|
Benzylisoquinoline
Substitution of the heterocycle isoquinoline at the C1 position by a benzyl group provides 1‑benzylisoquinoline, the most widely examined of the numerous benzylisoquinoline structural isomers. The 1-benzylisoquinoline moiety can be identified within numerous compounds of pharmaceutical interest, such as moxaverine; but most notably it is found within the structures of a wide variety of plant natural products, collectively referred to as benzylisoquinoline alkaloids. This class is exemplified in part by the following compounds: papaverine, noscapine, codeine, morphine, apomorphine, berberine, tubocurarine. Biosynthesis (''S'')- Norcoclaurine ( higenamine) has been identified as the central 1-benzyl-tetrahydro-isoquinoline precursor from which numerous complex biosynthetic pathways eventually emerge. These pathways collectively lead to the structurally disparate compounds comprising the broad classification of plant natural products referred to as benzylisoquinoline alkaloids ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzylisoquinoline Alkaloids
The benzylisoquinoline alkaloids are natural products that can be classified as isoquinoline alkaloids and are derived from benzylisoquinoline. They also include the benzyl(tetrahydro)isoquinoline alkaloids. Occurrence Benzylisoquinoline alkaloids are found in several Plant family, plant families, including the poppy family (Papaveraceae), the Annonaceae, annonaceae family, and the laurel family. Well-known representatives are primarily found in poppy plants, specifically those from which opium is derived, as well as in Actaea (plant), actaea. For instance, reticuline has been isolated from Annona reticulata. Known representatives Over 2500 biologically active derivatives are known from the benzylisoquinoline alkaloids.Bettina Ruff: ''Chemical and Biochemical Methods for the Stereoselective Synthesis of Complex Natural Products'', 199 pages, Verlag Logos Berlin (2012), ISBN 978-3-8325-3121-8, pp. 8 (). Based on their structure, the compounds can be divided into nume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noscapine
Noscapine, also known as narcotine, nectodon, nospen, anarcotine and (archaic) opiane, is a benzylisoquinoline alkaloid of the phthalideisoquinoline structural subgroup, which has been isolated from numerous species of the family Papaveraceae (poppy family). It lacks effects associated with opioids such as sedation, euphoria, or analgesia (pain-relief) and lacks addictive potential. Noscapine is primarily used for its antitussive (cough-suppressing) effects. Medical uses Noscapine is often used as an antitussive medication. A 2012 Dutch guideline, however, does not recommend its use for acute coughing. Side effects * Nausea * Vomiting * Loss of coordination * Hallucinations (auditory and visual) * Loss of sexual drive * Swelling of prostate * Loss of appetite * Dilated pupils * Increased heart rate * Shaking and muscle spasms * Chest pain * Increased alertness * Increased wakefulness * Loss of stereoscopic vision Interactions Noscapine can increase the effects o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
(S)-norcoclaurine Synthase
The enzyme (''S'')-norcoclaurine synthase () catalyzes the chemical reaction : 4-hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde + 4-(2-aminoethyl)benzene-1,2-diol (Dopamine) \rightleftharpoons (''S'')- norcoclaurine + HO This enzyme belongs to the family of lyases, specifically the hydro-lyases, which cleave carbon-oxygen bonds. The systematic name of this enzyme class is 4-hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde hydro-lyase dding dopamine (''S'')-norcoclaurine-forming''. Other names in common use include (''S'')-norlaudanosoline synthase, and 4-hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde hydro-lyase (adding dopamine). This enzyme participates in benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis Biosynthesis, i.e., chemical synthesis occurring in biological contexts, is a term most often referring to multi-step, enzyme-Catalysis, catalyzed processes where chemical substances absorbed as nutrients (or previously converted through biosynthe .... References * * * EC 4.2.1 Enzymes of unknown structure {{4.2-enzyme-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
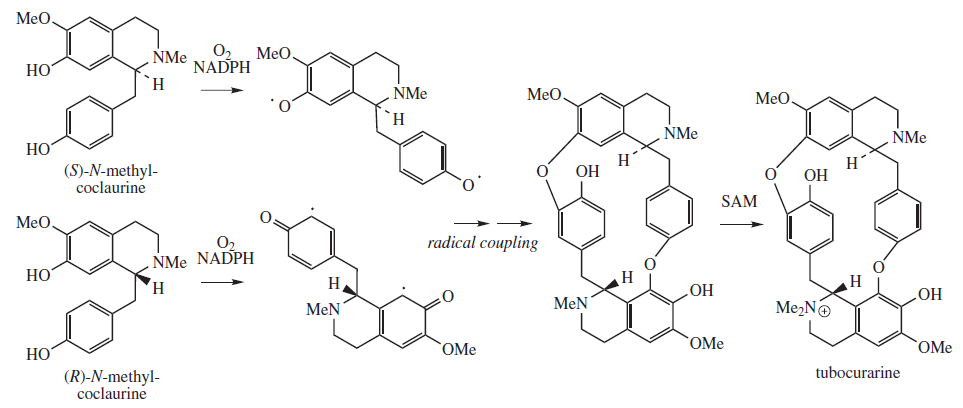
Tubocurarine
Tubocurarine (also known as ''d''-tubocurarine or DTC) is a toxic benzylisoquinoline alkaloid historically known for its use as an arrow poison. In the mid-1900s, it was used in conjunction with an anesthetic to provide skeletal muscle relaxation during surgery or mechanical ventilation. Safer alternatives, such as cisatracurium and rocuronium, have largely replaced it as an adjunct for clinical anesthesia and it is now rarely used. The specific form used was tubocurarine chloride, its hydrated hydrochloride salt. History Tubocurarine is a naturally occurring mono-quaternary alkaloid obtained from the bark of the Menispermaceous South American plant '' Chondrodendron tomentosum'', a climbing vine known to the European world since the Spanish conquest of South America. Curare had been used as a source of arrow poison by South American natives to hunt animals, and they were able to eat the animals' contaminated flesh subsequently without any adverse effects because tubocur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphine
Morphine, formerly also called morphia, is an opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin produced by drying the latex of opium poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as an analgesic (pain medication). There are multiple methods used to administer morphine: oral; sublingual administration, sublingual; via inhalation; intramuscular, injection into a muscle, Subcutaneous injection, injection under the skin, or injection into the spinal cord area; transdermal; or via rectal administration, rectal suppository. It acts directly on the central nervous system (CNS) to induce analgesia and alter perception and emotional response to pain. Physical and psychological dependence and tolerance may develop with repeated administration. It can be taken for both acute pain and chronic pain and is frequently used for pain from myocardial infarction, kidney stones, and during Childbirth, labor. Its maximum effect is reached after about 20 minutes when administ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubocurarine
Tubocurarine (also known as ''d''-tubocurarine or DTC) is a toxic benzylisoquinoline alkaloid historically known for its use as an arrow poison. In the mid-1900s, it was used in conjunction with an anesthetic to provide skeletal muscle relaxation during surgery or mechanical ventilation. Safer alternatives, such as cisatracurium and rocuronium, have largely replaced it as an adjunct for clinical anesthesia and it is now rarely used. The specific form used was tubocurarine chloride, its hydrated hydrochloride salt. History Tubocurarine is a naturally occurring mono-quaternary alkaloid obtained from the bark of the Menispermaceous South American plant '' Chondrodendron tomentosum'', a climbing vine known to the European world since the Spanish conquest of South America. Curare had been used as a source of arrow poison by South American natives to hunt animals, and they were able to eat the animals' contaminated flesh subsequently without any adverse effects because tubocur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norcoclaurine
Higenamine (norcoclaurine) is a chemical compound found in a variety of plants including ''Nandina domestica'' (fruit), ''Aconitum carmichaelii'' (root), '' Asarum heterotropioides'', '' Galium divaricatum'' (stem and vine), ''Annona squamosa'', and ''Nelumbo nucifera'' (lotus seeds). Higenamine is found as an ingredient in sports and weight loss dietary supplements sold in the US. The US Food and Drug Administration has received reports of adverse effects from higenamine-containing supplements since 2014, but higenamine's health risks remain poorly understood. Legality Higenamine, also known as norcoclaurine HCl, is legal to use within food supplements in the UK, EU, the USA and Canada. Its main use is within food supplements developed for weight management and sports supplements. Traditional formulations with higenamine have been used for thousands of years within Chinese medicine and come from a variety of sources including fruit and orchids. There are no studies comparing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
(S)-norcoclaurine
Higenamine (norcoclaurine) is a chemical compound found in a variety of plants including ''Nandina domestica'' (fruit), ''Aconitum carmichaelii'' (root), ''Asarum heterotropioides'', ''Galium divaricatum'' (stem and vine), ''Annona squamosa'', and ''Nelumbo nucifera'' (lotus seeds). Higenamine is found as an ingredient in sports and weight loss dietary supplements sold in the US. The US Food and Drug Administration has received reports of adverse effects from higenamine-containing supplements since 2014, but higenamine's health risks remain poorly understood. Legality Higenamine, also known as norcoclaurine Hydrochloride, HCl, is legal to use within food supplements in the United Kingdom, UK, European Union, EU, the United States, USA and Canada. Its main use is within food supplements developed for weight management and sports supplements. Traditional formulations with higenamine have been used for thousands of years within Chinese medicine and come from a variety of sources i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berberine
Berberine is a Quaternary ammonium cation, quaternary ammonium salt from the protoberberine group of benzylisoquinoline alkaloids, occurring naturally as a secondary metabolite in some plants including species of ''Berberis'', from which its name is derived. Due to their yellow pigmentation, raw ''Berberis'' materials were once commonly used to dye wool, leather, and wood. Under ultraviolet light, berberine shows a strong yellow fluorescence, making it useful in histology for staining heparin in mast cells. As a natural dye, berberine has a Colour Index International, color index of 75160. Biological sources The following plants are biological sources of berberine: * ''Berberis vulgaris'' (barberry) * ''Berberis aristata'' (tree turmeric) * ''Berberis thunbergii'' * ''Fibraurea tinctoria'' * ''Mahonia aquifolium'' (Oregon grape) * ''Hydrastis canadensis'' (goldenseal) * ''Xanthorhiza simplicissima'' (yellowroot) * ''Phellodendron amurense'' (Amur cork tree) * ''Coptis chinensis'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |