|
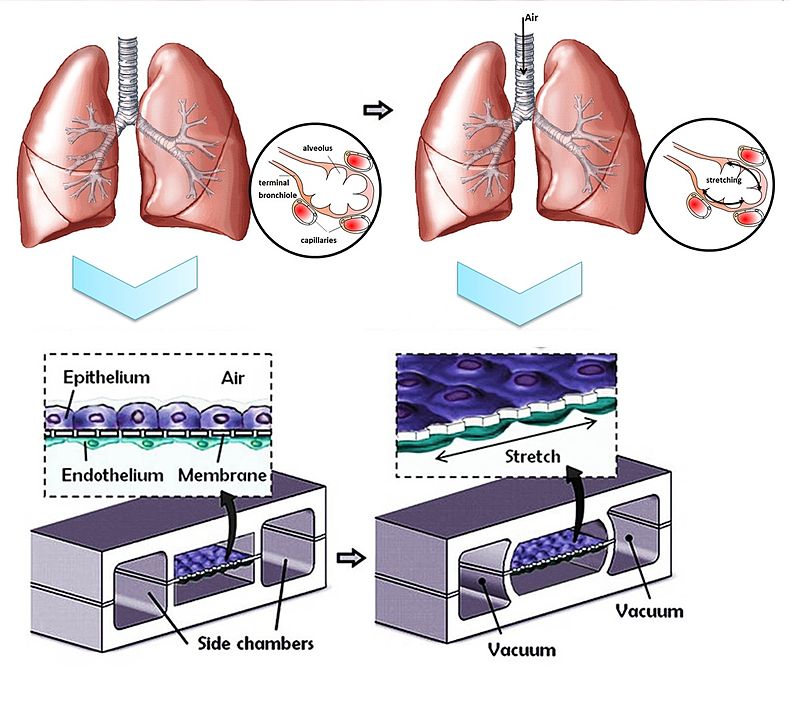
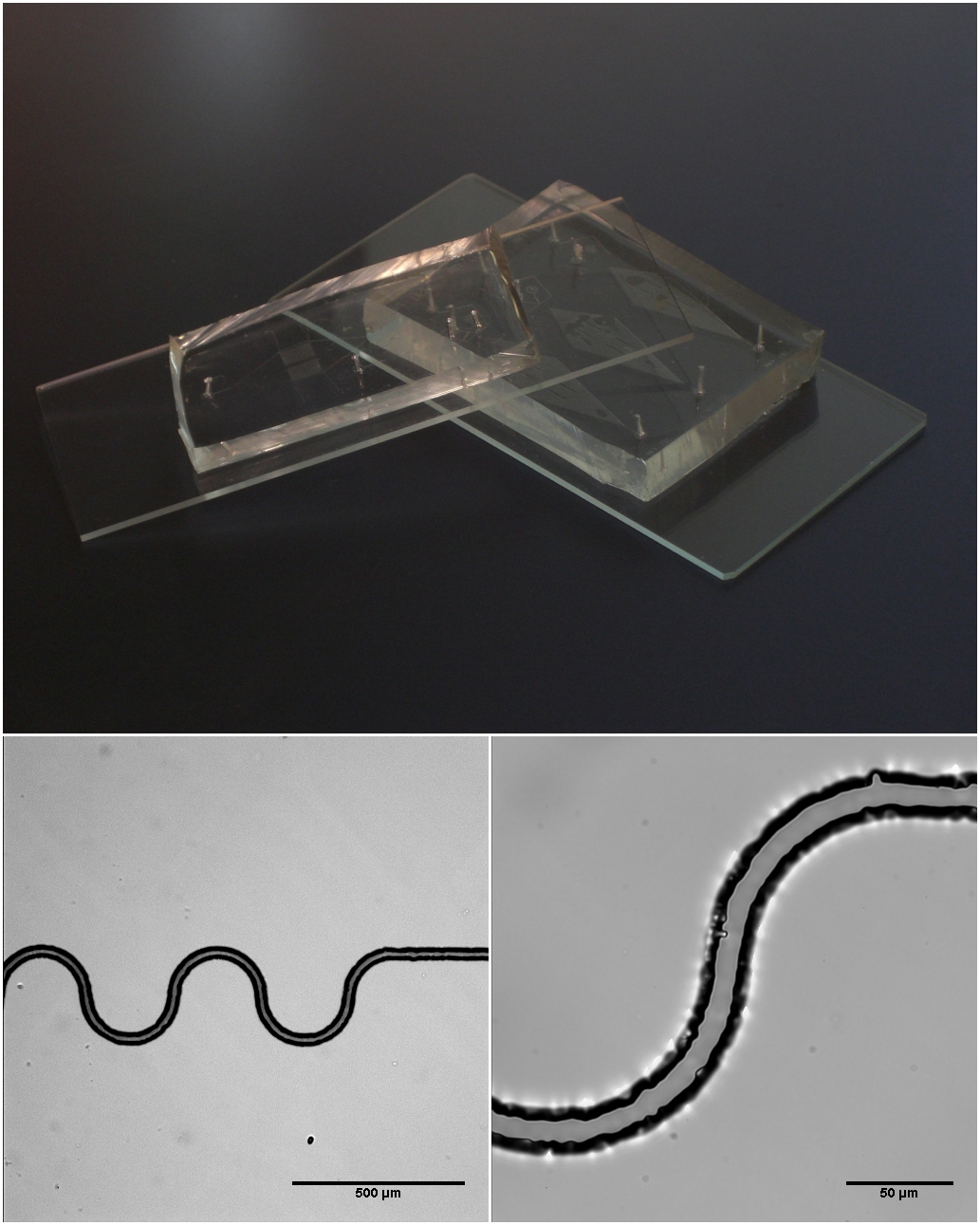
Brain-on-a-chip
An organ-on-a-chip (OOC) is a multi-channel 3D microfluidic cell culture, integrated circuit (chip) that simulates the activities, mechanics and physiological response of an entire organ or an organ system. It constitutes the subject matter of significant biomedical engineering research, more precisely in bio-MEMS. The convergence of labs-on-chips (LOCs) and cell biology has permitted the study of human physiology in an organ-specific context. By acting as a more sophisticated ''in vitro'' approximation of complex tissues than standard cell culture, they provide the potential as an alternative to animal models for drug development and toxin testing. Although multiple publications claim to have translated organ functions onto this interface, the development of these microfluidic applications is still in its infancy. Organs-on-chips vary in design and approach between different researchers. Organs that have been simulated by microfluidic devices include brain, lung, heart, kidney, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microfluidic
Microfluidics refers to a system that manipulates a small amount of fluids (10−9 to 10−18 liters) using small channels with sizes of ten to hundreds of micrometres. It is a multidisciplinary field that involves molecular analysis, molecular biology, and microelectronics. It has practical applications in the design of systems that process low volumes of fluids to achieve multiplexing, automation, and high-throughput screening. Microfluidics emerged in the beginning of the 1980s and is used in the development of inkjet printheads, DNA chips, lab-on-a-chip technology, micro-propulsion, and micro-thermal technologies. Typically, micro means one of the following features: * Small volumes (μL, nL, pL, fL) * Small size * Low energy consumption * Microdomain effects Typically microfluidic systems transport, mix, separate, or otherwise process fluids. Various applications rely on passive fluid control using capillary forces, in the form of capillary flow modifying elements, akin to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of various proteins and various other Biochemistry, biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the quadrants and regions of abdomen, right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm and mostly shielded by the lower right rib cage. Its other metabolic roles include carbohydrate metabolism, the production of a number of hormones, conversion and storage of nutrients such as glucose and glycogen, and the decomposition of red blood cells. Anatomical and medical terminology often use the prefix List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes#H, ''hepat-'' from ἡπατο-, from the Greek language, Greek word for liver, such as hepatology, and hepatitis The liver is also an accessory digestive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
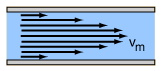
Laminar Flow
Laminar flow () is the property of fluid particles in fluid dynamics to follow smooth paths in layers, with each layer moving smoothly past the adjacent layers with little or no mixing. At low velocities, the fluid tends to flow without lateral mixing, and adjacent layers slide past one another smoothly. There are no cross-currents perpendicular to the direction of flow, nor eddies or swirls of fluids. In laminar flow, the motion of the particles of the fluid is very orderly with particles close to a solid surface moving in straight lines parallel to that surface. Laminar flow is a flow regime characterized by high momentum diffusion and low momentum convection. When a fluid is flowing through a closed channel such as a pipe or between two flat plates, either of two types of flow may occur depending on the velocity and viscosity of the fluid: laminar flow or turbulent flow. Laminar flow occurs at lower velocities, below a threshold at which the flow becomes turbulent. The thresh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lab-on-a-chip
A lab-on-a-chip (LOC) is a device that integrates one or several laboratory functions on a single integrated circuit (commonly called a "chip") of only millimeters to a few square centimeters to achieve automation and high-throughput screening. LOCs can handle extremely small fluid volumes down to less than pico-liters. Lab-on-a-chip devices are a subset of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) devices and sometimes called "micro total analysis systems" (μTAS). LOCs may use microfluidics, the physics, manipulation and study of minute amounts of fluids. However, strictly regarded "lab-on-a-chip" indicates generally the scaling of single or multiple lab processes down to chip-format, whereas "μTAS" is dedicated to the integration of the total sequence of lab processes to perform chemical analysis. History After the invention of microtechnology (≈1954) for realizing integrated semiconductor structures for microelectronic chips, these lithography-based technologies were soon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |