|
Automotive Thermoelectric Generator
An automotive thermoelectric generator (ATEG) is a device that converts some of the waste heat of an internal combustion engine (IC) into electricity using the Seebeck Effect. A typical ATEG consists of four main elements: A hot-side heat exchanger, a cold-side heat exchanger, Thermoelectricity, thermoelectric materials, and a compression assembly system. ATEGs can convert waste heat from an engine's coolant or exhaust into electricity. By reclaiming this otherwise lost energy, ATEGs decrease fuel consumed by the electric generator load on the engine. However, the cost of the unit and the extra fuel consumed due to its weight must be also considered. Operation principles In ATEGs, thermoelectric materials are packed between the hot-side and the cold-side heat exchangers. The thermoelectric materials are made up of p-n junction, p-type and n-type semiconductors, while the heat exchangers are metal plates with high thermal conductivity. The temperature difference between the tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waste Heat
Waste heat is heat that is produced by a machine, or other process that uses energy, as a byproduct of doing work. All such processes give off some waste heat as a fundamental result of the laws of thermodynamics. Waste heat has lower utility (or in thermodynamics lexicon a lower exergy or higher entropy) than the original energy source. Sources of waste heat include all manner of human activities, natural systems, and all organisms, for example, incandescent light bulbs get hot, a refrigerator warms the room air, a building gets hot during peak hours, an internal combustion engine generates high-temperature exhaust gases, and electronic components get warm when in operation. Instead of being "wasted" by release into the ambient environment, sometimes waste heat (or cold) can be used by another process (such as using hot engine coolant to heat a vehicle), or a portion of heat that would otherwise be wasted can be reused in the same process if make-up heat is added to the sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Efficiency
In thermodynamics, the thermal efficiency (\eta_) is a dimensionless performance measure of a device that uses thermal energy, such as an internal combustion engine, steam turbine, steam engine, boiler, furnace, refrigerator, ACs etc. For a heat engine, thermal efficiency is the ratio of the net work output to the heat input; in the case of a heat pump, thermal efficiency (known as the '' coefficient of performance'' or COP) is the ratio of net heat output (for heating), or the net heat removed (for cooling) to the energy input (external work). The efficiency of a heat engine is fractional as the output is always less than the input while the COP of a heat pump is more than 1. These values are further restricted by the Carnot theorem. Overview In general, energy conversion efficiency is the ratio between the useful output of a device and the input, in energy terms. For thermal efficiency, the input, Q_, to the device is heat, or the heat-content of a fuel that is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porsche
Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG, usually shortened to Porsche (; see below), is a German automobile manufacturer specializing in luxury, high-performance sports cars, SUVs and sedans, headquartered in Stuttgart, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. The company is owned by Volkswagen AG, a controlling stake of which is owned by Porsche Automobil Holding SE, usually shortened to Porsche SE. Porsche's current lineup includes the 718, 911, Panamera, Macan, Cayenne and Taycan. The origins of the company date to the 1930s when German Bohemian automotive engineer Ferdinand Porsche founded Porsche with Adolf Rosenberger, a keystone figure in the creation of German automotive manufacturer and Audi precursor Auto Union, and Austrian businessman Anton Piëch, who was, at the time, also Ferdinand Porsche's son in law. In its early days, it was contracted by the German government to create a vehicle for the masses, which later became the Volkswagen Beetle. After World War II, when Ferd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Back Pressure
Back pressure (or backpressure) is the term for a resistance to the desired flow of fluid through pipes. Obstructions or tight bends create backpressure via friction loss and pressure drop. In distributed systems in particular event-driven architecture, back pressure is a technique to regulate flow of data, ensuring that components do not become overwhelmed. Explanation A common example of backpressure is that caused by the exhaust system (consisting of the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, muffler and connecting pipes) of an automotive four-stroke engine, which has a negative effect on engine efficiency, resulting in a decrease of power output that must be compensated by increasing fuel consumption. In a piston-ported two-stroke engine, however, the situation is more complicated, due to the need to prevent unburned fuel/air mixture from passing right through the cylinders into the exhaust. During the exhaust phase of the cycle, backpressure is even more undesirable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Motors
General Motors Company (GM) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Automotive industry, automotive manufacturing company headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, United States. The company is most known for owning and manufacturing four automobile brands: Chevrolet, Buick, GMC (marque), GMC, and Cadillac, each a separate division of GM. By total sales, it has continuously been the largest automaker in the United States, and was the List of manufacturers by motor vehicle production, largest in the world for 77 years before losing the top spot to Toyota in 2008. General Motors operates manufacturing plants in eight countries. In addition to its four core brands, GM also holds interests in Chinese brands Baojun and SAIC-GM-Wuling, Wuling via SAIC-GM-Wuling, SAIC-GM-Wuling Automobile. GM further owns GM Defense, a namesake defense vehicles division which produces military vehicles for the United States government and military, the vehicle safety, security, and information ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphabet Energy
Alphabet Energy was a startup company founded in 2009 at the University of California, Berkeley by thermoelectrics expert Matthew L. Scullin and Peidong Yang. The company uses nanotechnology and materials science applications to create thermoelectric generators that are more cost effective than previous bismuth telluride-based devices. The company is based in Hayward, California. It started with a license to use silicon nanowire developed at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. They moved from UC Berkeley to offices in San Francisco in 2011, and later to Hayward. Alphabet has a number of patents related to the capture of waste heat for purposes of electricity generation. The company is working with tetrahedrite, a common mineral with thermoelectric properties. 2011's '' The Lean Startup: How Today's Entrepreneurs Use Continuous Innovation to Create Radically Successful Businesses'' describes Alphabet Energy's approach to product development as an example of the successful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michigan State University
Michigan State University (Michigan State or MSU) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in East Lansing, Michigan, United States. It was founded in 1855 as the Agricultural College of the State of Michigan, the first of its kind in the country. After the introduction of the Morrill Land-Grant Acts, Morrill Act in 1862, the state designated the college a land-grant institution in 1863, making it the first of the land-grant colleges in the United States. The college became coeducational in 1870. Today, Michigan State has facilities all across the state and over 634,000 alumni. Michigan State is a member of the Association of American Universities and is Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education, classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". The university's campus houses the Facility for Rare Isotope Beams, the W. J. Beal Botanical Garden, the Abrams Planetarium, the Wharton Center f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahedrite
Tetrahedrite is a copper antimony sulfosalt mineral with formula: . It is the antimony endmember of the continuous solid solution series with arsenic-bearing tennantite. Pure endmembers of the series are seldom if ever seen in nature. Of the two, the antimony rich phase is more common. Other elements also substitute in the structure, most notably iron and zinc, along with less common silver, mercury and lead. Bismuth also substitutes for the antimony site and ''bismuthian tetrahedrite'' or ''annivite'' is a recognized variety. The related, silver dominant, mineral species freibergite, although rare, is notable in that it can contain up to 18% silver. Mineralogy Tetrahedrite gets its name from the distinctive tetrahedron shaped cubic crystals. The mineral usually occurs in massive form, it is a steel gray to black metallic mineral with Mohs hardness of 3.5 to 4 and specific gravity of 4.6 to 5.2. Tetrahedrite occurs in low to moderate temperature hydrothermal veins and in some c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
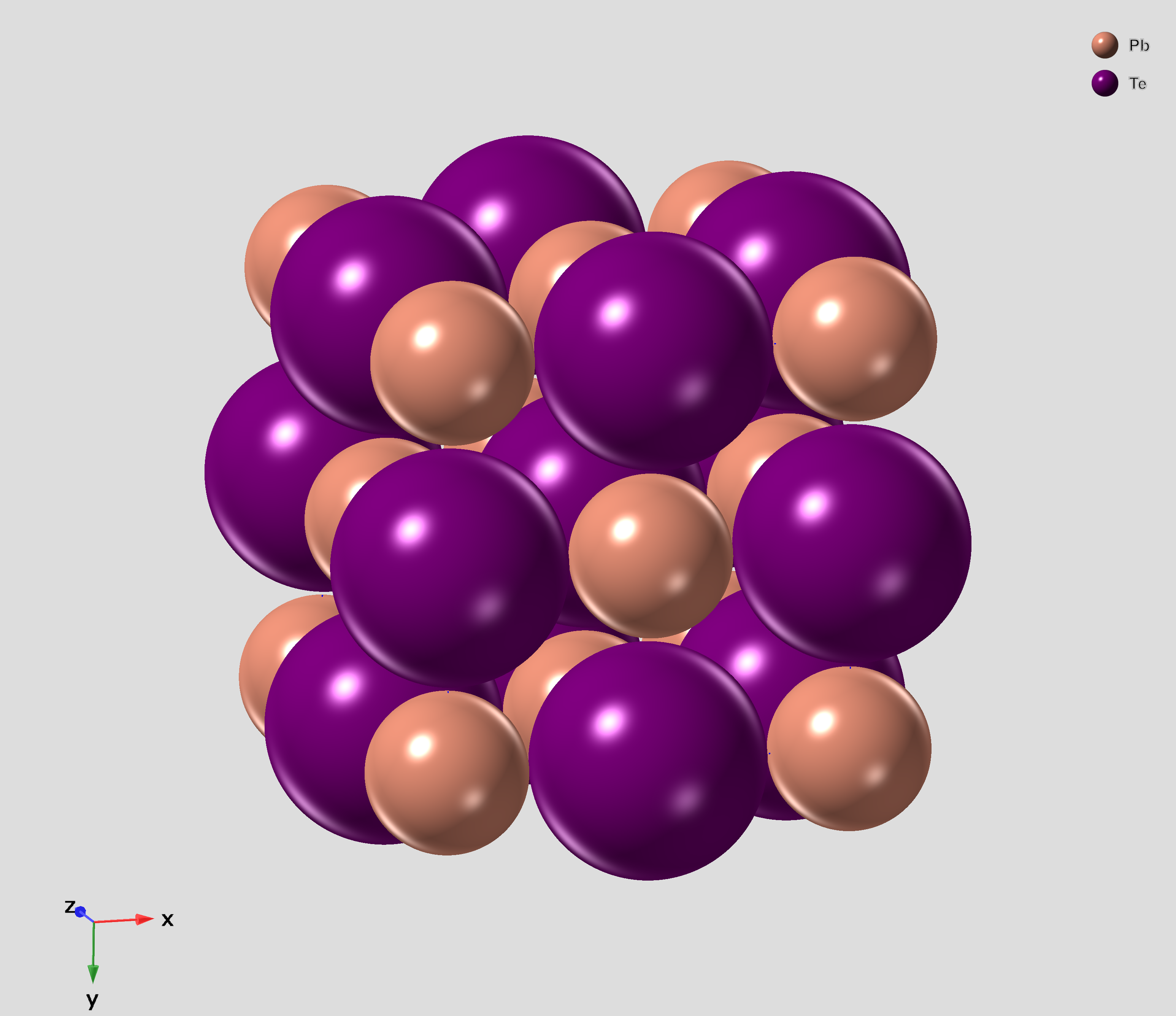
Lead Telluride
Lead telluride is a compound of lead (element), lead and tellurium (PbTe). It crystallizes in the NaCl crystal structure with Pb atoms occupying the cation and Te forming the anionic lattice. It is a narrow gap semiconductor with a band gap of 0.32 eV. It occurs naturally as the mineral altaite. Properties * Dielectric constant ~1000. * Electron Effective mass (solid-state physics), Effective mass ~ 0.01Electron rest mass, ''m''e * Hole mobility, μp = 600 cm2 V−1 s−1 (0 K); 4000 cm2 V−1 s−1 (300 K) * Seebeck coefficient: ~326 μV/K (undoped, at 300K), ~200 μV/K (Ag-doped) Applications PbTe has proven to be a very important intermediate Thermoelectric materials, thermoelectric material. The performance of thermoelectric materials can be evaluated by the figure of merit, ZT=S^2\sigma T/\kappa, in which S is the Seebeck coefficient, \sigma is the Electrical resistivity and conductivity, electrical conducti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bismuth Telluride
Bismuth telluride () is a gray powder that is a compound of bismuth and tellurium also known as bismuth(III) telluride. It is a semiconductor, which, when alloyed with antimony or selenium, is an efficient thermoelectric material for refrigeration or portable power generation. is a topological insulator, and thus exhibits thickness-dependent physical properties. Properties as a thermoelectric material Bismuth telluride is a narrow-gap layered semiconductor with a trigonal unit cell. The valence and conduction band structure can be described as a many-ellipsoidal model with 6 constant-energy ellipsoids that are centered on the reflection planes. cleaves easily along the trigonal axis due to Van der Waals bonding between neighboring tellurium atoms. Due to this, bismuth-telluride-based materials used for power generation or cooling applications must be polycrystalline. Furthermore, the Seebeck coefficient of bulk becomes compensated around room temperature, forcing the material ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skutterudite
Skutterudite is a cobalt arsenide mineral containing variable amounts of nickel and iron substituting for cobalt with the ideal formula CoAs3. Some references give the arsenic a variable formula subscript of 2–3. High nickel varieties are referred to as nickel-skutterudite, previously chloanthite. It is a hydrothermal ore mineral found in moderate to high temperature veins with other Ni-Co minerals. Associated minerals are arsenopyrite, native silver, erythrite, annabergite, nickeline, cobaltite, silver sulfosalts, native bismuth, calcite, siderite, barite and quartz. It is mined as an ore of cobalt and nickel with a by-product of arsenic. The crystal structure of this mineral has been found to be exhibited by several compounds with important technological uses. The mineral has a bright metallic luster, and is tin white or light steel gray in color with a black streak. The specific gravity is 6.5 and the hardness is 5.5–6. Its crystal structure is isometric with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
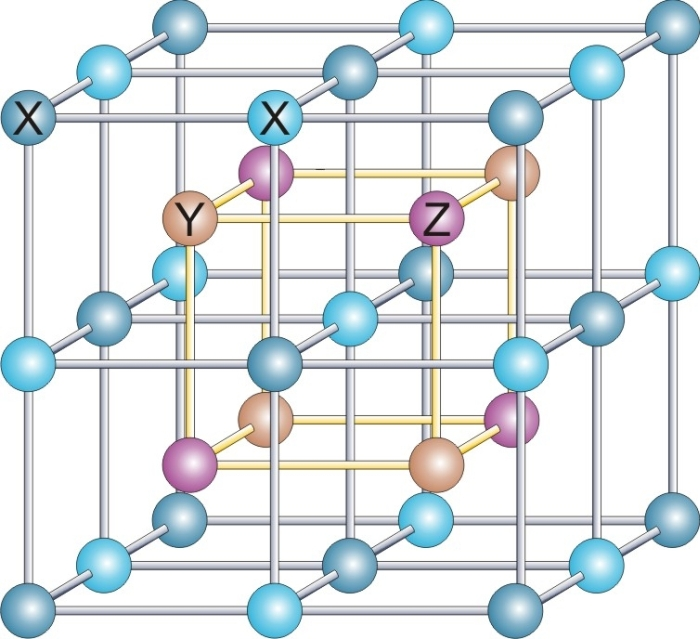
Heusler Alloy
Heusler compounds are magnetic intermetallics with face-centered cubic crystal structure and a composition of XYZ (half-Heuslers) or X2YZ (full-Heuslers), where X and Y are transition metals and Z is in the p-block. The term derives from the name of Germany, German mining engineer and chemist Friedrich Heusler, who studied such a compound (Cu2MnAl) in 1903. Many of these compounds exhibit properties relevant to spintronics, such as magnetoresistance, variations of the Hall effect, ferromagnetism, ferro-, antiferromagnetism, antiferro-, and ferrimagnetism, Half-metal, half- and semimetallicity, semiconductivity with spin filter ability, superconductivity, Topological insulator, topological band structure and are actively studied as thermoelectric materials. Their magnetism results from a double-exchange mechanism between neighboring magnetic ions. Manganese, which sits at the body centers of the cubic structure, was the magnetic ion in the first Heusler compound discovered. (See the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |