|
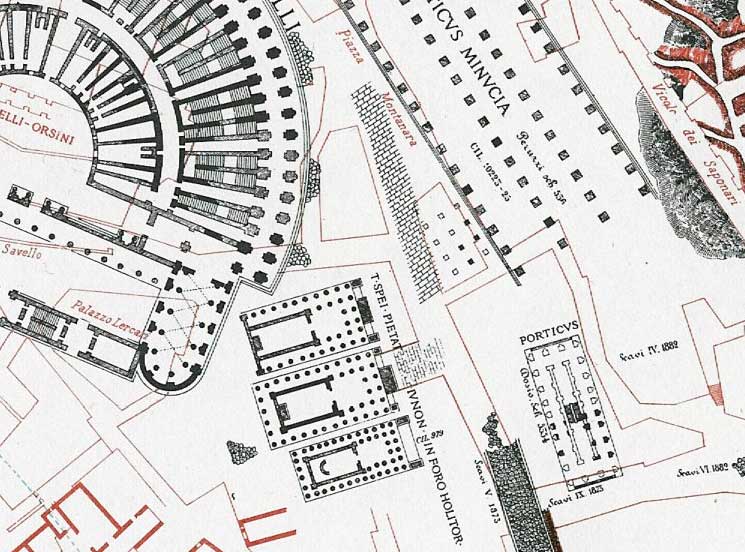
Temple Of Janus (Forum Holitorium)
The Temple of Janus () at the Forum Holitorium was a Roman temple dedicated to the god Janus, located between the Capitoline Hill and the Tiber River near the Circus Flaminius in the southern Campus Martius. The temple was built during the First Punic War, after the Temple of Janus in the Roman Forum. History The temple was built by Gaius Duilius in 3rd century BC after the 260 BC Roman victory at Mylae.Tacitus, ''Annals'', Book II, §49. It was probably built over an earlier shrine. Allegedly, the Senate was forbidden from meeting in the temple because their decree that the Fabii should go to the siege of Veii Veii (also Veius; ) was an important ancient Etruscan city situated on the southern limits of Etruria and north-northwest of Rome, Italy. It now lies in Isola Farnese, in the comune of Rome. Many other sites associated with and in the city-st ... was made in a temple of Janus, although some scholars consider this apocryphal. There were annual festivals at the te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Nicola In Carcere
San Nicola in Carcere (Italian, "Saint Nicholas in prison") is an ancient titular church and minor basilica in Rome near the Forum Boarium in rione Ripa. It is constructed in the remains of the three temples of the Forum Holitorium and is one of the traditional stational churches of Lent. The parish was suppressed in 1931 and it is now served by the Clerics Regular of the Mother of God from the nearby Santa Maria in Campitelli. History The first church on the site was probably built in the 6th century, and a 10th-century inscription may be seen on a fluted column next to the entrance, but the first definite dedication is from a plaque on the church dating to 1128. The inscriptions found in S. Angelo, a valuable source illustrating the history of the Basilica, have been collected and published by Vincenzo Forcella. It was constructed in and from the ruins of the Forum Holitorium and its Roman temples, along with a jail (carcer) which a tradition (supported by Pliny's histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaius Duilius
Gaius Duilius ( 260–231 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. As consul in 260 BC, during the First Punic War, he won Rome's first ever victory at sea by defeating the Carthaginians at the Battle of Mylae. He later served as censor in 258, and was appointed dictator to hold elections in 231, but never held another command. Background Gaius Duilius, whose father and grandfather were both named Marcus Duilius, belonged to an undistinguished family. One Caeso Duilius is recorded as consul in 336 BC, but the surname is otherwise only known historically and reliably from a few minor magistrates in the fourth century BC. Career Naval victory Duilius was one of the consuls for the year 260 BC, and was initially appointed to command Rome's land forces in Sicily against Carthage, as part of the First Punic War. His colleague in office, Gnaeus Cornelius Scipio, held charge of the fleet. The Romans built 120 warships and despatched them to Sicily in 260 BC for their crews to ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AD 17
__NOTOC__ AD 17 ( XVII) was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Flaccus and Rufus (or, less frequently, year 770 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination AD 17 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * May 26 – Germanicus returns to Rome as a conquering hero; he celebrates a triumph for his victories over the Cherusci, Chatti and other Germanic tribes west of the Elbe. * Emperor Tiberius sends Germanicus to the east, in order to lead a military campaign against Parthia. * Cappadocia (Asia Minor) becomes a Roman province. * Lucius Aelius Sejanus becomes Praetorian prefect. Africa * Tacfarinas, Numidian deserter from the Roman army,Tacitus, The Annals 2.52 begins a guerrilla war against the Romans. He leads his own Musulamii tribe and a coalit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus ( ; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was Roman emperor from AD 14 until 37. He succeeded his stepfather Augustus, the first Roman emperor. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC to Roman politician Tiberius Claudius Nero (father of Tiberius Caesar), Tiberius Claudius Nero and his wife, Livia Drusilla. In 38 BC, Tiberius's mother divorced his father and married Augustus. Following the untimely deaths of Augustus's two grandsons and adopted heirs, Gaius Caesar, Gaius and Lucius Caesar, Tiberius was designated Augustus's successor. Prior to this, Tiberius had proved himself an able diplomat and one of the most successful Roman generals: his conquests of Pannonia, Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia, Raetia, and (temporarily) parts of Germania laid the foundations for Roman Empire, the empire's northern frontier. Early in his career, Tiberius was happily married to Vipsania, daughter of Augustus's friend, distinguished general and intended heir, Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Adoption
Adoption in ancient Rome was primarily a legal procedure for transferring paternal power ''( potestas)'' to ensure succession in the male line within Roman patriarchal society. The Latin word ''adoptio'' refers broadly to "adoption", which was of two kinds: the transferral of ''potestas'' over a free person from one head of household to another; and ''adrogatio'', when the adoptee had been acting '' sui iuris'' as a legal adult but assumed the status of unemancipated son for purposes of inheritance. ''Adoptio'' was a longstanding part of Roman family law pertaining to paternal responsibilities such as perpetuating the value of the family estate and ancestral rites ''( sacra)'', which were concerns of the Roman property-owning classes and cultural elite. During the Principate, adoption became a way to ensure imperial succession. In contrast to modern adoption, Roman ''adoptio'' was neither designed nor intended to build emotionally satisfying families and support childrearing. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. The reign of Augustus initiated an Roman imperial cult, imperial cult and an era of regional hegemony, imperial peace (the or ) in which the Roman world was largely free of armed conflict. The Principate system of government was established during his reign and lasted until the Crisis of the Third Century. Octavian was born into an equites, equestrian branch of the plebeian Octavia gens, Octavia. Following his maternal great-uncle Julius Caesar's assassination of Julius Caesar, assassination in 44 BC, Octavian was named in Caesar's will as his Adoption in ancient Rome, adopted son and heir, and inherited Caesar's name, estate, and the loyalty of his legions. He, Mark Antony, and Marcus Lepidus formed the Second Triumvirat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of effective sole rule in 27 BC. The Western Roman Empire, western empire collapsed in 476 AD, but the Byzantine Empire, eastern empire lasted until the fall of Constantinople in 1453. By 100 BC, the city of Rome had expanded its rule from the Italian peninsula to most of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and beyond. However, it was severely destabilised by List of Roman civil wars and revolts, civil wars and political conflicts, which culminated in the Wars of Augustus, victory of Octavian over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, and the subsequent conquest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt. In 27 BC, the Roman Senate granted Octavian overarching military power () and the new title of ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portunalia
__NOTOC__ Portunus was the ancient Roman god of keys, doors, livestock and ports. He may have originally protected the warehouses where grain was stored, but later became associated with ports, perhaps because of folk associations between ''porta'' "gate, door" and ''portus'' "harbor", the "gateway" to the sea, or because of an expansion in the meaning of ''portus''. Portunus later became conflated with the Greek Palaemon. Portunus' festival, celebrated on August 17, the sixteenth day before the Kalends of September, was the Portunalia, a minor occasion in the Roman year. On this day, keys were thrown into a fire for good luck in a very solemn and lugubrious manner. His attribute was a key and his main temple in the city of Rome, the Temple of Portunus, was to be found in the Forum Boarium near the city's oldest riverine port, the , and the oldest stone bridge over the river, the Pons Aemilius. Portunus appears to be closely related to the god Janus, with whom he shares many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veii
Veii (also Veius; ) was an important ancient Etruscan city situated on the southern limits of Etruria and north-northwest of Rome, Italy. It now lies in Isola Farnese, in the comune of Rome. Many other sites associated with and in the city-state of Veii are in Formello, immediately to the north. Formello is named after the drainage channels that were first created by the Veians. Veii was the richest city of the Etruscan League. It was alternately at war and in alliance with the Roman Kingdom and later Republic for over 300 years. It eventually fell in the Battle of Veii to Roman general Camillus's army in 396 BC. Veii continued to be occupied after its capture by the Romans. The site is now a protected area, part of the Parco di Veio established by the regional authority of Lazio in 1997. Site City of Veii The city of Veii lies mainly on a tuff plateau in area. The Valchetta flows a few miles eastward to join the Tiber River on the south side of Labaro al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senatorial Decree
A (Latin: decree of the senate, plural: ) is a text emanating from the senate in Ancient Rome. It is used in the modern phrase ''senatus consultum ultimum''. Translated into French as , the term was also used during the French Consulate, the First French Empire and the Second French Empire. Republic In the case of the ancient Roman Senate under the Roman Kingdom, it was simply an opinion expressed by the senate, such as the '' Senatus consultum Macedonianum'' or the ''Senatus consultum de Bacchanalibus''. Under the Republic, it referred to a text promulgated by the senate on planned laws presented to the senate by a consul or praetor. Officially these ''consulta'' were merely advice given to the Republic's magistrates, but in practice magistrates often followed them to the letter.Byrd, 44 Despite only being an opinion, it was considered obligatory to have one before submitting the decision to a vote and moreover a hostile ''consultum'' from the senate almost systematically pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Senate
The Roman Senate () was the highest and constituting assembly of ancient Rome and its aristocracy. With different powers throughout its existence it lasted from the first days of the city of Rome (traditionally founded in 753 BC) as the Senate of the Roman Kingdom, to the Senate of the Roman Republic and Senate of the Roman Empire and eventually the Byzantine Senate of the Eastern Roman Empire, existing well into the post-classical era and Middle Ages. During the days of the Roman Kingdom, the Senate was generally little more than an advisory council to the king. However, as Rome was an electoral monarchy, the Senate also elected new Roman kings. The last king of Rome, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, was overthrown following a coup d'état led by Lucius Junius Brutus, who founded the Roman Republic. During the early Republic, the Senate was politically weak, while the various executive Roman magistrates who appointed the senators for life (or until expulsion by Roma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annals (Tacitus)
The ''Annals'' () by Roman historian and senator Tacitus is a history of the Roman Empire from the reign of Tiberius to that of Nero, the years AD 14–68. The ''Annals'' are an important source for modern understanding of the history of the Roman Empire during the 1st century AD. Tacitus' final work, modern historians generally consider it his magnum opus which historian Ronald Mellor says represents the "pinnacle of Roman historical writing". Tacitus' ''Histories'' and ''Annals'' together amounted to 30 books, although some scholars disagree about which work to assign some books to, traditionally 14 are assigned to ''Histories'' and 16 to ''Annals''. Of the 30 books referred to by Jerome about half have survived. Modern scholars believe that as a Roman senator, Tacitus had access to '' Acta Senatus''—the Roman senate's records—which provided a solid basis for his work. Although Tacitus refers to part of his work as "my annals", the title of the work ''Annals'' used tod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |