|
Body Height (typography)
In typography, the body height or point size refers to the height of the space in which a glyph is defined. Originally, in metal typesetting, the body height or the font (or point) size was defined by the height of the lead cuboid ( metal sort) on which the actual font face is moulded. The body height of a metal sort defined the point size, and was usually slightly larger than the distance between the ascender and descender to allow additional space between the lines of text. More space might be achieved by inserting thin long pieces of lead between the lines of text (that is ''leading''). In digital fonts, the body is now a virtual, imaginary area, whose height still equals the point size as it did in metal type. The distance between one baseline and the next is the sum of the body height and the leading, often expressed as "characters per inch vertically" (as in ) or lines of text per inch (not to be confused with lines per inch, a measure of printed photograph resoluti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typography Line Terms
Typography is the art and technique of arranging type to make written language legible, readable and appealing when displayed. The arrangement of type involves selecting typefaces, point sizes, line lengths, line spacing, letter spacing, and spaces between pairs of letters. The term ''typography'' is also applied to the style, arrangement, and appearance of the letters, numbers, and symbols created by the process. Type design is a closely related craft, sometimes considered part of typography; most typographers do not design typefaces, and some type designers do not consider themselves typographers. Typography also may be used as an ornamental and decorative device, unrelated to the communication of information. Typography is also the work of graphic designers, art directors, manga artists, comic book artists, and, now, anyone who arranges words, letters, numbers, and symbols for publication, display, or distribution, from clerical workers and newsletter writers t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leading
In typography, leading ( ) is the space between adjacent lines of type; the exact definition varies. In hand typesetting, leading is the thin strips of lead (or aluminium) that were inserted between lines of type in the composing stick to increase the vertical distance between them. The thickness of the strip is called leading and is equal to the difference between the size of the type and the distance from one baseline (typography), baseline to the next. For instance, given a type size of 10 Point (typography), points and a distance between baselines of 12 points, the leading would be 2 points. The term is still used in modern page layout, page-layout software such as QuarkXPress, the Affinity Suite, and Adobe InDesign. Consumer-oriented word-processing software often talks of line spacing or, more accurately, interline spacing. Origins The word comes from lead strips that were put between set lines of lead type, hence the pronunciation "ledding" and not "lee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-height
upright 2.0, alt=A diagram showing the line terms used in typography In typography, the x-height, or corpus size, is the distance between the baseline and the mean line of lowercase letters in a typeface. Typically, this is the height of the letter ''x'' in the font (the source of the term), as well as the letters ''v'', ''w'', and ''z''. (Curved letters such as ''a'', ''c'', ''e'', ''m'', ''n'', ''o'', ''r'', ''s'', and ''u'' tend to exceed the x-height slightly, due to overshoot; ''i'' has a dot that tends to go above x-height.) One of the most important dimensions of a font, x-height defines how high lowercase letters without ascenders are compared to the cap height of uppercase letters. Display typefaces intended to be used at large sizes, such as on signs and posters, vary in x-height. Many have high x-heights to be read clearly from a distance. This, though, is not universal: some display typefaces such as Cochin and Koch-Antiqua intended for publicity uses have low x ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Em (typography)
An em (from ''Quad (typography), em quadrat'') is a Typographic unit, unit in the field of typography, equal to the currently specified Point (typography), point size. It corresponds to the Body height (typography), body height of the typeface. For example, one em in a 16-point typeface is 16 points. Therefore, this unit is the same for all typefaces at a given point size. The Whitespace character#Unicode, em space is one ''em'' wide. Typographic measurements using this unit are frequently expressed in decimal notation (e.g., 0.7 em) or as fractions of 100 or 1000 (e.g., em or em). The number of pixels per em varies depending on system. History In Sort (typesetting), metal type, the point size (and hence the ''em'', from ''em quad, em quadrat'') was equal to the line height of the metal body from which the letter rises. In metal type, the physical size of a letter could not normally exceed the em. A digital font's design space in digital type is called the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
En (typography)
An en (from English '' en quadrat'') is a typographic unit, half of the width of an em. By definition, it is equivalent to half of the body height of the typeface (e.g., in 16- point type it is 8 points). The en is sometimes referred to as the "nut", to avoid confusion with the similar-sounding "em". The en dash () and en space () are each one ''en'' wide. In English, the en dash is commonly used for inclusive ranges (e.g., "pages 12–17" or "August 7, 1988 – November 26, 2005"), to connect prefixes to open compounds (e.g., "pre–World War II"). The en-dash is also increasingly used to replace the long dash ("—", also called an em dash or em rule). When using it to replace a long dash, spaces are needed either side of it – like so. This is standard practice in the German language, where the hyphen is the only dash without spaces on either side ( line breaks are not spaces ''per se''). History Some sources claim the term "en" was derived from the letter "n", which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body (typography)
In typography, the point is the smallest unit of measure. It is used for measuring font size, leading, and other items on a printed page. The size of the point has varied throughout printing's history. Since the 18th century, the size of a point has been between 0.18 and 0.4 millimeters. Following the advent of desktop publishing in the 1980s and 1990s, digital printing has largely supplanted the letterpress printing and has established the desktop publishing (DTP) point as the ''de facto'' standard. The DTP point is defined as of an inch (or exactly 0.352 mm) and, as with earlier American point sizes, is considered to be of a pica. In metal type, the point size of a font describes the height of the metal body on which that font's characters were cast. In digital type, letters of a computer font are designed around an imaginary space called an '' em square''. When a point size of a font is specified, the font is scaled so that its em square has a side length of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lines Per Inch
Lines per inch (LPI) is a measurement of printing resolution. A line consists of halftones that is built up by physical ink dots made by the printer device to create different tones. Specifically LPI is a measure of how close together the lines in a halftone grid are. The quality of printer device or screen determines how high the LPI will be. High LPI indicates greater detail and sharpness. Printed magazines and newspapers often use a halftone system. Typical newsprint paper is not very dense, and has relatively high dot gain or color bleeding, so newsprint is usually around 85 LPI. Higher-quality paper, such as that used in commercial magazines, has less dot gain, and can range up to 300 LPI with quality glossy (coated) paper. In order to effectively utilize the entire range of available LPI in a halftone system, an image selected for printing generally must have 1.5 to 2 times as many samples per inch (SPI). For instance, if the target output device is capable of printin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baseline (typography)
In European and West Asian typography and penmanship, the baseline is the line upon which most letters ''sit'' and below which descenders extend. In the example to the right, the letter 'p' has a descender; the other letters sit on the (red) baseline. Most, though not all, typefaces are similar in the following ways as regards the baseline: *capital letters sit on the baseline. The most common exceptions are the J and Q. *All lining figures sit on the baseline: *Some text figures have descenders: *The following lowercase letters have descenders: g j p q y. *Glyphs with rounded lower and upper extents (0 3 6 8 c C G J o O Q) dip very slightly below the baseline (" overshoot") to create the optical illusion that they sit on the baseline, and rise above the x-height or capital height to create the illusion that they have the same height as flat glyphs (such as those for H x X 1 5 7). Peter Karow's ''Digital Typefaces'' suggests that typical overshoot is about 1.5%. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Descender
In typography and handwriting, a descender is the portion of a grapheme that extends below the Baseline (typography), baseline of a typeface, font. For example, in the letter ''y'', the descender is the "tail", or that portion of the diagonal line which lies below the ''v'' created by the two lines converging. In the letter ''p'', it is the stem reaching down past the ''ɒ''. In most fonts, descenders are reserved for lowercase characters such as ''g'', ''j'', ''q'', ''p'', ''y'', and sometimes ''f''. Some fonts, however, also use descenders for some Numerical digit, numerals (typically ''3'', ''4'', ''5'', ''7'', and ''9''). Such numerals are called old-style numerals. (Some Italic type, italic fonts, such as Computer Modern, Computer Modern italic, put a descender on the numeral ''4'' but not on any other numerals. Such fonts are not considered old-style.) Some fonts also use descenders for the tails on a few uppercase letters such as ''J'' and ''Q''. The parts of characters t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typography
Typography is the art and technique of Typesetting, arranging type to make written language legibility, legible, readability, readable and beauty, appealing when displayed. The arrangement of type involves selecting typefaces, Point (typography), point sizes, line lengths, line spacing, letter spacing, and Kerning, spaces between pairs of letters. The term ''typography'' is also applied to the style, arrangement, and appearance of the letters, numbers, and symbols created by the process. Type design is a closely related craft, sometimes considered part of typography; most typographers do not design typefaces, and some type designers do not consider themselves typographers. Typography also may be used as an ornamental and decorative device, unrelated to the communication of information. Typography is also the work of graphic designers, art directors, manga artists, comic book artists, and, now, anyone who arranges words, letters, numbers, and symbols for publication, display, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
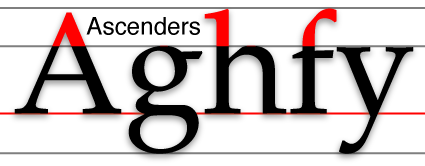
Ascender (typography)
In typography and handwriting, an ascender is the portion of a Lower case, minuscule grapheme, letter in a Latin-derived alphabet that extends above the mean line of a typeface, font. That is, the part of a lower-case letter that is taller than the font's x-height. Ascenders, together with descenders, increase the recognizability of words. For this reason, many situations that require high legibility such as road signs avoid using solely capital letters (i.e. all-caps). Studies made at the start of the construction of the British motorway network concluded that words with mixed-case letters were much easier to read than "all-caps" and a special font was designed for motorway signs. These then became universal across the UK. See Road signs in the United Kingdom. In many fonts intended for body text, such as Bembo and Garamond, ascenders rise above the cap height of the capital letters. References {{Typography terms [Baidu] |
Point (typography)
In typography, the point is the smallest unit of measure. It is used for measuring font size, leading, and other items on a printed page. The size of the point has varied throughout printing's history. Since the 18th century, the size of a point has been between 0.18 and 0.4 millimeters. Following the advent of desktop publishing in the 1980s and 1990s, digital printing has largely supplanted the letterpress printing and has established the desktop publishing (DTP) point as the ''de facto'' standard. The DTP point is defined as of an inch (or exactly 0.352 mm) and, as with earlier American point sizes, is considered to be of a pica. In metal type, the point size of a font describes the height of the metal body on which that font's characters were cast. In digital type, letters of a computer font are designed around an imaginary space called an '' em square''. When a point size of a font is specified, the font is scaled so that its em square has a side length ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |