|
Biorock
Biorock (also seacrete) is a cement-like engineering material formed when a small electric current is passed between underwater metal electrodes placed in seawater causing dissolved minerals to accrete onto the cathode to form a thick layer of limestone. This 'accretion process' can be used to create building materials or to create artificial 'electrified reefs' for the benefit of corals and other sea-life. Discovered by Wolf Hilbertz in 1976, biorock was protected by patents and a trademark which have now expired. History During the 1970s Professor Wolf Hilbertz, an architect by training, was studying seashells and reefs at the School of Architecture at the University of Texas. He was thinking about how humans could emulate the way coral grow. After preliminary work in 1975, in 1976 he discovered that by passing electric currents through salt water, over time a thick layer of various materials including limestone deposited on the cathode. Later experiments showed that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrified Reef
An electric reef (also electrified reef) is an artificial reef made from biorock, being limestone that forms rapidly in seawater on a metal structure from dissolved minerals in the presence of a small electric current. The first reefs of this type were created by Wolf Hilbertz and Thomas J. Goreau in the 1980s. By 2011 there were examples in over 20 countries. History Artificial reefs have been built since the 1950s using materials including sunken ships and concrete blocks. While artificial reefs have been effective at boosting fish populations and are valuable areas for benthic organisms and other marine life (e.g. sponges) to colonise, they are less viable for coral restoration due to the slow growth of corals and their susceptibility to environmental changes. In the 1970s, whilst studying how seashells and reefs grow, Wolf Hilbertz discovered a simple method of creating limestone from minerals dissolved in seawater, which he called biorock. Together with Thomas J. Goreau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolf Hilbertz
Wolf Hartmut Hilbertz (April 16, 1938August 11, 2007) was a German-born futurist architect, inventor, and marine scientist. Notable contributions to science include the discovery of artificial mineral accretion / biorock and its use to create artificial reefs and other structures using electricity to attract materials already found in ocean water. Personal life Early life Wolf Hilbertz was born in Gütersloh, (Germany) in 1938, the first child of Rudolf Hilbertz (1909–1995) and Erna Hilbertz, née Uslat (1906–2008). His parents had quite different personalities; whereas his father was artistic and inventive, thinking up one of the first electric razors, his mother had a more down to earth, practical approach. While his father would have liked to become an artist, circumstances forced him to start working in a bank, whereas his mother enjoyed her occupation, channeling her forceful personality into her job as a school teacher. After Wolf Hilbertz was born, the family moved to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
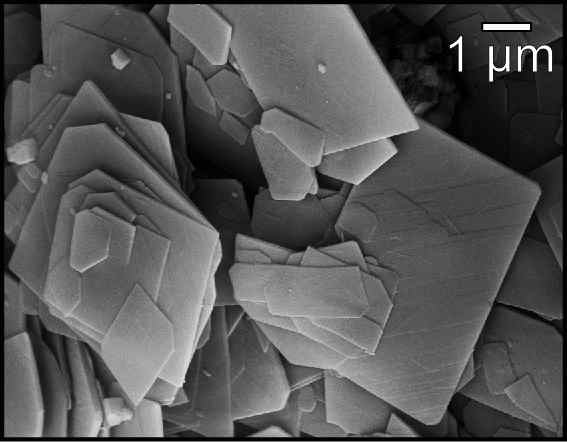
Zoom On A Biorock Structure
Zoom may refer to: Arts, entertainment and media Film * ''Zoom'' (2006 film), starring Tim Allen * ''Zoom'' (2015 film), a Canada-Brazil film by Pedro Morelli * ''Zoom'' (2016 Kannada film), a Kannada film * ''Zoom'' (2016 Sinhala film), a Sri Lankan film Music * Zoom (dance music group), a Eurodance group formed in Denmark * ''Zoom'' (The Knack album), 1998 * ''Zoom'' (Electric Light Orchestra album), 2001 * ''Zoom'' (Noah23 album), 2011 * ''Zoom'' (Rachid Taha album) * ''Zoom'', an album by Alvin Lee * "Zoom" (Dr. Dre song), 1998 * "Zoom" (Fat Larry's Band song), 1982 * "Zoom" (Jessi song), 2022 * "Zoom" (Lil Boosie song), 2006 * "Zoom", a song by the Commodores from their self-titled album * "Zoom", a song by Last Dinosaurs from the album '' In a Million Years'' * "Zoom", a song by Red Velvet from the extended play '' The ReVe Festival 2022 – Birthday'' * "Zoom!", a song by Super Furry Animals from the album ''Love Kraft'' * "Zoom", a song by Soda Stereo from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Carbonate
Calcium carbonate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is a common substance found in Rock (geology), rocks as the minerals calcite and aragonite, most notably in chalk and limestone, eggshells, gastropod shells, shellfish skeletons and pearls. Materials containing much calcium carbonate or resembling it are described as calcareous. Calcium carbonate is the active ingredient in agricultural lime and is produced when calcium ions in hard water react with carbonate ions to form limescale. It has medical use as a calcium supplement or as an antacid, but excessive consumption can be hazardous and cause hypercalcemia and digestive issues. Chemistry Calcium carbonate shares the typical properties of other carbonates. Notably, it: *reacts with acids, releasing carbonic acid which quickly disintegrates into carbon dioxide and water: : *releases carbon dioxide upon heating, called a thermal decomposition reaction, or calcination (to above 840 °C in the case of ), t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Sequestration
Carbon sequestration is the process of storing carbon in a carbon pool. It plays a crucial role in Climate change mitigation, limiting climate change by reducing the amount of Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. There are two main types of carbon sequestration: biologic (also called ''biosequestration'') and geologic. Biologic carbon sequestration is a naturally occurring process as part of the carbon cycle. Humans can enhance it through deliberate actions and use of technology. Carbon dioxide () is naturally captured from the atmosphere through biological, chemical, and physical processes. These processes can be accelerated for example through changes in land use and agricultural practices, called carbon farming. Artificial processes have also been devised to produce similar effects. This approach is called carbon capture and storage. It involves using technology to capture and sequester (store) that is produced from human activities under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosphere is the outer region of a star, which includes the layers above the opaque photosphere; stars of low temperature might have outer atmospheres containing compound molecules. The atmosphere of Earth is composed of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), argon (0.9%), carbon dioxide (0.04%) and trace gases. Most organisms use oxygen for respiration; lightning and bacteria perform nitrogen fixation which produces ammonia that is used to make nucleotides and amino acids; plants, algae, and cyanobacteria use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. The layered composition of the atmosphere minimises the harmful effects of sunlight, ultraviolet radiation, solar wind, and cosmic rays and thus protects the organisms from genetic damage. The curr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at normally-encountered concentrations it is odorless. As the source of carbon in the carbon cycle, atmospheric is the primary carbon source for life on Earth. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared, infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. Carbon dioxide is soluble in water and is found in groundwater, lakes, ice caps, and seawater. It is a trace gas Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, in Earth's atmosphere at 421 parts per million (ppm), or about 0.042% (as of May 2022) having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm or about 0.028%. Burning fossil fuels is the main cause of these increased concentrations, which are the primary cause of climate change.IPCC (2022Summary for pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
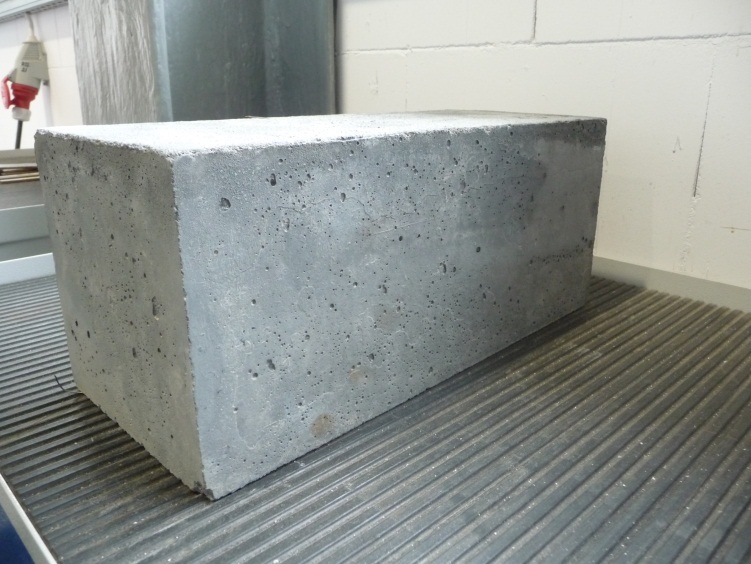
Concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of aggregate bound together with a fluid cement that cures to a solid over time. It is the second-most-used substance (after water), the most–widely used building material, and the most-manufactured material in the world. When aggregate is mixed with dry Portland cement and water, the mixture forms a fluid slurry that can be poured and molded into shape. The cement reacts with the water through a process called hydration, which hardens it after several hours to form a solid matrix that binds the materials together into a durable stone-like material with various uses. This time allows concrete to not only be cast in forms, but also to have a variety of tooled processes performed. The hydration process is exothermic, which means that ambient temperature plays a significant role in how long it takes concrete to set. Often, additives (such as pozzolans or superplasticizers) are included in the mixture to improve the physical prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compressive Strength
In mechanics, compressive strength (or compression strength) is the capacity of a material or Structural system, structure to withstand Structural load, loads tending to reduce size (Compression (physics), compression). It is opposed to ''tensile strength'' which withstands loads tending to elongate, resisting Tension (physics), tension (being pulled apart). In the study of strength of materials, compressive strength, tensile strength, and shear strength can be analyzed independently. Some materials fracture at their compressive strength limit; others Plasticity (physics), deform irreversibly, so a given amount of Deformation (engineering), deformation may be considered as the limit for compressive load. Compressive strength is a key value for Structural engineering, design of structures. Compressive strength is often measured on a universal testing machine. Measurements of compressive strength are affected by the specific test method and conditions of measurement. Compressive s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydromagnesite
Hydromagnesite is a hydrated magnesium carbonate mineral with the formula . It generally occurs associated with the weathering products of magnesium containing minerals such as serpentine group, serpentine or brucite. It occurs as incrustations and vein or fracture fillings in ultramafic rocks and serpentinites, and occurs in hydrothermally altered Dolomite (rock), dolomite and marble. Hydromagnesite commonly appears in caves as speleothems and "moonmilk", deposited from water that has seeped through magnesium rich rocks. It is the most common cave carbonate after calcite and aragonite. The mineral thermally decomposes, over a temperature range of approximately 220 °C to 550 °C, releasing water and carbon dioxide leaving a magnesium oxide residue. Hydromagnesite was first described in 1836 for an occurrence in Hoboken, New Jersey. Stromatolites in an alkaline (pH greater than 9) freshwater lake (Lake Salda, Salda Gölü) in southern Turkey are made of hydromagnesite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicarbonate
In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogencarbonate) is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid. It is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula . Bicarbonate serves a crucial biochemical role in the physiological pH buffering system. The term "bicarbonate" was coined in 1814 by the English chemist William Hyde Wollaston. The name lives on as a trivial name. Chemical properties The bicarbonate ion (hydrogencarbonate ion) is an anion with the empirical formula and a molecular mass of 61.01 daltons; it consists of one central carbon atom surrounded by three oxygen atoms in a trigonal planar arrangement, with a hydrogen atom attached to one of the oxygens. It is isoelectronic with nitric acid (). The bicarbonate ion carries a negative one formal charge and is an amphiprotic species which has both acidic and basic properties. It is both the conjugate base of carbonic acid (); and the conjugate acid of , t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorel Cement
Sorel cement (also known as magnesia cement or magnesium oxychloride) is a Cement#Non-hydraulic cement, non-hydraulic cement first produced by the Frenchman, French chemist Stanislas Sorel in 1867.Sorel Stanislas (1867).Sur un nouveau ciment magnésien. ''Comptes Rendus Hebdomadaires des Séances de l'Académie des Sciences'', volume 65, pages 102–104. In fact, in 1855, before working with magnesium compounds, Stanislas Sorel first developed a two-component cement by mixing zinc oxide powder with a solution of zinc chloride.Sorel Stanislas (1856). Procédé pour la formation d'un ciment très-solide par l'action d'un chlorure sur l'oxyde de zinc. Bulletin de la Société d'Encouragement pour l'Industrie Nationale, 55, 51–53. In a few minutes he obtained a dense material harder than limestone. Only a decade later, Sorel replaced zinc with magnesium in his formula and also obtained a cement with similar favorable properties. This new type of cement was compressive strength, stro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |