|
Battle Of Mylae
The Battle of Mylae took place in 260 BC during the First Punic War and was the first real naval battle between Carthage and the Roman Republic. This battle was key in the Roman victory of Mylae (present-day Milazzo) as well as Sicily itself. It also marked Rome's first naval triumph and also the first use of the ''corvus'' in battle.Tacitus, The Annals 2.49 Prelude Inspired by success in the battle of Agrigentum, the Romans sought to win all of Sicily, but required naval power to do so. In order to challenge the already prominent Carthaginian naval forces, Rome built a fleet of one hundred quinqueremes and twenty triremes.Polybius, ''The General History of Polybius,'' Book I, p. 24 The famous Greek historian Polybius wrote that Rome used a wrecked Carthaginian quinquereme captured at Messina as a model for the entire fleet, and that the Romans would have otherwise had no basis for design.Polybius, ''The General History of Polybius,'' Book I, p. 25 However, this may have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Punic War
The First Punic War (264–241 BC) was the first of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the early 3rd century BC. For 23 years, in the longest continuous conflict and greatest naval war of antiquity, the two powers struggled for supremacy. The war was fought primarily on the Mediterranean island of Sicily and its surrounding waters, and also in North Africa. After immense losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were defeated and Rome gained territory from Carthage. The war began in 264 BC with the Romans gaining a foothold on Sicily at Messana (modern Messina). The Romans then pressed Syracuse, the only significant independent power on the island, into allying with them and laid siege to Carthage's main base at Akragas. A large Carthaginian army attempted to lift the siege in 262 BC but was heavily defeated at the Battle of Akragas. The Romans then built a navy to challenge the Carthaginians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Punic War
The Second Punic War (218 to 201 BC) was the second of Punic Wars, three wars fought between Ancient Carthage, Carthage and Roman Republic, Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean Basin, Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Roman Italy, Italy and Iberia, but also on the islands of Sicily and Sardinia and, towards the end of the war, in North Africa. After immense materiel and human losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were once again defeated. Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedonia, Kingdom of Syracuse, Syracuse and several Numidians, Numidian kingdoms were drawn into the fighting, and Celtiberians, Iberian and Gauls, Gallic forces fought on both sides. There were three main Theater (military), military theatres during the war: Italy, where Hannibal defeated the Roman legions repeatedly, with occasional subsidiary campaigns in Sicily, Sardinia and Greece; Iberia, where Hasdrubal (Barcid), Hasdru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Censor
The censor was a magistrate in ancient Rome who was responsible for maintaining the census, supervising public morality, and overseeing certain aspects of the government's finances. Established under the Roman Republic, power of the censor was limited in subject matter but absolute within his sphere: in matters reserved for the censors, no magistrate could oppose his decisions, and only another censor who succeeded him could cancel those decisions. Censors were also given unusually long terms of office; unlike other elected offices of the Republic, which (excluding certain priests elected for life) had terms of 12 months or less, censors' terms were generally 18 months to 5 years (depending on the era). The censorate was thus highly prestigious, preceding all other regular magistracies in dignity if not in power and reserved with rare exceptions for former Roman consul, consuls. Attaining the censorship would thus be considered the crowning achievement of a Roman politician on the ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Nicola In Carcere
San Nicola in Carcere (Italian, "Saint Nicholas in prison") is an ancient titular church and minor basilica in Rome near the Forum Boarium in rione Ripa. It is constructed in the remains of the three temples of the Forum Holitorium and is one of the traditional stational churches of Lent. The parish was suppressed in 1931 and it is now served by the Clerics Regular of the Mother of God from the nearby Santa Maria in Campitelli. History The first church on the site was probably built in the 6th century, and a 10th-century inscription may be seen on a fluted column next to the entrance, but the first definite dedication is from a plaque on the church dating to 1128. The inscriptions found in S. Angelo, a valuable source illustrating the history of the Basilica, have been collected and published by Vincenzo Forcella. It was constructed in and from the ruins of the Forum Holitorium and its Roman temples, along with a jail (carcer) which a tradition (supported by Pliny's histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
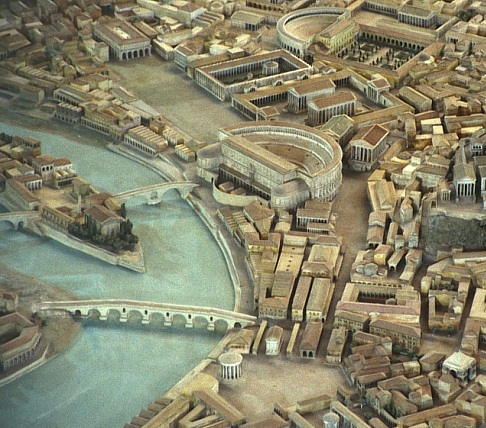
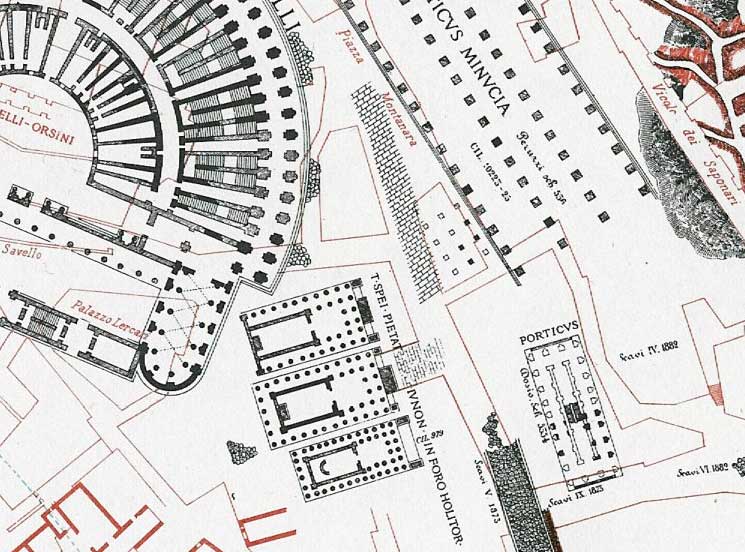
Forum Holitorium
The Forum Holitorium or Olitorium (Latin for the "Market of the Vegetable Sellers"; ) is an archaeological area of Rome, Italy, on the slopes of the Capitoline Hill. It was located outside the Carmental Gate in the Campus Martius, crowded between the cattle market (Forum Boarium) and buildings located in the Circus Flaminius. In ancient times it was the fruit and vegetable market, while the area of the adjacent Forum Boarium served as meat market. At its northern end were the temples of Bellona, goddess of war, and Apollo Medicus. It also included a sacred area with three small temples dedicated to Janus, Spes and Juno Sospita. The sacred area The construction of the sacred area of the forum dates back to the Republican age, more precisely to the period between the first and the second Punic War. Subsequently, at the time of Caesar (1st century BC), it underwent renovations which involved the demolition of a fourth temple: it was built by Manius Acilius Glabrio (consul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple Of Janus (Forum Holitorium)
The Temple of Janus () at the Forum Holitorium was a Roman temple dedicated to the god Janus, located between the Capitoline Hill and the Tiber River near the Circus Flaminius in the southern Campus Martius. The temple was built during the First Punic War, after the Temple of Janus in the Roman Forum. History The temple was built by Gaius Duilius in 3rd century BC after the 260 BC Roman victory at Mylae.Tacitus, ''Annals'', Book II, §49. It was probably built over an earlier shrine. Allegedly, the Senate was forbidden from meeting in the temple because their decree that the Fabii should go to the siege of Veii Veii (also Veius; ) was an important ancient Etruscan city situated on the southern limits of Etruria and north-northwest of Rome, Italy. It now lies in Isola Farnese, in the comune of Rome. Many other sites associated with and in the city-st ... was made in a temple of Janus, although some scholars consider this apocryphal. There were annual festivals at the te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Triumph
The Roman triumph (') was a civil ceremony and religious rite of ancient Rome, held to publicly celebrate and sanctify the success of a military commander who had led Roman forces to victory in the service of the state or, in some historical traditions, one who had successfully completed a foreign war. On the day of his triumph, the general wore a crown of laurel and an all-purple, gold-embroidered triumphal '' toga picta'' ("painted" toga), regalia that identified him as near-divine or near-kingly. In some accounts, his face was painted red, perhaps in imitation of Rome's highest and most powerful god, Jupiter. The general rode in a four-horse chariot through the streets of Rome in unarmed procession with his army, captives, and the spoils of his war. At Jupiter's temple on the Capitoline Hill, he offered sacrifice and the tokens of his victory to Jupiter. In Republican tradition, only the Senate could grant a triumph. The origins and development of this honour are obscur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sesterces
The ''sestertius'' (: ''sestertii'') or sesterce (: sesterces) was an ancient Roman coin. During the Roman Republic it was a small, silver coin issued only on rare occasions. During the Roman Empire it was a large brass coin. The name ''sestertius'' means "two and one half", referring to its nominal value of two and a half '' asses'' (a bronze Roman coin, singular ''as''), a value that was useful for commerce because it was one quarter of a denarius, a coin worth ten ''asses''. The name is derived from ''semis'', "half" and ''tertius'', "third", in which "third" refers to the third ''as'': the sestertius was worth two full ''asses'' and half of a third. English-language sources routinely use the original Latin form ''sestertius'', plural ''sestertii''; but older literature frequently uses ''sesterce'', plural ''sesterces'', ''terce'' being the English equivalent of ''tertius''. A modern shorthand for values in sestertii is IIS (Unicode 𐆘), in which the Roman numeral ''II'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capitoline Museum
The Capitoline Museums () are a group of art and archaeological museums in Piazza del Campidoglio, on top of the Capitoline Hill in Rome, Italy. The historic seats of the museums are Palazzo dei Conservatori and Palazzo Nuovo, facing on the central trapezoidal piazza in a plan conceived by Michelangelo in 1536 and executed over a period of more than 400 years. The Capitoline Museums, known for its exhibitions of works related to the history of ancient Rome and the Capitoline Hill, which was the political and religious center of the city, express the greatness of Roman civilization and its precious legacy that helped influence modern Western society. The museums display works from the ancient world (Greek, Roman, Etruscan and Egyptian), the Middle Ages and the Renaissance. They house masterpieces such as the ''Equestrian Statue of Marcus Aurelius'', the ''Capitoline Wolf'', the ''Dying Gaul'', the Bust of ''Medusa'' by Bernini, ancient sculptures, paintings (with works by artist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victory Column
A victory column, or monumental column or triumphal column, is a monument in the form of a column, erected in memory of a heroic commemoration, including victorious battle, war, or revolution. The column typically stands on a base and is crowned with a victory symbol, such as a statue. The statue may represent the goddess Victoria (mythology), Victoria; in Germany, the female embodiment of the nation, Germania (personification), Germania; in the United States either the female embodiment of the nation Liberty (personification), Liberty or Columbia (personification), Columbia; in the United Kingdom, the female embodiment Britannia, an eagle, or a naval war hero depicted as a helmeted woman, wielding a trident, shield and olive branch. Monumental columns List of Roman victory columns Of the columns listed above, the following are the Roman columns. Ancient Rome, Roman triumphal columns were either monolithic Column, pillars or composed of column drums; in the later case, these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rostral Column
A rostral column is a type of victory column originating in ancient Greece and Rome, where they were erected to commemorate a naval military victory. Its defining characteristic is the integrated prows or Naval ram, rams of ships, representing captured or destroyed enemy ships. The name derives from the Latin Rostrum (ship), ''rostrum'' meaning the bow of a naval vessel. Rostral columns of the modern world include the Columbus Monument (New York City), Columbus Monument at Columbus Circle in New York City, and the paired Old Saint Petersburg Stock Exchange and Rostral Columns, Saint Petersburg Rostral Columns. List of notable rostral columns Ancient * Columna Rostrata C. Duilii ("Rostral Column of Gaius Duilius"), celebrating the naval Battle of Mylae (260 BC); formerly in the Roman Forum, some remnants of the inscription are now in the Capitoline Museum. Modern * the Grenville Column, monument to Thomas Grenville (Royal Navy officer), Royal Navy officer Thomas Grenville ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamilcar (Drepanum)
__NOTOC__ Hamilcar (, ) was a general who succeeded to the command of the Carthaginians in the First Punic War. He defeated Rome's allies at the Battle of Thermae in 259 BC and killed 4,000–6,000 of them with the help of surprise and good use of military intelligence. He then captured the towns of Enna and Camarina that same year with the assistance of traitors. He was defeated at the Battle of Tyndaris in 257 BC, losing 18 ships and sinking 9 Roman ships. He failed to prevent the Roman landing in Africa, being defeated at the Ecnomus in 256 BC, one of the largest naval battles in antiquity, with the loss of 94 ships, to the Romans' 24. After the Roman invasion of Africa, Hamilcar was recalled by Carthage from Sicily. He was defeated by Marcus Atilius Regulus at the Battle of Adys The battle of Adys (or Adis) took place in late 256 BC during the First Punic War between a Carthaginian army jointly commanded by Bostar, Hamilcar and Hasdrubal and a Roman army led by M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |