|
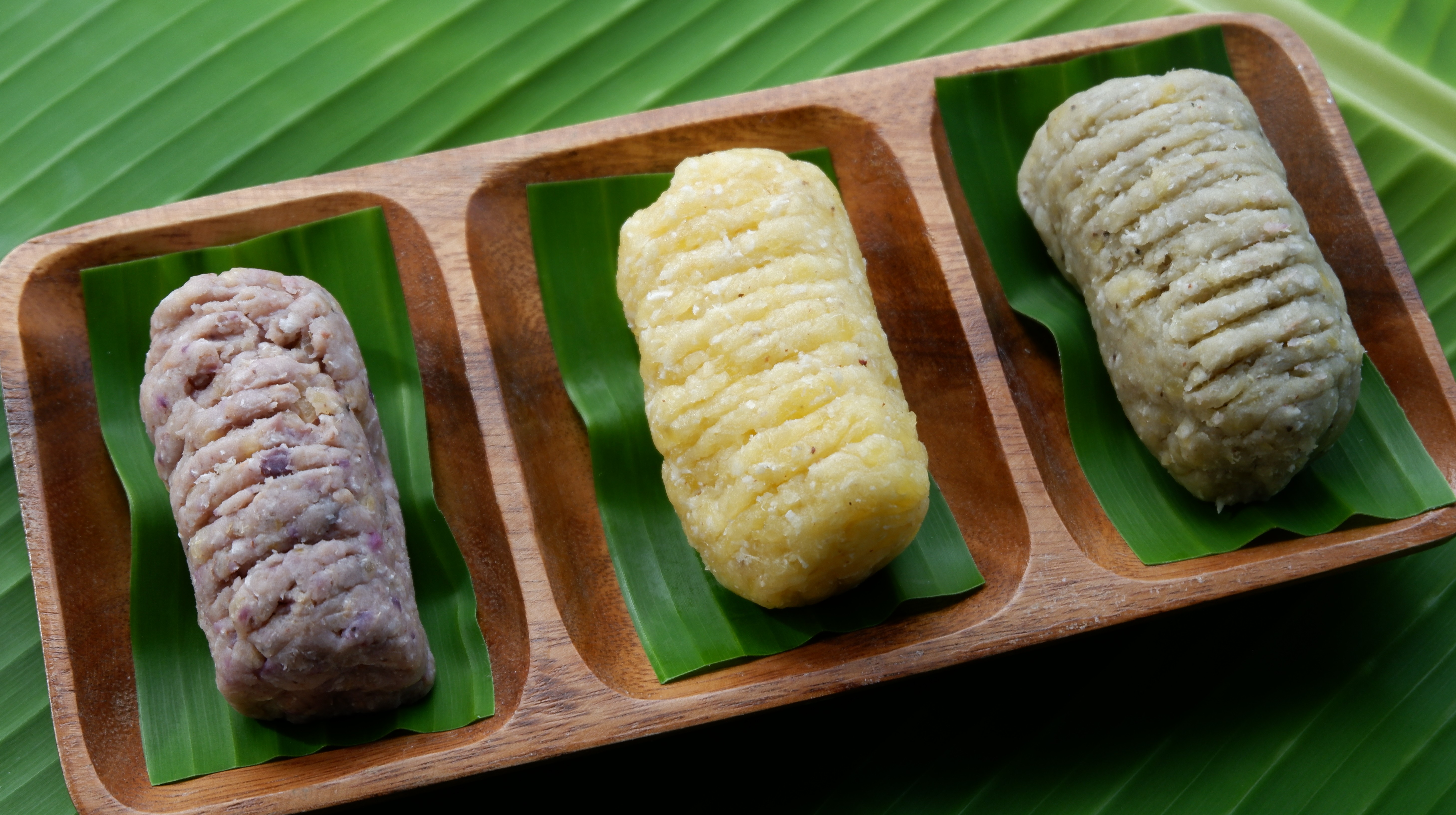
Binagol
''Binagol'' is a Filipino sweet steamed delicacy of the Waray people made from mashed giant taro corms, condensed milk, sugar, coconut milk, and egg yolks. It is distinctively placed in half of a coconut shell and then wrapped in banana leaves and twine. The name means "placed in a coconut shell", from the Visayan ''bagol'' (coconut shell). ''Binagol'' traditionally uses the corms of the giant taro (locally known as ''talyan'' or ''talian''); however, the corms of the taro (known in Tagalog as ''gabi'' and in Eastern Visayas, where the delicacy originates, as ''gaway'') is also alternatively used. It is a type of '' nilupak''. See also * Kalamay * Moron (food) * Ube halaya ''Ube halaya'' or ''halayang ube'' (also spelled ''halea'', ''haleya''; ) is a Filipino cuisine, Filipino dessert made from boiled and mashed purple yam (''Dioscorea alata'', locally known as ''ube''). Ube halaya is the main base in ube/purple ... References {{Philippine cuisine Foods containing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ube Halaya
''Ube halaya'' or ''halayang ube'' (also spelled ''halea'', ''haleya''; ) is a Filipino cuisine, Filipino dessert made from boiled and mashed purple yam (''Dioscorea alata'', locally known as ''ube''). Ube halaya is the main base in ube/purple yam flavored-pastries and ube ice cream. It can also be incorporated in other desserts such as ''halo-halo''. It is also commonly anglicized as ube jam, or called by its original native name, ''nilupak na ube''. History The Philippines shows the highest phenotype, phenotypic diversity of ube (''Dioscorea alata''), making it one of the likely Vavilov center, centers of origin of ube plant domestication, domestication. Remains of ube have been recovered from the Ille Cave archaeological site of Palawan (c. 11,000 BP). Preparation The main ingredient is peeled and boiled Dioscorea alata, purple yam which is grated and mashed. The mashed yam, with condensed milk (originally sweetened coconut milk), are added to a saucepan where butter or mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giant Taro
''Alocasia macrorrhizos'' is a species of flowering plant in the arum family (Araceae) that it is native to rainforests of Maritime Southeast Asia, New Guinea, and Queensland and has long been cultivated in South Asia, the Philippines, many Pacific islands, and elsewhere in the tropics. Common names include giant taro, giant alocasia, ape, biga, and pia. In Australia it is known as the cunjevoi (a term which also refers to a marine animal). History The giant taro was originally domesticated in the Philippines, but are known from wild specimens to early Austronesians in Taiwan. From the Philippines, they spread outwards to the rest of Maritime Southeast Asia and eastward to Oceania where it became one of the staple crops of Pacific Islanders. They are one of the four main species of aroids (taros) cultivated by Austronesians primarily as a source of starch, the others being ''Amorphophallus paeoniifolius'', ''Colocasia esculenta'', and ''Cyrtosperma merkusii'', each with multiple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filipino Cuisine
Filipino cuisine is composed of the cuisines of more than a hundred distinct Ethnic groups in the Philippines, ethnolinguistic groups found throughout the Philippines, Philippine archipelago. A majority of mainstream Filipino dishes that comprise Filipino cuisine are from the food traditions of various ethnolinguistic groups and tribes of the archipelago, including the Ilocano people, Ilocano, Pangasinan people, Pangasinan, Kapampangan people, Kapampangan, Tagalog people, Tagalog, Bicolano people, Bicolano, Visayan, Chavacano, and Maranao people, Maranao ethnolinguistic groups. The dishes associated with these groups evolved over the centuries from a largely indigenous (largely Austronesian peoples, Austronesian) base shared with maritime Southeast Asia with varied influences from Chinese cuisine, Chinese, Spanish cuisine, Spanish, and American cuisine, American cuisines, in line with the major waves of influence that had enriched the cultures of the archipelago, and adapted us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalamay
''Kalamay'' (also spelled ''calamay'', literally "sugar") is a sticky sweet delicacy that is popular in many regions of the Philippines. It is made of coconut milk, brown sugar, and ground glutinous rice. It can also be flavored with margarine, peanut butter, or vanilla. ''Kalamay'' can be eaten alone, but is usually used as a sweetener for a number of Filipino people, Filipino desserts and beverages. It is related to the Chamorro people, Chamorro dessert called Kalamai (dessert), kalamai. Preparation ''Kalamay'' is made by extracting coconut milk from grated coconuts twice. Glutinous rice is added to the first batch of coconut milk and the mixture is ground into a paste. Brown sugar is added to the second batch of coconut milk and boiled for several hours to make ''latík''. The mixture of ground glutinous rice and coconut milk is then poured into the ''latík'' and stirred until the consistency becomes very thick. It can be served hot or at room temperature especially when ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a total area of roughly 300,000 square kilometers, which are broadly categorized in Island groups of the Philippines, three main geographical divisions from north to south: Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao. With a population of over 110 million, it is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, twelfth-most-populous country. The Philippines is bounded by the South China Sea to the west, the Philippine Sea to the east, and the Celebes Sea to the south. It shares maritime borders with Taiwan to the north, Japan to the northeast, Palau to the east and southeast, Indonesia to the south, Malaysia to the southwest, Vietnam to the west, and China to the northwest. It has Ethnic groups in the Philippines, diverse ethnicities and Culture o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taro
Taro (; ''Colocasia esculenta'') is a root vegetable. It is the most widely cultivated species of several plants in the family Araceae that are used as vegetables for their corms, leaves, stems and Petiole (botany), petioles. Taro corms are a food staple in Culture of Africa, African, Oceania, Oceanic, East Asian, Southeast Asian and South Asian cultures (similar to Yam (vegetable), yams). Taro is believed to be one of the earliest cultivated plants. Common names The English term '':wikt:taro#English, taro'' was :wikt:taro#Maori, borrowed from the Māori language when James Cook, Captain Cook first observed ''Colocasia'' plantations in New Zealand in 1769. The form ''taro'' or ''talo'' is widespread among Polynesian languages:*''talo'': taro (''Colocasia esculenta'') – entry in the ''Polynesian Lexicon Project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foods Containing Coconut
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin and contains essential nutrients such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is ingested by an organism and assimilated by the organism's cells to provide energy, maintain life, or stimulate growth. Different species of animals have different feeding behaviours that satisfy the needs of their metabolisms and have evolved to fill a specific ecological niche within specific geographical contexts. Omnivorous humans are highly adaptable and have adapted to obtaining food in many different ecosystems. Humans generally use cooking to prepare food for consumption. The majority of the food energy required is supplied by the industrial food industry, which produces food through intensive agriculture and distributes it through complex food processing and food distribution systems. This system of conventional agriculture relies he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moron (food)
Moron or Morón may refer to: * Moron (psychology), disused term for a person with a mental age between 7 and 10 People * Morón (surname), various people so named * Edgar Moron (1941–2023), German politician Places Ancient world * Moron (ancient city), mentioned by the Greek geographer Strabo Argentina * Morón, Buenos Aires, a city in Greater Buenos Aires, Argentina * Roman Catholic Diocese of Morón, Argentina * Morón Partido, a district in Buenos Aires Province Mongolia * Mörön, a town * Mörön, Khentii, a district Spain * Morón de la Frontera, also known as Morón, a municipality ** Morón Air Base, in Morón de la Frontera United States * Moron, later renamed Taft, California, a city * Moron Lake, a lake in Alaska Elsewhere * Morón, Cuba, a city * Moron, Grand'Anse, Haiti, a commune * Morong, Bataan, the Philippines, a municipality formerly known as Moron * Morón, Venezuela, a town * Moron (mountain), in Switzerland, part of the Jura Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nilupak
Nilupak is a class of traditional Filipino delicacies made from mashed or pounded starchy foods mixed with coconut milk (or condensed milk and butter) and sugar. They are molded into various shapes and traditionally served on banana leaves with toppings of grated young coconut (''buko''), various nuts, cheese, butter, or margarine. It is also known as nilusak, linusak, niyubak, linupak, or lubi-lubi, among many other names, in the various languages of the Philippines. It is also known as minukmok in Quezon. Names The term ''nilupak'' means "mashed" or "pounded", from the Tagalog verb ''lupak'', "to pound nto a pulp(with a mortar and pestle)". It is also known as ''nilusak'' in Visayan regions with the same meaning. They were traditionally pounded in large stone or wood mortar and pestle. In Philippine Spanish, ''nilupak'' was known as ''jalea'' ("jam"), which became spelled as '' halaya'', ''haleya'', or ''halea'' in the native languages. This term is especially used for ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
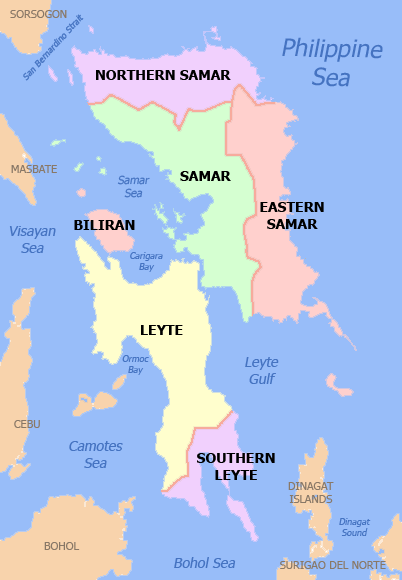
Eastern Visayas
Eastern Visayas (; ; ; ) is an administrative region in the Philippines, designated as Region VIII. It consists of three main islands: Samar, Leyte, and Biliran. The region has six provinces: Biliran, Leyte, Northern Samar, Samar, Eastern Samar, Southern Leyte, one independent city, Ormoc, and one highly urbanized city, Tacloban (its regional center and largest city). The highly urbanized city of Tacloban is the sole regional center. These provinces and cities occupy the easternmost islands of the Visayas group of islands, hence the region's name. Some historians believe that the oldest ancient kingdom in the Philippines is found in this region, the Lakanate of Lawan, which plays a significant role in the Polynesian and Austronesian intermigration. Eastern Visayas faces the Philippine Sea to the east. The region's most famous landmark is the San Juanico Bridge, which links the islands of Samar and Leyte. As of 2020, the Eastern Visayas region has a population o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tagalog Language
Tagalog ( ,According to the ''OED'' anMerriam-Webster Online Dictionary ; ''Baybayin'': ) is an Austronesian language spoken as a first language by the ethnic Tagalog people, who make up a quarter of the population of the Philippines, and as a second language by the majority, mostly as or through Filipino language, Filipino. Its de facto Standard language, standardized and codified form, officially named ''Filipino'', is the national language of the Philippines, and is one of the nation's two official languages, alongside Philippine English, English. Tagalog, like the other and as one of the regional languages of the Philippines, which majority are Austronesian languages, Austronesian, is one of the auxiliary official languages of the Philippines in the regions and also one of the auxiliary media of instruction therein. Tagalog is closely related to other Philippine languages, such as the Bikol languages, the Bisayan languages, Ilocano language, Ilocano, Kapampangan language, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coconut Milk
Coconut milk is a plant milk extracted from the grated pulp of mature coconuts. The opacity and rich taste of the milky-white liquid are due to its high oil content, most of which is saturated fat. Coconut milk is a traditional food ingredient used in Southeast Asia, Oceania, South Asia, and East Africa. It is also used for cooking in the Caribbean, Central America, northern parts of South America and West Africa, where coconuts were introduced during the colonial era. Coconut milk is differentiated into subtypes based on fat content. They can be generalized into coconut cream (or thick coconut milk) with the highest amount of fat; coconut milk (or thin coconut milk) with a maximum of around 20% fat; and coconut skim milk with negligible amounts of fat. This terminology is not always followed in commercial coconut milk sold in Western countries. Coconut milk can also be used to produce milk substitutes (differentiated as "coconut milk beverages"). These products are not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |