|
Battle Of Peregonovka
The Battle of Peregonovka () or Battle of Perehonivka () was a September 1919 military conflict in which the Revolutionary Insurgent Army of Ukraine defeated the Volunteer Army. After retreating west across Ukraine for four months and 600 kilometers, the Insurgent Army turned east and surprised the Volunteer Army. The Insurgent Army reclaimed its capital of Huliaipole within ten days. Background In mid-June 1919, Andrei Shkuro, the commander of the Kuban Cossacks, took advantage of the discord between the Bolsheviks and Ukrainian anarchists to raid the Insurgent capital of Huliaipole, forcing the Insurgent Army into a retreat towards right-bank Ukraine. The Insurgent Army fell back hundreds of kilometers to the west, eventually reaching Kherson, then under the control of the Otaman Nykyfor Hryhoriv. Their alliance with him did not last long, as the Insurgents assassinated him for his connections with the White movement and his participation in antisemitic pogroms. Strengt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cucuteni–Trypillia Culture
The Cucuteni–Trypillia culture, also known as the Cucuteni culture or Trypillia culture is a Neolithic–Chalcolithic archaeological culture ( 5050 to 2950 BC) of Southeast Europe. It extended from the Carpathian Mountains to the Dniester and Dnieper regions, centered on modern-day Moldova and covering substantial parts of western Ukraine and northeastern Romania, encompassing an area of , with a diameter of 500 km (300 mi; roughly from Kyiv in the northeast to Brașov in the southwest). The majority of Cucuteni–Trypillia settlements were of small size, high density (spaced 3 to 4 kilometres apart), concentrated mainly in the Siret, Prut and Dniester river valleys. During its middle phase (c. 4100 to 3500 BC), populations belonging to the Cucuteni–Trypillia culture built some of the largest settlements in Eurasia, some of which contained as many as three thousand structures and were possibly inhabited by 20,000 to 46,000 people. The 'mega-sites' of the culture, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2nd Azov Corps
The 2nd Azov Corps was a military formation of the Revolutionary Insurgent Army of Ukraine, one of the 4 corps that was created on 1 September 1919, and existed until 1920. History On 1 September 1919, a meeting of insurgents was held in Dobrovelychkivka, at which a delegate was elected from each regiment. The meeting discussed the question of the further political existence of the Makhnovshchina as an independent organism. They also discussed the issue of reorganizing the insurgent regiments into a single army that would be effective in guerrilla warfare. The meeting elected a Military Revolutionary Council, as the central command of the insurgents. The insurgent regiments led by Nestor Makhno were officially named the Revolutionary Insurgent Army of Ukraine (RIAU). Viktor Belash was in charge of organizing the army. Belash developed the structure of the RIAU, which consisted of four corps (three active and one reserve), each built from a number of divisions, which were in tur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ataman
Ataman (variants: ''otaman'', ''wataman'', ''vataman''; ; ) was a title of Cossack and haidamak leaders of various kinds. In the Russian Empire, the term was the official title of the supreme military commanders of the Cossack armies. The Ukrainian version of the same word is '' hetman''. ''Otaman'' in Ukrainian Cossack forces was a position of a lower rank. Etymology The etymologies of the words ''ataman'' and '' hetman'' are disputed. There may be several independent Germanic and Turkic origins for seemingly cognate forms of the words, all referring to the same concept. The ''hetman'' form cognates with German '' Hauptmann'' ('captain', literally 'head-man') by the way of Czech or Polish, like several other titles. The Russian term ''ataman'' is probably connected to Old East Slavic ''vatamanŭ,'' and cognates with Turkic ''odoman'' ( Ottoman Turks). The term ''ataman'' may have also had a lingual interaction with Polish ''hetman'' and German ''hauptmann''. Suggestions hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
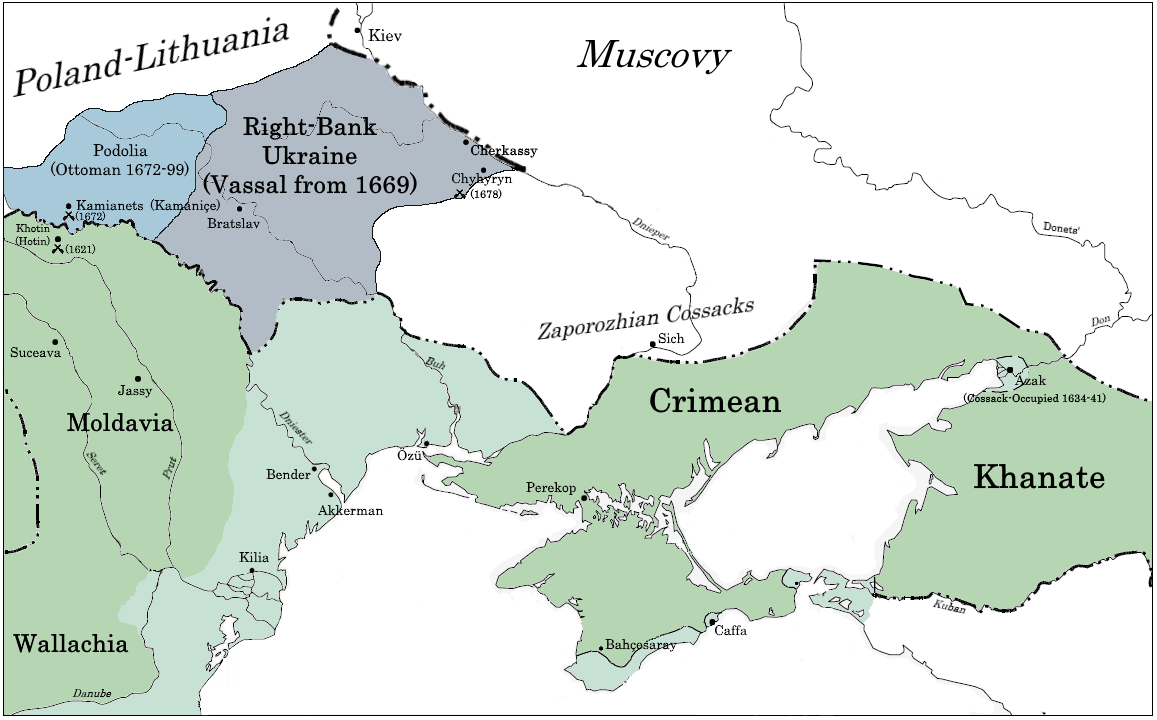
Right-bank Ukraine
The Right-bank Ukraine is a historical and territorial name for a part of modern Ukraine on the right (west) bank of the Dnieper River, corresponding to the modern-day oblasts of Vinnytsia, Zhytomyr, Kirovohrad, as well as the western parts of Kyiv and Cherkasy. It was separated from the left bank during the Ruin. Right-bank Ukraine is bordered by the historical regions of Volhynia and Podolia to the west, Moldavia to the southwest, Yedisan and Zaporizhzhia to the south, left-bank Ukraine to the east, and Polesia to the north. Main cities of the region include Cherkasy, Kropyvnytskyi, Bila Tserkva, Zhytomyr and Oleksandriia. History Since the Middle Ages, the region formed part of the Khazar Khanate, Kievan Rus', Mongol Empire, Golden Horde, Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Poland. Right-bank Ukraine was the target of slave raids by Tatars from the Black Sea steppes. The history of right- and left-bank Ukraine is closely associated with the Khmelnyt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anarchism In Ukraine
Anarchism in Ukraine has its roots in the democratic and egalitarian organization of the Zaporozhian Cossacks, who inhabited the region up until the 18th century. Philosophical anarchism first emerged from the radicalism (historical), radical movement during the Ukrainian national revival, finding a literary expression in the works of Mykhailo Drahomanov, who was himself inspired by the libertarian socialism of Pierre-Joseph Proudhon. The spread of populism, populist ideas by the Narodniks also lay the groundwork for the adoption of anarchism by Ukraine's working classes, gaining notable circulation in the History of the Jews in Ukraine, Jewish communities of the Pale of Settlement. By the outbreak of the 1905 Russian Revolution, 1905 Revolution, a specifically anarchist movement had risen to prominence in Ukraine. The ideas of anarcho-communism, anarcho-syndicalism and individualist anarchism all took root in Ukrainian revolutionary circles, with syndicalism itself developing a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin, were a radical Faction (political), faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) which split with the Mensheviks at the 2nd Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, Second Party Congress in 1903. The Bolshevik party, formally established in 1912, seized power in Russia in the October Revolution of 1917, and was later renamed the Russian Communist Party, All-Union Communist Party, and ultimately the Communist Party of the Soviet Union. Its ideology, based on Leninism, Leninist and later Marxism–Leninism, Marxist–Leninist principles, became known as Bolshevism. The origin of the RSDLP split was Lenin's support for a smaller party of professional revolutionaries, as opposed to the Menshevik desire for a broad party membership. The influence of the factions fluctuated in the years up to 1912, when the RSDLP formally split in two. The political philosophy of the Bolsheviks was based on the Leninist pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuban Cossacks
Kuban Cossacks (; ), or Kubanians (, ''kubantsy''; , ''kubantsi''), are Cossacks who live in the Kuban region of Russia. Most of the Kuban Cossacks are descendants of different major groups of Cossacks who were re-settled to the western Northern Caucasus in the late 18th century (estimated 230,000 to 650,000 initial migrants). The western part of the region (Taman Peninsula and adjoining region to the northeast) was settled by the Black Sea Cossack Host who were originally the Zaporozhian Cossacks of Ukraine, from 1792. The eastern and southeastern part of the host was previously administered by the Khopyour and Kuban regiments of the Caucasus Line Cossack Host and Don Cossacks, who were re-settled from the Don Cossacks, Don from 1777. The Kuban Cossack Host (Кубанское казачье войско), the administrative and military unit composed of Kuban Cossacks, formed in 1860 and existed until 1918. During the Russian Civil War, the Kuban Cossacks proclaimed the Kuba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrei Shkuro
Andrei Grigoriyevich Shkuro (; ; – 17 January 1947) was a Russian military officer of Cossack origin. He was a lieutenant general (1919) of the White Army, and later a Nazi collaborator. Biography Early life He was born in the ''stanitsa'' of Pashkovskaya (now part of Krasnodar) in Kuban Oblast into a Cossack family. Shkuro graduated from Cossack Sotnya of the Nikolaevsky Cavalry School in 1907 and served in the Kuban Cossack Host. During World War I, Shkuro became the commander of a special partisan unit which executed several daring raids behind German lines. During the war, Shkuro was promoted to the rank of colonel for his heroic performance. Russian Civil War In the spring of 1918, after the establishment of the Bolshevik régime, Shkuro organized an anti-Bolshevik Cossack unit in the area of Batalpashinsk in the Caucasus. In May and June 1918 he raided Stavropol, Yessentuki and Kislovodsk. After officially joining Denikin's Volunteer Army, he became the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huliaipole
Huliaipole ( ; ) is a small city in Polohy Raion, Zaporizhzhia Oblast, Ukraine. It is known as the birthplace of Ukrainian anarchist revolutionary Nestor Makhno. In January 2022, it had an estimated population of Huliaipole was attacked by Russian forces during the Russian invasion of Ukraine and sustained heavy damage, placing it on one of the lines of contact separating Ukrainian and Russian forces. History Prior to the annexation of the Crimean Khanate by the Russian Empire, the area was mostly settled by the Zaporozhian Cossacks and the nomadic Lesser Nogai Horde. The settlement arose during the 1770s, after the construction of the on the former lands of the Zaporozhian Sich, as part of the Russian Empire's policy to populate and develop the conquered Zaporozhian lands. When Catherine the Great dissolved the Sich, the local Cossacks either fled into exile or were brought into serfdom, with the residents of what is now Huliaipole falling under the yoke of the Shab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and the Battle of France, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas battl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field Gun
A field gun is a field artillery piece. Originally the term referred to smaller guns that could accompany a field army on the march, that when in combat could be moved about the battlefield in response to changing circumstances (field artillery), as opposed to guns installed in a fort (Royal Garrison Artillery, garrison artillery or coastal artillery), or to siege cannons and mortar (weapon), mortars which are too large to be moved quickly, and would be used only in a prolonged siege. Perhaps the most famous use of the field gun in terms of advanced tactics was Napoleon Bonaparte's use of very large wheels on the guns that allowed them to be moved quickly even during a battle. By moving the guns from point to point during a battle, enemy formations could be broken up to be handled by the infantry or cavalry wherever they were massing, dramatically increasing the overall effectiveness of the attack. World War I As the evolution of artillery continued, almost all guns of any siz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |