|
Bullatacin
Bullatacin is a bis(tetrahydrofuranoid) fatty acid lactone found in some fruits from Annonaceae family. It is a member of the class of compounds known as acetogenin Acetogenins are a class of polyketide natural products found in plants of the family Annonaceae. They are characterized by linear 32- or 34-carbon chains containing oxygenated functional groups including hydroxyls, ketones, epoxides, tetrahydr ...s. References Furanones Tetrahydrofurans Secondary alcohols Polyketides NADH dehydrogenase inhibitors {{organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyketides
Polyketides are a class of natural products derived from a precursor molecule consisting of a chain of alternating ketone (or reduced forms of a ketone) and methylene groups: (-CO-CH2-). First studied in the early 20th century, discovery, biosynthesis, and application of polyketides has evolved. It is a large and diverse group of secondary metabolites caused by its complex biosynthesis which resembles that of fatty acid synthesis. Because of this diversity, polyketides can have various medicinal, agricultural, and industrial applications. Many polyketides are medicinal or exhibit acute toxicity. Biotechnology has enabled discovery of more naturally-occurring polyketides and evolution of new polyketides with novel or improved bioactivity. History Naturally produced polyketides by various plants and organisms have been used by humans since before studies on them began in the 19th and 20th century. In 1893, J. Norman Collie synthesized detectable amounts of orcinol by heating deh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahydrofuran
Tetrahydrofuran (THF), or oxolane, is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4O. The compound is classified as heterocyclic compound, specifically a cyclic ether. It is a colorless, water- miscible organic liquid with low viscosity. It is mainly used as a precursor to polymers. Being polar and having a wide liquid range, THF is a versatile solvent. Production About 200,000 tonnes of tetrahydrofuran are produced annually. The most widely used industrial process involves the acid-catalyzed dehydration of 1,4-butanediol. Ashland/ISP is one of the biggest producers of this chemical route. The method is similar to the production of diethyl ether from ethanol. The butanediol is derived from condensation of acetylene with formaldehyde followed by hydrogenation. DuPont developed a process for producing THF by oxidizing ''n''-butane to crude maleic anhydride, followed by catalytic hydrogenation. A third major industrial route entails hydroformylation of allyl alcohol foll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
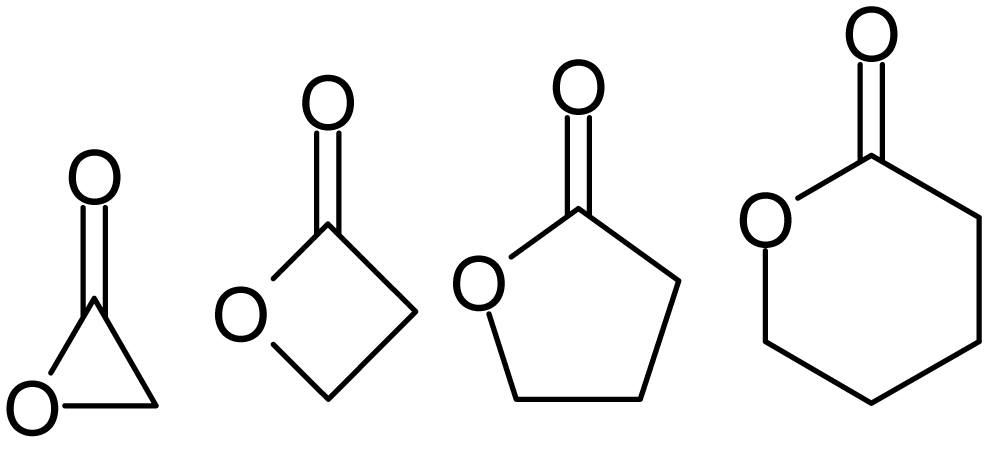
Lactone
Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters, containing a 1-oxacycloalkan-2-one structure (), or analogues having unsaturation or heteroatoms replacing one or more carbon atoms of the ring. Lactones are formed by intramolecular esterification of the corresponding hydroxycarboxylic acids, which takes place spontaneously when the ring that is formed is five- or six-membered. Lactones with three- or four-membered rings (α-lactones and β-lactones) are very reactive, making their isolation difficult. Special methods are normally required for the laboratory synthesis of small-ring lactones as well as those that contain rings larger than six-membered. Nomenclature Lactones are usually named according to the precursor acid molecule (''aceto'' = 2 carbon atoms, ''propio'' = 3, ''butyro'' = 4, ''valero'' = 5, ''capro'' = 6, etc.), with a ''-lactone'' suffix and a Greek letter prefix that specifies the number of carbon atoms in the heterocycle — that is, the distance between the relevant -OH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annonaceae
The Annonaceae are a family of flowering plants consisting of trees, shrubs, or rarely lianas commonly known as the custard apple family or soursop family. With 108 accepted genera and about 2400 known species, it is the largest family in the Magnoliales. Several genera produce edible fruit, most notably ''Annona'', ''Anonidium'', ''Asimina'', '' Rollinia'', and '' Uvaria''. Its type genus is ''Annona''. The family is concentrated in the tropics, with few species found in temperate regions. About 900 species are Neotropical, 450 are Afrotropical, and the remaining are Indomalayan. Description The species are mostly tropical, some are mid-latitude, deciduous or evergreen trees and shrubs, with some lianas, with aromatic bark, leaves, and flowers. ; Stems, stalks and leaves: Bark is fibrous and aromatic. Pith septate (fine tangential bands divided by partitions) to diaphragmed (divided by thin partitions with openings in them). Branching distichous (arranged in two rows/on one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetogenin
Acetogenins are a class of polyketide natural products found in plants of the family Annonaceae. They are characterized by linear 32- or 34-carbon chains containing oxygenated functional groups including hydroxyls, ketones, epoxides, tetrahydrofurans and tetrahydropyrans. They are often terminated with a lactone or butenolide. Over 400 members of this family of compounds have been isolated from 51 different species of plants. Many acetogenins are characterized by neurotoxicity. Examples include: * Annonacin * Annonins * Bullatacin * Uvaricin Structure Structurally, acetogenins are a series of C-35/C-37 compounds usually characterized by a long aliphatic chain bearing a terminal methyl-substituted α,β-unsaturated γ-lactone ring, as well as one to three tetrahydrofuran (THF) rings. These THF rings are located along the hydrocarbon chain, along with a number of oxygenated moieties (hydroxyls, acetoxyls, ketones, epoxides) and/or double bonds. Research Acetoge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Organic Chemistry
''The Journal of Organic Chemistry'', colloquially known as ''JOC'', is a peer-reviewed scientific journal for original contributions of fundamental research in all branches of theory and practice in organic and bioorganic chemistry. It is published by the publishing arm of the American Chemical Society, with 24 issues per year. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal had a 2017 impact factor of 4.805 and it is the journal that received the most cites (100,091 in 2017) in the field of organic chemistry. According to Web of Knowledge (and as December 2012), eleven papers from the journal have received more than 1,000 citations, with the most cited paper having received 7,967 citations. The current editor-in-chief is Scott J. Miller from Yale University. Indexing ''J. Org. Chem.'' is currently indexed in: See also *Organic Letters *Organometallics ''Organometallics'' is a biweekly journal published by the American Chemical Society. Its area of focus is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Alcohols
In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term ''alcohol'' originally referred to the primary alcohol ethanol (ethyl alcohol), which is used as a drug and is the main alcohol present in alcoholic drinks. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest examples, includes all compounds which conform to the general formula . Simple monoalcohols that are the subject of this article include primary (), secondary () and tertiary () alcohols. The suffix ''-ol'' appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority. When a higher priority group is present in the compound, the prefix ''hydroxy-'' is used in its IUPAC name. The suffix ''-ol'' in non-IUPAC names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance is an alcohol. However, some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |