|
Centring
Centring, centre, centering"Centering 2, Centring 2" def. 1. Whitney, William Dwight, and Benjamin E. Smith. ''The Century dictionary and cyclopedia''. vol. 2. New York: Century Co., 1901. p. 885., or center is a type of falsework: the temporary structure upon which the stones of an arch or vault are laid during construction. Until the keystone is inserted an arch has no strength and needs the centring to keep the voussoirs in their correct relative positions. A simple centring without a truss is called a common centring. A cross piece connecting centring frames is called a lag or bolst.Ching, Frank (1995). ''A visual dictionary of architecture''. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold. p. 3. . Centring is normally made of wood timbers, a relatively straightforward structure in a simple arch or vault; but with more complex shapes involving double curvature, such as a dome or the bottle-shaped flue in a Norman-period kitchen, clay or sand bound by a weak lime mortar would be used. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dome
A dome () is an architectural element similar to the hollow upper half of a sphere. There is significant overlap with the term cupola, which may also refer to a dome or a structure on top of a dome. The precise definition of a dome has been a matter of controversy and there are a wide variety of forms and specialized terms to describe them. A dome can rest directly upon a Rotunda (architecture), rotunda wall, a Tholobate, drum, or a system of squinches or pendentives used to accommodate the transition in shape from a rectangular or square space to the round or polygonal base of the dome. The dome's apex may be closed or may be open in the form of an Oculus (architecture), oculus, which may itself be covered with a roof lantern and cupola. Domes have a long architectural lineage that extends back into prehistory. Domes were built in ancient Mesopotamia, and they have been found in Persian architecture, Persian, Ancient Greek architecture, Hellenistic, Ancient Roman architecture, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
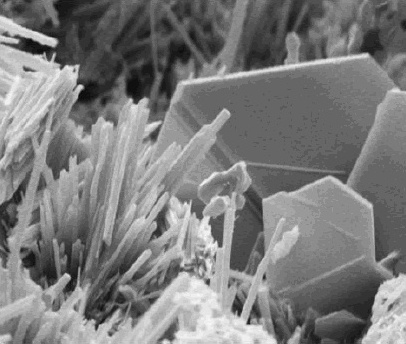
Calcium Hydroxide
Calcium hydroxide (traditionally called slaked lime) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca( OH)2. It is a colorless crystal or white powder and is produced when quicklime ( calcium oxide) is mixed with water. Annually, approximately 125 million tons of calcium hydroxide are produced worldwide. Calcium hydroxide has many names including hydrated lime, caustic lime, builders' lime, slaked lime, cal, and pickling lime. Calcium hydroxide is used in many applications, including food preparation, where it has been identified as E number E526. Limewater, also called milk of lime, is the common name for a saturated solution of calcium hydroxide. Solubility Calcium hydroxide is moderately soluble in water, as seen for many dihydroxides. Its solubility increases from 0.66 g/L at 100 °C to 1.89 g/L at 0 °C. Its solubility product ''K''sp of 5.02 at 25 °C, its dissociation in water is large enough that its solutions are basic according to the following ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catenary
In physics and geometry, a catenary ( , ) is the curve that an idealized hanging chain or wire rope, cable assumes under its own weight when supported only at its ends in a uniform gravitational field. The catenary curve has a U-like shape, superficially similar in appearance to a parabola, which it is not. The curve appears in the design of certain types of Catenary arch, arches and as a cross section of the catenoid—the shape assumed by a soap film bounded by two parallel circular rings. The catenary is also called the alysoid, chainette,#MathWorld, MathWorld or, particularly in the materials sciences, an example of a funicular curve, funicular. Rope statics describes catenaries in a classic statics problem involving a hanging rope. Mathematically, the catenary curve is the Graph of a function, graph of the hyperbolic cosine function. The surface of revolution of the catenary curve, the catenoid, is a minimal surface, specifically a minimal surface of revolution. A ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semicircular Arch
In architecture, a semicircular arch is an arch with an intrados (inner surface) shaped like a semicircle. This type of arch was adopted and very widely used by the Romans, thus becoming permanently associated with Roman architecture. Terminology When the arch construction involves the Roman techniques (either wedge-like stone voussoirs or thin Roman bricks), it is known as a Roman arch. The semicircular arch is also known as a round arch. Description The rise (height) of a round arch is limited to of its span, so it looks more "grounded" than a parabolic arch or a pointed arch. Whenever a higher semicircular arch was required (for example, for a narrow arch to match the height of a nearby broad one), either stilting or horseshoe shape were used, thus creating a stilted arch and horseshoe arch respectively. These "shifts and dodges" were immediately dropped once the pointed arch with its malleable proportions was adopted. Still, "the Romanesque arch is beautiful a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiln
A kiln is a thermally insulated chamber, a type of oven, that produces temperatures sufficient to complete some process, such as hardening, drying, or Chemical Changes, chemical changes. Kilns have been used for millennia to turn objects made from clay into pottery, Tile, tiles and bricks. Various industries use rotary kilns for pyroprocessing (to calcinate ores, such as limestone to Lime (material), lime for Cement kiln, cement) and to transform many other materials. Etymology According to the Oxford English Dictionary, kiln was derived from the words cyline, cylene, cyln(e) in Old English, in turn derived from Latin ''culina'' ('kitchen'). In Middle English, the word is attested as kulne, kyllne, kilne, kiln, kylle, kyll, kil, kill, keele, kiele. In Greek the word ''καίειν, kaiein'', means 'to burn'. Pronunciation The word 'kiln' was originally pronounced 'kil' with the 'n' silent, as is referenced in ''Webster's Dictionary of 1828'' and in ''English Words as Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
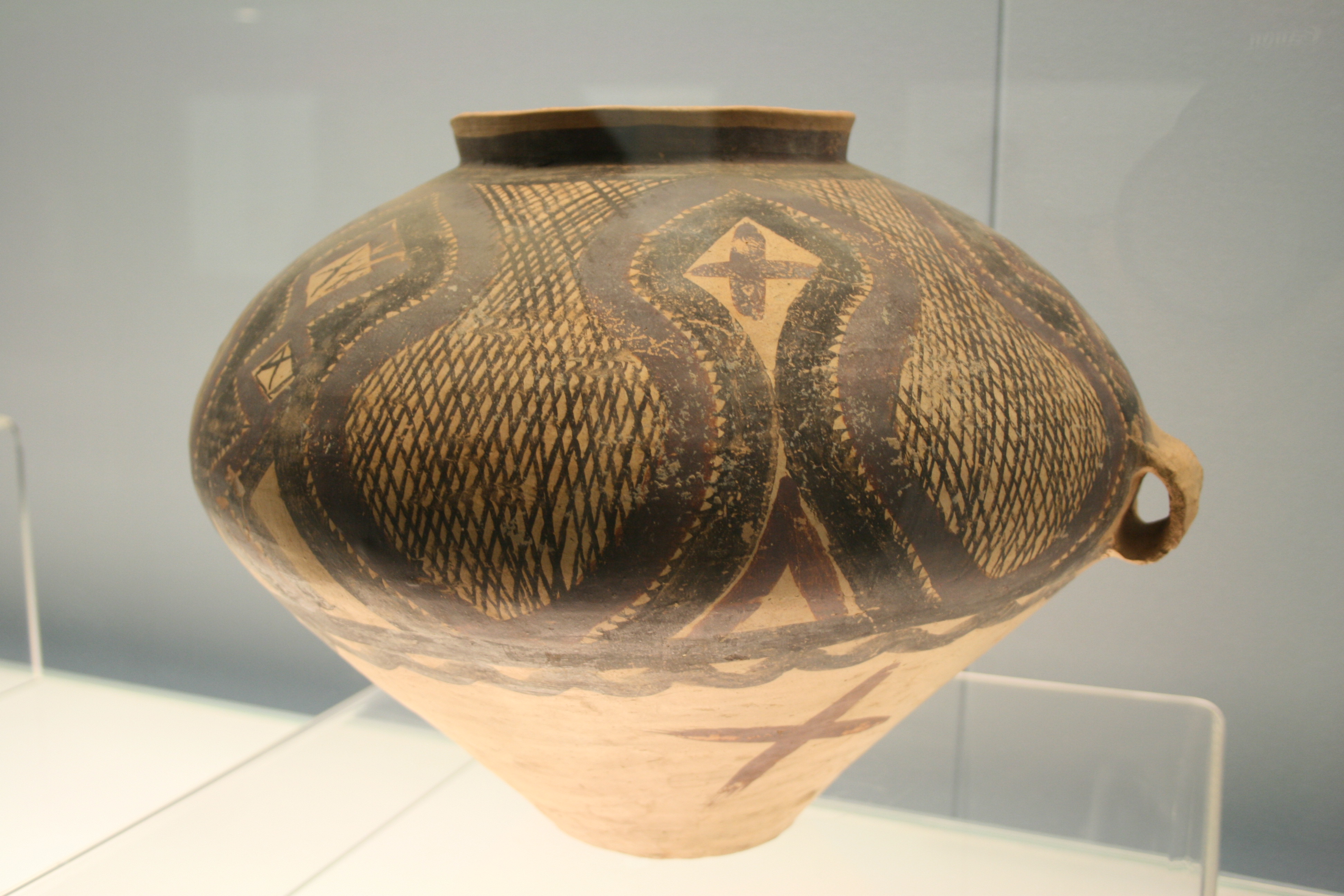
Pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other raw materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. The place where such wares are made by a ''potter'' is also called a ''pottery'' (plural ''potteries''). The definition of ''pottery'', used by the ASTM International, is "all fired ceramic wares that contain clay when formed, except technical, structural, and refractory products". End applications include tableware, ceramic art, decorative ware, toilet, sanitary ware, and in technology and industry such as Insulator (electricity), electrical insulators and laboratory ware. In art history and archaeology, especially of ancient and prehistoric periods, pottery often means only vessels, and sculpture, sculpted figurines of the same material are called terracottas. Pottery is one of the Timeline of historic inventions, oldest human inventions, originating before the Neolithic, Neolithic period, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
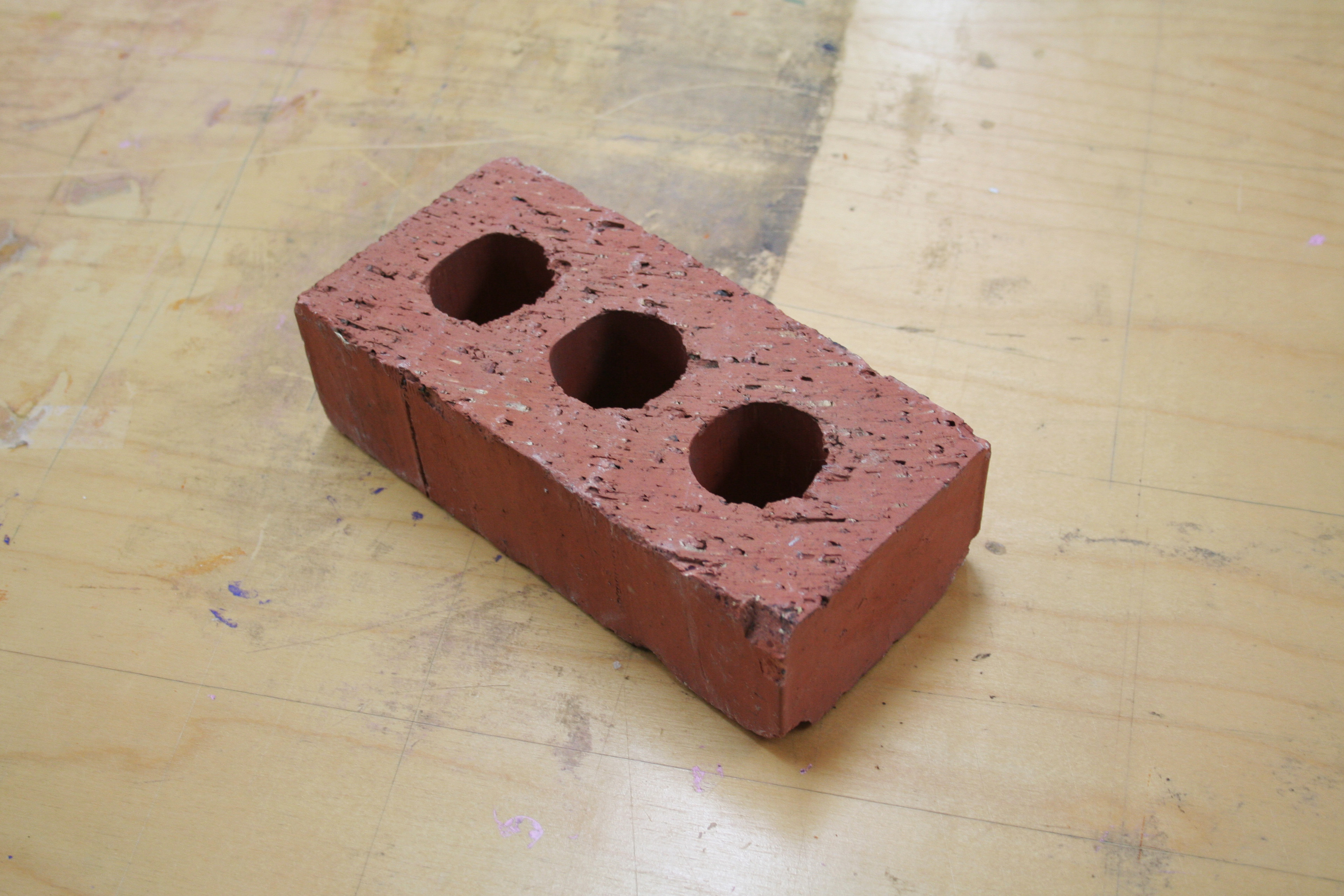
Brick
A brick is a type of construction material used to build walls, pavements and other elements in masonry construction. Properly, the term ''brick'' denotes a unit primarily composed of clay. But is now also used informally to denote building units made of other materials or other chemically cured construction blocks. Bricks can be joined using Mortar (masonry), mortar, adhesives or by interlocking. Bricks are usually produced at brickworks in numerous classes, types, materials, and sizes which vary with region, and are produced in bulk quantities. Concrete masonry unit, ''Block'' is a similar term referring to a rectangular building unit composed of clay or concrete, but is usually larger than a brick. Lightweight bricks (also called lightweight blocks) are made from expanded clay aggregate. Fired bricks are one of the longest-lasting and strongest building materials, sometimes referred to as artificial stone, and have been used since . Air-dried bricks, also known as mudbricks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
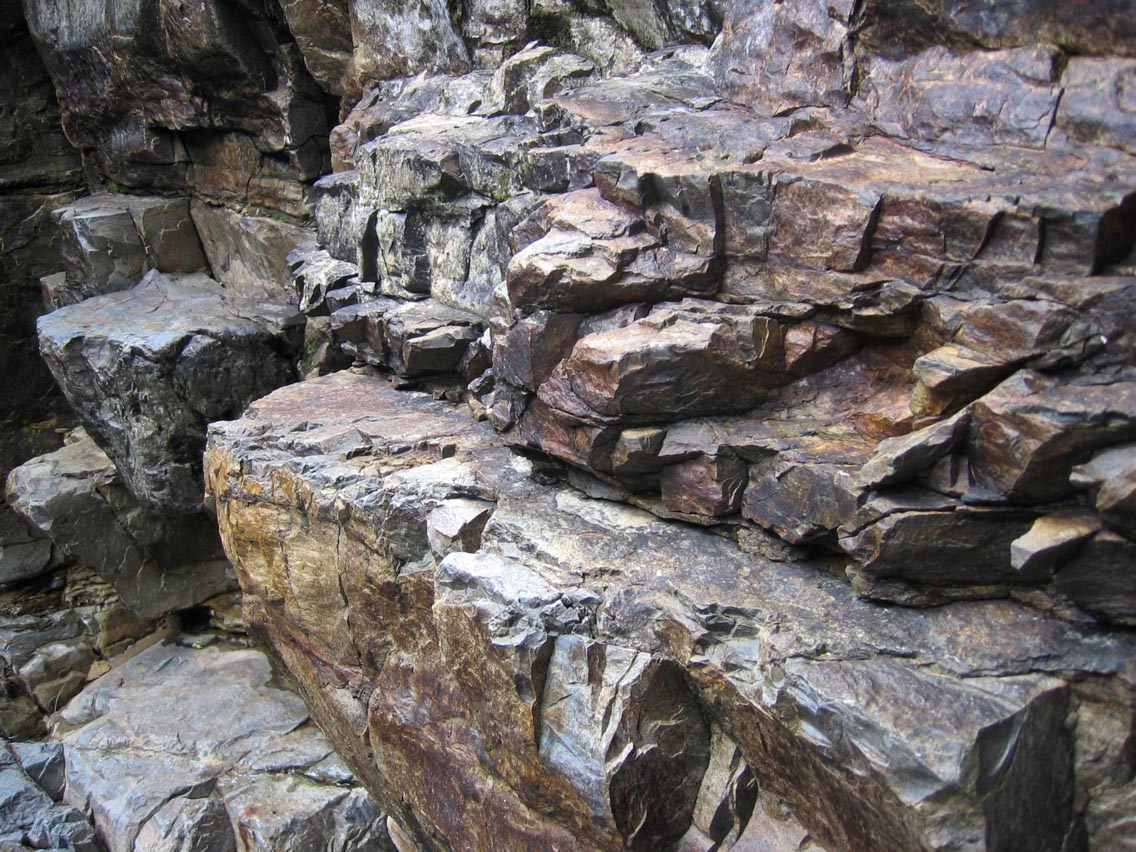
Rock (geology)
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its Chemical compound, chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks form the Earth's outer solid layer, the Earth's crust, crust, and most of its interior, except for the liquid Earth's outer core, outer core and pockets of magma in the asthenosphere. The study of rocks involves multiple subdisciplines of geology, including petrology and mineralogy. It may be limited to rocks found on Earth, or it may include planetary geology that studies the rocks of other celestial objects. Rocks are usually grouped into three main groups: igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks and metamorphic rocks. Igneous rocks are formed when magma cools in the Earth's crust, or lava cools on the ground surface or the seabed. Sedimentary rocks are formed by diagenesis and lithification of sediments, which in turn are formed by the weathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mortar (masonry)
Mortar is a workable paste which hardens to bind building blocks such as stones, bricks, and concrete masonry units, to fill and seal the irregular gaps between them, spread the weight of them evenly, and sometimes to add decorative colours or patterns to masonry walls. In its broadest sense, mortar includes pitch, asphalt, and soft clay, as those used between bricks, as well as cement mortar. The word "mortar" comes from the Old French word ''mortier'', "builder's mortar, plaster; bowl for mixing." (13c.). Cement mortar becomes hard when it cures, resulting in a rigid aggregate (composite) , aggregate structure; however, the mortar functions as a weaker component than the building blocks and serves as the sacrificial element in the masonry, because mortar is easier and less expensive to repair than the building blocks. Bricklayers typically make mortars using a mixture of sand, a binder, and water. The most common binder since the early 20th century is Portland cement, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolinite, ). Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impurities, such as a reddish or brownish colour from small amounts of iron oxide. Clays develop plasticity (physics), plasticity when wet but can be hardened through Pottery#Firing, firing. Clay is the longest-known ceramic material. Prehistoric humans discovered the useful properties of clay and used it for making pottery. Some of the earliest pottery shards have been radiocarbon dating, dated to around 14,000 BCE, and Clay tablet, clay tablets were the first known writing medium. Clay is used in many modern industrial processes, such as paper making, cement production, and chemical filtration, filtering. Between one-half and two-thirds of the world's population live or work in buildings made with clay, often baked into brick, as an essenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sand
Sand is a granular material composed of finely divided mineral particles. Sand has various compositions but is usually defined by its grain size. Sand grains are smaller than gravel and coarser than silt. Sand can also refer to a textural class of soil or soil type; i.e., a soil containing more than 85 percent sand-sized particles by mass. The composition of sand varies, depending on the local rock sources and conditions, but the most common constituent of sand in inland continental settings and non-tropical coastal settings is silica (silicon dioxide, or SiO2), usually in the form of quartz. Calcium carbonate is the second most common type of sand. One such example of this is aragonite, which has been created over the past 500million years by various forms of life, such as coral and shellfish. It is the primary form of sand apparent in areas where reefs have dominated the ecosystem for millions of years, as in the Caribbean. Somewhat more rarely, sand may be composed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |