|
Boiling Point Elevation
Boiling-point elevation is the phenomenon whereby the boiling point of a liquid (a solvent) will be higher when another compound is added, meaning that a solution has a higher boiling point than a pure solvent. This happens whenever a non-volatile solute, such as a salt, is added to a pure solvent, such as water. The boiling point can be measured accurately using an ebullioscope. Explanation The ''boiling point elevation'' is a colligative property, which means that boiling point elevation is dependent on the number of dissolved particles but not their identity. It is an effect of the dilution of the solvent in the presence of a solute. It is a phenomenon that happens for all solutes in all solutions, even in ideal solutions, and does not depend on any specific solute–solvent interactions. The boiling point elevation happens both when the solute is an electrolyte, such as various salts, and a nonelectrolyte. In thermodynamic terms, the origin of the boiling point elevation is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boiling Point
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the pressure surrounding the liquid and the liquid changes into a vapor. The boiling point of a liquid varies depending upon the surrounding environmental pressure. A liquid in a partial vacuum, i.e., under a lower pressure, has a lower boiling point than when that liquid is at atmospheric pressure. Because of this, water boils at 100°C (or with scientific precision: ) under standard pressure at sea level, but at at altitude. For a given pressure, different liquids will boiling, boil at different temperatures. The normal boiling point (also called the atmospheric boiling point or the atmospheric pressure boiling point) of a liquid is the special case in which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the defined atmospheric pressure at sea level, one Atmosphere (unit), atmosphere. At that temperature, the vapor pressure of the liquid becomes sufficient to overcome atmospheric pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clausius–Clapeyron Relation
The Clausius–Clapeyron relation, in chemical thermodynamics, specifies the temperature dependence of pressure, most importantly vapor pressure, at a discontinuous phase transition between two phases of matter of a single constituent. It is named after Rudolf Clausius and Benoît Paul Émile Clapeyron. However, this relation was in fact originally derived by Sadi Carnot in his '' Reflections on the Motive Power of Fire'', which was published in 1824 but largely ignored until it was rediscovered by Clausius, Clapeyron, and Lord Kelvin decades later. Kelvin said of Carnot's argument that "nothing in the whole range of Natural Philosophy is more remarkable than the establishment of general laws by such a process of reasoning." Kelvin and his brother James Thomson confirmed the relation experimentally in 1849–50, and it was historically important as a very early successful application of theoretical thermodynamics. Its relevance to meteorology and climatology is the increase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
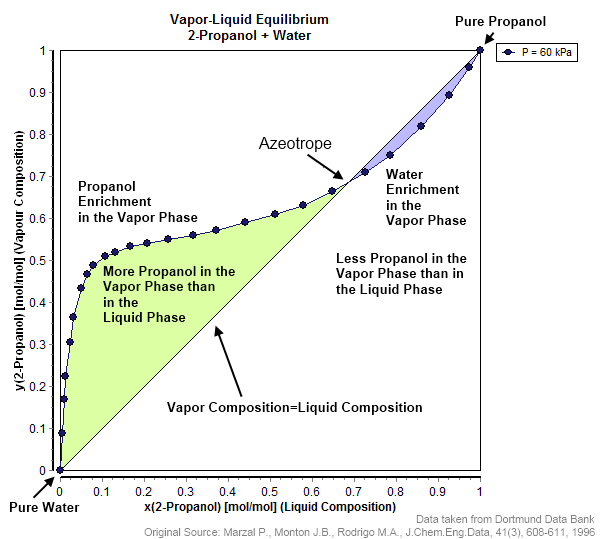
Azeotrope
An azeotrope () or a constant heating point mixture is a mixture of two or more liquids whose proportions cannot be changed by simple distillation.Moore, Walter J. ''Physical Chemistry'', 3rd e Prentice-Hall 1962, pp. 140–142 This happens because when an azeotrope is boiled, the vapour has the same proportions of constituents as the unboiled mixture. Knowing an azeotrope's behavior is important for distillation. Each azeotrope has a characteristic boiling point. The boiling point of an azeotrope is either less than the boiling point temperatures of any of its constituents (a positive azeotrope), or greater than the boiling point of any of its constituents (a negative azeotrope). For both positive and negative azeotropes, it is not possible to separate the components by fractional distillation and azeotropic distillation is usually used instead. For technical applications, the pressure-temperature-composition behavior of a mixture is the most important, but other important ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideal Solution
An ideal solution or ideal mixture is a solution that exhibits thermodynamic properties analogous to those of a mixture of ideal gases. The enthalpy of mixing is zero as is the volume change on mixing. The vapor pressures of all components obey Raoult's law across the entire range of concentrations, and the activity coefficient (which measures deviation from ideality) is equal to one for each component. The concept of an ideal solution is fundamental to both thermodynamics and chemical thermodynamics and their applications, such as the explanation of colligative properties. Physical origin Ideality of solutions is analogous to ideality for gases, with the important difference that intermolecular interactions in liquids are strong and cannot simply be neglected as they can for ideal gases. Instead we assume that the mean strength of the interactions are the same between all the molecules of the solution. More formally, for a mix of molecules of A and B, then the interacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Chloride
Calcium chloride is an inorganic compound, a Salt (chemistry), salt with the chemical formula . It is a white crystalline solid at room temperature, and it is highly soluble in water. It can be created by neutralising hydrochloric acid with calcium hydroxide. Calcium chloride is commonly encountered as a Water of crystallization, hydrated solid with generic formula , where ''n'' = 0, 1, 2, 4, and 6. These compounds are mainly used for de-icing and dust control. Because the anhydrous salt is Hygroscopic, hygroscopic and deliquescent, it is used as a desiccant.Robert Kemp, Suzanne E. Keegan "Calcium Chloride" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2000, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. History Calcium chloride was apparently discovered in the 15th century but wasn't studied properly until the 18th century. It was historically called "fixed Salammoniac, sal ammoniac" () because it was synthesized during the distillation of ammonium chloride with lime and was nonvolatile (while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Chloride
Sodium chloride , commonly known as Salt#Edible salt, edible salt, is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. It is transparent or translucent, brittle, hygroscopic, and occurs as the mineral halite. In its edible form, it is commonly used as a condiment and curing (food preservation), food preservative. Large quantities of sodium chloride are used in many industrial processes, and it is a major source of sodium and chlorine compounds used as feedstocks for further Chemical synthesis, chemical syntheses. Another major application of sodium chloride is deicing of roadways in sub-freezing weather. Uses In addition to the many familiar domestic uses of salt, more dominant applications of the approximately 250 million tonnes per year production (2008 data) include chemicals and de-icing.Westphal, Gisbert ''et al.'' (2002) "Sodium Chloride" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim . Chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sucrose
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula . For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined from either sugarcane or sugar beet. Sugar mills – typically located in tropical regions near where sugarcane is grown – crush the cane and produce raw sugar which is shipped to other factories for refining into pure sucrose. Sugar beet factories are located in temperate climates where the beet is grown, and process the beets directly into refined sugar. The Sugar refinery, sugar-refining process involves washing the raw sugar crystals before dissolving them into a sugar syrup which is filtered and then passed over carbon to remove any residual colour. The sugar syrup is then concentrated by boiling under a vacuum and crystallized as the final purification process to produce crystals of pure sucrose that are clear, odorless, and sweet. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Van 't Hoff Factor
The van 't Hoff factor (named after Dutch chemist Jacobus Henricus van 't Hoff) is a measure of the effect of a solute on colligative properties such as osmotic pressure, relative lowering in vapor pressure, boiling-point elevation and freezing-point depression. The van 't Hoff factor is the ratio between the ''actual concentration'' of particles produced when the substance is dissolved and the ''formal concentration'' that would be expected from its chemical formula. For most non-electrolytes dissolved in water, the van 't Hoff factor is essentially 1. For most ionic compounds dissolved in water, the van 't Hoff factor is equal to the number of discrete ions in a formula unit of the substance. This is true for ideal solutions only, as occasionally ion pairing occurs in solution. At a given instant a small percentage of the ions are paired and count as a single particle. Ion pairing occurs to some extent in all electrolyte solutions. This causes the measured van&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissociation (chemistry)
Dissociation in chemistry is a general process in which molecules (or ionic compounds such as salt (chemistry), salts, or coordination complex, complexes) separate or split into other things such as atoms, ions, or radical (chemistry), radicals, usually in a reversible manner. For instance, when an acid dissolves in water, a covalent bond between an electronegativity, electronegative atom and a hydrogen atom is broken by heterolytic fission, which gives a proton (H+) and a negative ion. Dissociation is the opposite of association or recombination. Dissociation constant For reversible dissociations in a chemical equilibrium :AB A + B the dissociation constant ''K''d is the ratio of dissociated to undissociated compound :K_d = \mathrm where the brackets denote the equilibrium concentrations of the species. Dissociation degree The dissociation degree \alpha is the fraction of original solute molecules that have dissociated. It is usually indicated by the Greek symbol α. More acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colligative Properties
In chemistry, colligative properties are those properties of solutions that depend on the ratio of the number of solute particles to the number of solvent particles in a solution, and not on the nature of the chemical species present. The number ratio can be related to the various units for concentration of a solution such as molarity, molality, normality (chemistry), etc. The assumption that solution properties are independent of nature of solute particles is exact only for ideal solutions, which are solutions that exhibit thermodynamic properties analogous to those of an ideal gas, and is approximate for dilute real solutions. In other words, colligative properties are a set of solution properties that can be reasonably approximated by the assumption that the solution is ideal. Only properties which result from the dissolution of a nonvolatile solute in a volatile liquid solvent are considered.KL Kapoor ''Applications of Thermodynamics'' Volume 3 They are essentially s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Of Vaporization
In thermodynamics, the enthalpy of vaporization (symbol ), also known as the (latent) heat of vaporization or heat of evaporation, is the amount of energy (enthalpy) that must be added to a liquid substance to Phase transition, transform a quantity of that substance into a gas. The enthalpy of vaporization is a function of the pressure and temperature at which the transformation (vaporization or evaporation) takes place. The enthalpy of vaporization is often quoted for the normal boiling point, normal boiling temperature of the substance. Although tabulated values are usually corrected to 298 Kelvin, K, that correction is often smaller than the Significant figures, uncertainty in the measured value. The heat of vaporization is temperature-dependent, though a constant heat of vaporization can be assumed for small temperature ranges and for reduced temperature . The heat of vaporization diminishes with increasing temperature and it vanishes completely at a certain point cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |