|
Blue Field Entoptic Phenomenon
The blue field entoptic phenomenon is an entoptic phenomenon characterized by the appearance of tiny bright dots (nicknamed blue-sky sprites) moving quickly along undulating pathways in the visual field, especially when looking into bright blue light such as the sky. The dots are short-lived, visible for about one second or less, and travel short distances along seemingly random, undulating paths. Some of them seem to follow the same path as other dots before them. The dots may appear elongated along the path, like tiny worms. The dots' rate of travel appears to vary in synchrony with the heartbeat: they briefly accelerate at each beat. The dots appear in the central field of view, within 15 degrees from the fixation point. The left and right eye see different, seemingly random, dot patterns; a person viewing through both eyes sees a combination of both left and right visual field disturbances. While seeing the phenomenon, lightly pressing inward on the sides of the eyeballs at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entoptic Phenomenon
Entoptic phenomena (), occasionally and incorrectly referred to as entopic phenomena, are visual effects whose source is within the human eye itself. In Helmholtz's words: "Under suitable conditions, light falling on the eye may render visible, certain objects within the eye itself. These perceptions are called ''entoptical''." Overview Entoptic images have a physical basis in the image cast upon the retina. Hence, they are different from optical illusions, which are caused by the visual system and characterized by a visual percept that (loosely said) appears to differ from reality. Because entoptic images are caused by phenomena within the observer's own eye, they share one feature with optical illusions and hallucinations: the observer cannot share a direct and specific view of the phenomenon with others. Helmholtz commented on entoptic phenomena which could be seen easily by some observers, but could not be seen at all by others. This variance is not surprising because the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Blood Cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), referred to as erythrocytes (, with -''cyte'' translated as 'cell' in modern usage) in academia and medical publishing, also known as red cells, erythroid cells, and rarely haematids, are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate's principal means of delivering oxygen () to the body tissue (biology), tissues—via blood flow through the circulatory system. Erythrocytes take up oxygen in the lungs, or in fish the gills, and release it into tissues while squeezing through the body's capillary, capillaries. The cytoplasm of a red blood cell is rich in hemoglobin (Hb), an iron-containing biomolecule that can bind oxygen and is responsible for the red color of the cells and the blood. Each human red blood cell contains approximately 270 million hemoglobin molecules. The cell membrane is composed of proteins and lipids, and this structure provides properties essential for physiological Cell (biology), cell function such as erythrocyte deformabil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmology
Ophthalmology (, ) is the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and surgery of eye diseases and disorders. An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a medical degree, a doctor specialising in ophthalmology must pursue additional postgraduate residency training specific to that field. In the United States, following graduation from medical school, one must complete a four-year residency in ophthalmology to become an ophthalmologist. Following residency, additional specialty training (or fellowship) may be sought in a particular aspect of eye pathology. Ophthalmologists prescribe medications to treat ailments, such as eye diseases, implement laser therapy, and perform surgery when needed. Ophthalmologists provide both primary and specialty eye care—medical and surgical. Most ophthalmologists participate in academic research on eye diseases at some point in their training and many inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Phenomena
Optical phenomena are any observable events that result from the interaction of light and matter. All optics, optical phenomena coincide with Quantum mechanics, quantum phenomena. Common optical phenomena are often due to the interaction of light from the Sun or Moon with the atmosphere, clouds, water, dust, and other particulates. One common example is the rainbow, when light from the Sun is reflected and refracted by water droplets. Some phenomena, such as the green ray, are so rare they are sometimes thought to be mythical. Others, such as Fata Morgana (mirage), Fata Morganas, are commonplace in favored locations. Other phenomena are simply interesting aspects of optics, or optical effects. For instance, the colors generated by a dispersive prism, prism are often shown in classrooms. Scope ''Optical phenomena encompass a broad range of events, including those caused by atmospheric optical properties, other natural occurrences, man-made effects, and interactions involving hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floater
Floaters or eye floaters are sometimes visible deposits (e.g., the shadows of tiny structures of protein or other cell debris projected onto the retina) within the eye's vitreous humour ("the vitreous"), which is normally transparent, or between the vitreous and retina.Cline D; Hofstetter HW; Griffin JR. ''Dictionary of Visual Science''. 4th ed. Butterworth-Heinemann, Boston 1997. They can become particularly noticeable when looking at a blank surface or an open monochromatic space, such as a blue sky. Each floater can be measured by its size, shape, consistency, refractive index, and motility. They are also called ''muscae volitantes'' (Latin for 'flying flies'), or ''mouches volantes'' (from the same phrase in French). The vitreous usually starts out transparent, but imperfections may gradually develop as one ages. The common type of floater, present in most people's eyes, is due to these degenerative changes of the vitreous. The perception of floaters, which may be annoying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entoptic Phenomenon
Entoptic phenomena (), occasionally and incorrectly referred to as entopic phenomena, are visual effects whose source is within the human eye itself. In Helmholtz's words: "Under suitable conditions, light falling on the eye may render visible, certain objects within the eye itself. These perceptions are called ''entoptical''." Overview Entoptic images have a physical basis in the image cast upon the retina. Hence, they are different from optical illusions, which are caused by the visual system and characterized by a visual percept that (loosely said) appears to differ from reality. Because entoptic images are caused by phenomena within the observer's own eye, they share one feature with optical illusions and hallucinations: the observer cannot share a direct and specific view of the phenomenon with others. Helmholtz commented on entoptic phenomena which could be seen easily by some observers, but could not be seen at all by others. This variance is not surprising because the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Snow
Visual snow syndrome (VSS) is an uncommon neurological condition in which the primary symptom is visual snow, a persistent flickering white, black, transparent, or colored dots across the whole visual field. It is distinct from the ''symptom'' of visual snow itself, which can also be caused by several other causes; these cases are referred to as "VSS mimics." Other names for the syndrome include "scotopic sensitivity syndrome", "Meares-Irlen syndrome", and "asfedia." Other common symptoms are palinopsia, enhanced entoptic phenomena, photophobia, and tension headaches. The condition is typically always present and has no known cure, as viable treatments are still under research. Astigmatism, although not presumed connected to these visual disturbances, is a common comorbidity. Migraines and tinnitus are common comorbidities that are both associated with a more severe presentation of the syndrome. The cause of the syndrome is unclear. The underlying mechanism is believed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitreous Humor
The vitreous body (''vitreous'' meaning "glass-like"; , ) is the clear gel that fills the space between the lens and the retina of the eyeball (the vitreous chamber) in humans and other vertebrates. It is often referred to as the vitreous humor (also spelled humour), from Latin meaning liquid, or simply "the vitreous". Vitreous fluid or "liquid vitreous" is the liquid component of the vitreous gel, found after a vitreous detachment. It is not to be confused with the aqueous humor, the other fluid in the eye that is found between the cornea and lens. Structure The vitreous humor is a transparent, colorless, gelatinous mass that fills the space in the eye between the lens and the retina. It is surrounded by a layer of collagen called the vitreous membrane (or hyaloid membrane or vitreous cortex) separating it from the rest of the eye. It makes up four-fifths of the volume of the eyeball. The vitreous humour is fluid-like near the centre, and gel-like near the edges. The vitreou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floater
Floaters or eye floaters are sometimes visible deposits (e.g., the shadows of tiny structures of protein or other cell debris projected onto the retina) within the eye's vitreous humour ("the vitreous"), which is normally transparent, or between the vitreous and retina.Cline D; Hofstetter HW; Griffin JR. ''Dictionary of Visual Science''. 4th ed. Butterworth-Heinemann, Boston 1997. They can become particularly noticeable when looking at a blank surface or an open monochromatic space, such as a blue sky. Each floater can be measured by its size, shape, consistency, refractive index, and motility. They are also called ''muscae volitantes'' (Latin for 'flying flies'), or ''mouches volantes'' (from the same phrase in French). The vitreous usually starts out transparent, but imperfections may gradually develop as one ages. The common type of floater, present in most people's eyes, is due to these degenerative changes of the vitreous. The perception of floaters, which may be annoying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fovea Centralis
The ''fovea centralis'' is a small, central pit composed of closely packed Cone cell, cones in the eye. It is located in the center of the ''macula lutea'' of the retina. The ''fovea'' is responsible for sharp central visual perception, vision (also called foveal vision), which is necessary in humans for activities for which visual detail is of primary importance, such as reading (activity), reading and driving. The fovea is surrounded by the ''parafovea'' belt and the ''perifovea'' outer region. The ''parafovea'' is the intermediate belt, where the Retinal ganglion cell, ganglion cell layer is composed of more than five layers of cells, as well as the highest density of cones; the ''perifovea'' is the outermost region where the ganglion cell layer contains two to four layers of cells, and is where visual acuity is below the optimum. The ''perifovea'' contains an even more diminished density of cones, having 12 per 100 micrometres versus 50 per 100 micrometres in the most centra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
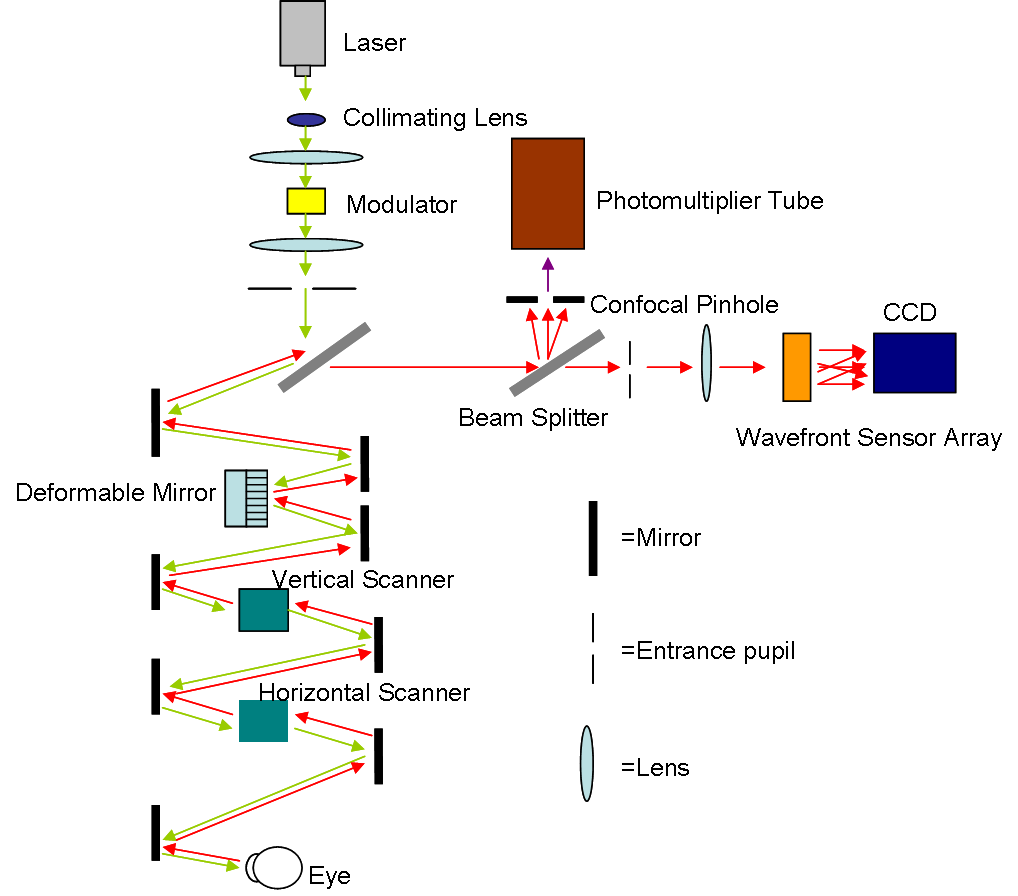
Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscopy
Scanning laser ophthalmoscopy (SLO) is a method of examination of the eye. It uses the technique of confocal laser scanning microscopy for diagnostic imaging of the retina or cornea of the human eye. As a method used to image the retina with a high degree of spatial sensitivity, it is helpful in the diagnosis of glaucoma, macular degeneration, and other retinal disorders. It has further been combined with adaptive optics technology to provide sharper images of the retina."Roorda Lab" — (last accessed: 9 December 2006) Published on October 25, 2006—(last accessed: 9 December 2006) Scanning laser ophthalmoscopy SLO utilizes horizontal and vertical scanning mirrors to scan a specific region of ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptive Optics
Adaptive optics (AO) is a technique of precisely deforming a mirror in order to compensate for light distortion. It is used in Astronomy, astronomical telescopes and laser communication systems to remove the effects of Astronomical seeing, atmospheric distortion, in microscopy, optical fabrication and in retinal imaging systems to reduce optical aberrations. Adaptive optics works by measuring the distortions in a wavefront and compensating for them with a device that corrects those errors such as a deformable mirror or a liquid crystal array. Adaptive optics should not be confused with active optics, which work on a longer timescale to correct the primary mirror geometry. Other methods can achieve resolving power exceeding the limit imposed by atmospheric distortion, such as speckle imaging, aperture synthesis, and lucky imaging, or by moving outside the atmosphere with space-based telescope, space telescopes, such as the Hubble Space Telescope. History Adaptive optics was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |