|
Carbendazim
Carbendazim is a fungicide, a member benzimidazole fungicides. It is a metabolite of benomyl. The fungicide is used to control plant diseases in cereals and fruits, including citrus, bananas, strawberries, macadamia nuts, pineapples, and pomes. A 4.7% solution of carbendazim hydrochloride, sold as Eertavas, is marketed as a treatment for Dutch elm disease. Other uses It is also employed as a casting worm control agent in amenity turf situations such as golf greens, tennis courts etc. and in some countries is licensed for that use only. Safety, regulation, controversy High doses of carbendazim destroy the testicles of laboratory animals. Maximum pesticide residue limits (MRLs) for fresh produce in the EU are between 0.1 and 0.7 mg/kg with the exception of loquat fruits, which is set at 2 mg/kg. The limits for more commonly consumed citrus and pome fruits are between 0.1 and 0.2 mg/kg. Use of this fungicide on macadamia plantations has proven controversial in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzimidazole Fungicide
Benzimidazole fungicides are a class of fungicides including benomyl, carbendazim (MBC), thiophanate-methyl, thiabendazole and fuberidazole. They can control many ascomycetes and basidiomycetes, but not oomycetes. They are applied to cereals, fruits, vegetables and vines, and are also used in postharvest handling of crops. The solubility of benzimidazole fungicides is low at physiological pH and becomes high at low pH. In plants, carbendazim, thiabendazole and fuberidazole are mobile, i.e. systemic, and benomyl and thiophanate-methyl are converted to carbendazim. This conversion also occurs in soils and animals. In soil and water, carbendazim is mainly degraded by microbes. They are metabolized through hydrolysis and photolysis in plants. These fungicides kill cells during mitosis by distorting the mitotic spindle; β-tubulin, a protein important in forming the cytoskeleton, is targeted. They mostly inhibit polymerization of β-tubulin by interacting with it directly, but other i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungicide
Fungicides are pesticides used to kill parasitic fungi or their spores. Fungi can cause serious damage in agriculture, resulting in losses of yield and quality. Fungicides are used both in agriculture and to fight fungal infections in animals, including humans. Fungicides are also used to control oomycetes, which are not taxonomically/genetically fungi, although sharing similar methods of infecting plants. Fungicides can either be contact, translaminar or systemic. Contact fungicides are not taken up into the plant tissue and protect only the plant where the spray is deposited. Translaminar fungicides redistribute the fungicide from the upper, sprayed leaf surface to the lower, unsprayed surface. Systemic fungicides are taken up and redistributed through the xylem vessels. Few fungicides move to all parts of a plant. Some are locally systemic, and some move upward. Most fungicides that can be bought retail are sold in liquid form, the active ingredient being present at 0.08% i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzimidazoles
Benzimidazole is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound. This bicyclic compound may be viewed as fused rings of the aromatic compounds benzene and imidazole. It is a white solid that appears in form of tabular crystals. Preparation Benzimidazole was discovered during research on vitamin B12. The benzimidazole nucleus was found to be a stable platform on which drugs could be developed. Benzimidazole is produced by condensation of o-phenylenediamine with formic acid, or the equivalent trimethyl orthoformate: :C6H4(NH2)2 + HC(OCH3)3 → C6H4N(NH)CH + 3 CH3OH 2-Substituted derivatives are obtained when the condensation is conducted with aldehydes in place of formic acid, followed by oxidation. Reactions Benzimidazole is a base: :C6H4N(NH)CH + H+ → 6H4(NH)2CHsup>+ It can also be deprotonated with stronger bases: :C6H4N(NH)CH + LiH → Li 6H4N2CH + H2 The imine can be alkylated and also serves as a ligand in coordination chemistry. The most pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
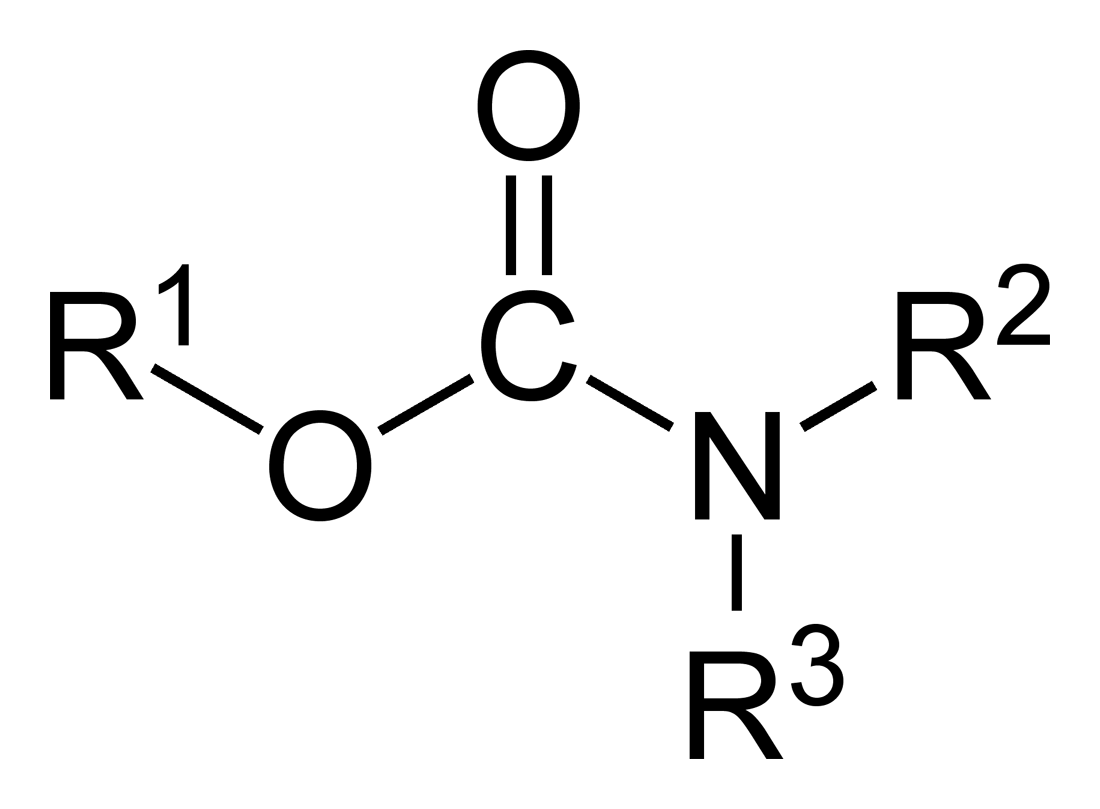
Carbamates
In organic chemistry, a carbamate is a category of organic compounds with the general formula and structure , which are formally derived from carbamic acid (). The term includes organic compounds (e.g., the ester ethyl carbamate), formally obtained by replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms by other organic functional groups; as well as salts with the carbamate anion (e.g. ammonium carbamate). Polymers whose repeat units are joined by carbamate like groups are an important family of plastics, the polyurethanes. See for clarification. Properties While carbamic acids are unstable, many carbamate esters and salts are stable and well known. Equilibrium with carbonate and bicarbonate In water solutions, the carbamate anion slowly equilibrates with the ammonium cation and the carbonate or bicarbonate anions: : : Calcium carbamate is soluble in water, whereas calcium carbonate is not. Adding a calcium salt to an ammonium carbamate/carbonate solution will precipitate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocrine Disruptors
Endocrine disruptors, sometimes also referred to as hormonally active agents, endocrine disrupting chemicals, or endocrine disrupting compounds are chemicals that can interfere with endocrine (or hormonal) systems. These disruptions can cause numerous adverse human health outcomes, including alterations in sperm quality and fertility; abnormalities in sex organs‚ endometriosis‚ early puberty‚ altered nervous system or immune function; certain cancers; respiratory problems; metabolic issues; diabetes, obesity, or cardiovascular problems; growth, neurological and learning disabilities, and more. Found in many household and industrial products, endocrine disruptors "interfere with the synthesis, secretion, transport, binding, action, or elimination of natural hormones in the body that are responsible for development, behavior, fertility, and maintenance of homeostasis (normal cell metabolism)." Any system in the body controlled by hormones can be derailed by hormone disrupto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) also often called cholinesterase inhibitors, inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase from Hydrolysis, breaking down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine into choline and acetate, thereby increasing both the level and duration of action of acetylcholine in the central nervous system, Autonomic ganglion, autonomic ganglia and neuromuscular junctions, which are rich in acetylcholine receptors. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are one of two types of cholinesterase inhibitors; the other being Butyrylcholinesterase#Inhibitors, butyryl-cholinesterase inhibitors. Acetylcholinesterase is the primary member of the cholinesterase, cholinesterase enzyme family. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are classified as reversible, irreversible, or quasi-irreversible (also called pseudo-irreversible). Mechanism of action Organophosphates Organophosphates like TEPP, tetraethyl pyrophosphate (TEPP) and sarin inhibit cholinesterases, enzymes that hydrolyze the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queensland
Queensland ( , commonly abbreviated as Qld) is a States and territories of Australia, state in northeastern Australia, and is the second-largest and third-most populous state in Australia. It is bordered by the Northern Territory, South Australia and New South Wales to the west, south-west and south, respectively. To the east, Queensland is bordered by the Coral Sea and the Pacific Ocean; to the state's north is the Torres Strait, separating the Australian mainland from Papua New Guinea, and the Gulf of Carpentaria to the north-west. With an area of , Queensland is the world's List of country subdivisions by area, sixth-largest subnational entity; it List of countries and dependencies by area, is larger than all but 16 countries. Due to its size, Queensland's geographical features and climates are diverse, and include tropical rainforests, rivers, coral reefs, mountain ranges and white sandy beaches in its Tropical climate, tropical and Humid subtropical climate, sub-tropical c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macadamia
''Macadamia'' is a genus of four species of trees in the flowering plant family Proteaceae. They are indigenous to Australia—specifically, northeastern New South Wales and central and southeastern Queensland. Two species of the genus are commercially important for their fruit, the macadamia nut (or simply macadamia). Global production in 2015 was . Other names include Queensland nut, bush nut, maroochi nut or bauple nut. It was an important source of Bush tucker, bushfood for the Aboriginal Australians, Aboriginal peoples. The nut was first commercially produced on a wide scale in Hawaii, where Australian seeds were introduced in the 1880s, and which for more than a century was the world's largest producer. South Africa has been the world's largest producer of the macadamia since the 2010s. The macadamia is the only widely grown food plant that is native to Australia. Description ''Macadamia'' is a genus of evergreen trees that grows tall. The leaves are arranged in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loquat
The loquat (''Eriobotrya japonica'', Chinese: 枇杷; Pinyin: pípá) is a large evergreen shrub or tree grown commercially for its orange fruit. It is also cultivated as an ornamental plant. The loquat is in the family Rosaceae, subfamily Spiraeoideae, tribe Pyreae, subtribe Pyrinae. It is native to the cooler hill regions of south-central China. In Japan, the loquat has been grown for over 1,000 years. It has been introduced to regions with subtropical to mild temperate climates throughout the world. ''Eriobotrya japonica'' formerly was thought to be closely related to the genus ''Mespilus'' and is still sometimes mistakenly known as the Japanese medlar, which is the name it takes in other European languages, such as in Spanish or in Italian. It is also known as Japanese plum and Chinese plum. Etymology The name loquat derives from Cantonese ''lou4 gwat1'' (). The phrase 'black orange' originally referred to unripened kumquats, which are dark green in color, but the name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vermicompost
Vermicompost (vermi-compost) is the product of the decomposition process using various species of worms, usually red wigglers, white worms, and other earthworms, to create a mixture of decomposing vegetable or food waste, bedding materials, and vermicast. This process is called vermicomposting, with the rearing of worms for this purpose is called vermiculture. Vermicast (also called worm castings, worm humus, worm poop, worm manure, or worm faeces) is the end-product of the breakdown of organic matter by earthworms. These excreta have been shown to contain reduced levels of contaminants and a higher saturation of nutrients than the organic materials before vermicomposting. Vermicompost contains water-soluble nutrients which may be extracted as vermiwash and is an excellent, nutrient-rich organic fertilizer and soil conditioner.Coyne, Kelly and Erik Knutzen. ''The Urban Homestead: Your Guide to Self-Sufficient Living in the Heart of the City.'' Port Townsend: Process Self Relia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |