbrian pipers. In a survey of the bagpipes in the Pitt Rivers Museum, Oxford University, the organologist Anthony Baines wrote: "It is perhaps the most civilized of the bagpipes, mak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chanter 05PNW 034
The chanter is the part of the bagpipe upon which the player creates the melody. It consists of a number of finger-holes, and in its simpler forms looks similar to a recorder. On more elaborate bagpipes, such as the Northumbrian bagpipes or the Uilleann pipes, it also may have a number of keys, to increase the instrument's range and/or the number of keys (in the modal sense) it can play in. Like the rest of the bagpipe, they are often decorated with a variety of substances, including metal (silver/nickel/gold/brass), bone, ivory, or plastic mountings. Cylindrical vs. conical bore Chanters come in two main types, parallel and non-parallel bored (although there is no clear dividing line between the two). This refers to the shape of the internal bore of the chanter. On the Great Highland Bagpipe, the internal bore is conical: it is this that gives the chanter its exceptional volume. The Northumbrian pipes, on the other hand, have a parallel bore, giving them a much sweete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Highland Bagpipe
The great Highland bagpipe ( 'the great pipe') is a type of bagpipe native to Scotland, and the Scottish analogue to the great Irish warpipes. It has acquired widespread recognition through its usage in the British Armed Forces, British military and in pipe bands throughout the world. The bagpipe of any kind is first attested in Scotland around 1400. The earliest references to bagpipes in Scotland are in a military context, and it is in that context that the great Highland bagpipe became established in the British military and achieved the widespread prominence it enjoys today, whereas other bagpipe traditions throughout Europe, ranging from Portugal to Russia, almost universally went into decline by the late 19th and early 20th century. Though widely famous for its role in military and civilian pipe bands, the great Highland bagpipe is also used for a solo virtuosic style called ''pìobaireachd'', ''ceòl mòr'', or simply pibroch. Through development over the centuries, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zampogna
Zampogna (, , ) is a generic term for a number of Italian double chantered bagpipes that can be found throughout areas in Latium. The tradition is now mostly associated with Christmas, and the most famous Italian carol, " Tu scendi dalle stelle" (You Come Down From the Stars), is derived from traditional ''zampogna'' music. However, there is an ongoing resurgence of the instrument in secular use seen with the increasing number of folk music festivals and folk music in each December by Italian ensembles. Construction All chanters and drones are fixed into a single round stock that the bag is attached to. Each chanter is tuned differently, according to the tradition it represents, and there are dozens. Typically, the double-reeded versions will have a soprano chanter on the right and a bass chanter on the left (called, respectively, ''ritta'' and ''manga''—meaning 'right' and 'left'—in the tradition of Southern Latium) with an alto drone (''bordone'' being the generic name); ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major Third
In music theory, a third is a Interval (music), musical interval encompassing three staff positions (see Interval (music)#Number, Interval number for more details), and the major third () is a third spanning four Semitone, half steps or two Whole step, whole steps. Along with the minor third, the major third is one of two commonly occurring thirds. It is described as ''major'' because it is the larger interval of the two: The major third spans four semitones, whereas the minor third only spans three. For example, the interval from C to E is a major third, as the note E lies four semitones above C, and there are three staff positions from C to E. Diminished third, Diminished and augmented thirds are shown on the musical staff the same number of lines and spaces apart, but contain a different number of semitones in pitch (two and five). Harmonic and non-harmonic thirds The major third may be derived from the harmonic series (music), harmonic series as the interval be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
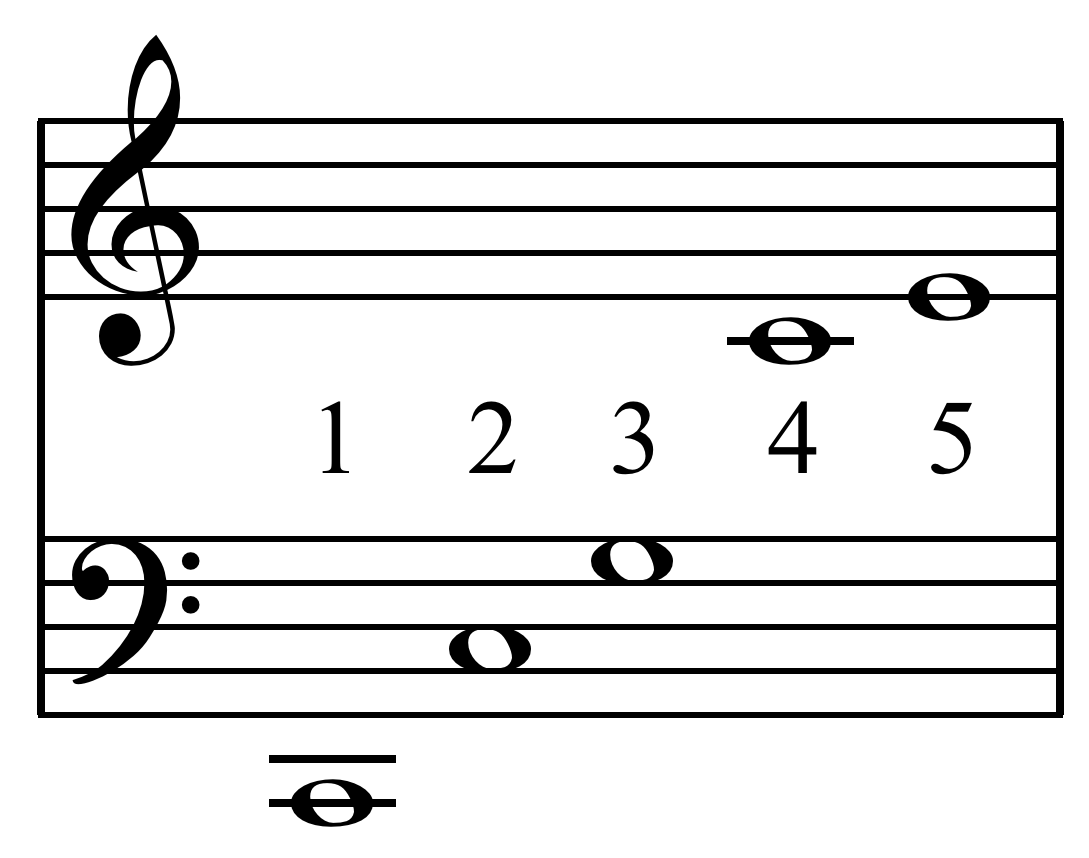
Just Intonation
In music, just intonation or pure intonation is a musical tuning, tuning system in which the space between notes' frequency, frequencies (called interval (music), intervals) is a natural number, whole number ratio, ratio. Intervals spaced in this way are said to be pure, and are called just intervals. Just intervals (and chords created by combining them) consist of tones from a single harmonic series (music), harmonic series of an implied fundamental frequency, fundamental. For example, in the diagram, if the notes G3 and C4 (labelled 3 and 4) are tuned as members of the harmonic series of the lowest C, their frequencies will be 3 and 4 times the fundamental frequency. The interval ratio between C4 and G3 is therefore 4:3, a just fourth (music), fourth. In Western musical practice, bowed instruments such as violins, violas, cellos, and double basses are tuned using pure fifths or fourths. In contrast, keyboard instruments are rarely tuned using only pure intervals—the desire fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpathian Basin
The Pannonian Basin, with the term Carpathian Basin being sometimes preferred in Hungarian literature, is a large sedimentary basin situated in southeastern Central Europe. After the Treaty of Trianon following World War I, the geomorphological term Pannonian Plain was also used for roughly the same region, referring to the lowlands in the area occupied by the Pannonian Sea during the Pliocene Epoch, however some consider the term "Pannonian Plain" not only unhistorical but also topologically erroneous. Terminology The term Pannonian Plain refers to the lowland parts of the Pannonian Basin as well as those of some adjoining regions like Lower Austria, Moravia, and Silesia (Czech Republic and Poland). The lands adjoining the plain proper are sometimes also called ''peri-Pannonian''. In English language, the terms "Pannonian Basin" and "Carpathian Basin" may sometimes be used synonymously, although the latter holds an irredentist Hungarian connotation. The name "Pannonian" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Müsa
The müsa, or müsa appenninica, is a bagpipe from the Apennines of north-west Italy which was commonly used to accompany the piffero in the folk music of the Quattro Province: the ‘Four Provinces’ of (Pavia, Alessandria, Genoa and Piacenza). In the 1930s, however, the instrument fell into disfavour and was generally displaced by the accordion Accordions (from 19th-century German language, German ', from '—"musical chord, concord of sounds") are a family of box-shaped musical instruments of the bellows-driven free reed aerophone type (producing sound as air flows past a Reed (mou .... Discografia *1986: I Suonatori delle quattro province - ''Musica trdizionale dell'Appennino'' - Robi Droli *1987: Baraban - ''I canti rituali, i balli, il piffero'' - ACB *1993: I Suonatori delle quattro province - ''Racconti a colori'' - Robi Droli *2001: I Müsetta - ''La vulp la vâ 'ntla vigna'' - Folkclub-Ethnosuoni *2003: Enerbia - ''Così lontano l’azzurro'' - EDT *2004: Mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major Sixth
In music theory, a sixth is a musical interval encompassing six note letter names or staff positions (see Interval number for more details), and the major sixth is one of two commonly occurring sixths. It is qualified as ''major'' because it is the larger of the two. The major sixth spans nine semitones. Its smaller counterpart, the minor sixth, spans eight semitones. For example, the interval from C up to the nearest A is a major sixth. It is a sixth because it encompasses six note letter names (C, D, E, F, G, A) and six staff positions. It is a major sixth, not a minor sixth, because the note A lies nine semitones above C. Diminished and augmented sixths (such as C to A and C to A) span the same number of note letter names and staff positions, but consist of a different number of semitones (seven and ten, respectively). A commonly cited example of a melody featuring the major sixth as its opening is " My Bonnie Lies Over the Ocean".Blake Neely, ''Piano For Dummies'', se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |