|
Asymmetric Epoxidation
Asymmetric epoxidation is a subset of asymmetric catalytic oxidations. Epoxidations convert prochiral (and other) alkenes to chiral epoxide derivatives. In asymmetric epoxidation, the two chiral products are produced in unequal amounts. The same catalysts are useful in the diastereoselective epoxidations, whereby one chiral alkene epoxidizes more rapidly than its enantiomer. Two popular versions of asymmetric epoxidations are: *Sharpless epoxidation, which uses titanium-based catalyst and tartrate esters as the chiral ligand. This methodology is one of the premier enantioselective chemical reactions. It is used to prepare 2,3-epoxyalcohols from primary and secondary allylic alcohols.Hill, J. G.; Sharpless, K. B.; Exon, C. M.; Regenye, R. '' Org. Synth.'', Coll. Vol. 7, p. 461 (1990); Vol. 63, p. 66 (1985).Article) *Jacobsen epoxidation, which uses a manganese-based catalyst supported by a chiral salen ligand. *Shi epoxidation, which uses a chiral organocatalyst and potassium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymmetric Catalytic Oxidation
Asymmetric catalytic oxidation is a technique of oxidizing various substrates to give an enantio-enriched product using a catalyst. Typically, but not necessarily, asymmetry is induced by the chirality of the catalyst. Typically, but again not necessarily, the methodology applies to organic substrates. Functional groups that can be prochiral and readily susceptible to oxidation include certain alkenes and thioethers. Challenging but pervasive prochiral substrates are C-H bonds of alkanes. Instead of introducing oxygen, some catalysts, biological and otherwise, enantioselectively introduce halogens, another form of oxidation. Reactions according to substrate Hydrocarbons Typically a prochiral C-H bond is converted to a chiral alcohol. Many examples of this important reaction result from the action of cytochrome P450, which allows these enzymes to process prodrugs and xenobiotics. Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylases also catalyze hydroxylations. Alkenes The oxidatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, or olefin, is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. The double bond may be internal or at the terminal position. Terminal alkenes are also known as Alpha-olefin, α-olefins. The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) Preferred IUPAC name, recommends using the name "alkene" only for Open-chain compound, acyclic hydrocarbons with just one double bond; alkadiene, alkatriene, etc., or polyene for acyclic hydrocarbons with two or more double bonds; cycloalkene, cycloalkadiene, etc. for Cyclic compound, cyclic ones; and "olefin" for the general class – cyclic or acyclic, with one or more double bonds. Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups (also known as mono-enes) form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula with ''n'' being a >1 natural number (which is two hydrogens less than the corresponding alkane). When ''n'' is four or more, isomers are possible, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
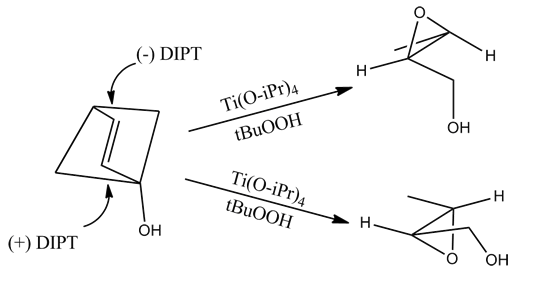
Sharpless Epoxidation
The Sharpless epoxidation reaction is an enantioselective chemical reaction to prepare 2,3-epoxyalcohols from primary and secondary allylic alcohols. The oxidizing agent is ''tert''-butyl hydroperoxide. The method relies on a catalyst formed from titanium tetra(isopropoxide) and diethyl tartrate. 2,3-Epoxyalcohols can be converted into diols, aminoalcohols, and ethers. The reactants for the Sharpless epoxidation are commercially available and relatively inexpensive. K. Barry Sharpless published a paper on the reaction in 1980 and was awarded the 2001 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this and related work on asymmetric oxidations. The prize was shared with William S. Knowles and Ryōji Noyori. Catalyst 5–10 mol% of the catalyst is typical. The presence of 3Å molecular sieves (3Å MS) is necessary. The structure of the catalyst is uncertain although it is thought to be a dimer of []. Selectivity The epoxidation of allylic alcohols is a well-utilized conversion in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enantiomer
In chemistry, an enantiomer (Help:IPA/English, /ɪˈnænti.əmər, ɛ-, -oʊ-/ Help:Pronunciation respelling key, ''ih-NAN-tee-ə-mər''), also known as an optical isomer, antipode, or optical antipode, is one of a pair of molecular entities which are mirror images of each other and non-superposable. Enantiomer molecules are like right and left hands: one cannot be superposed onto the other without first being converted to its mirror image. It is solely a relationship of chirality (chemistry), chirality and the permanent three-dimensional relationships among molecules or other chemical structures: no amount of re-orientation of a molecule as a whole or conformational isomerism, conformational change converts one chemical into its enantiomer. Chemical structures with chirality rotate plane-polarized light. A mixture of equal amounts of each enantiomer, a ''racemic mixture'' or a ''racemate'', does not rotate light. Stereoisomers include both enantiomers and diastereomers. Diaste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemistry, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. When chemical reactions occur, the atoms are rearranged and the reaction is accompanied by an Gibbs free energy, energy change as new products are generated. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the Atomic nucleus, nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive Chemical element, elements where both electronic and nuclear changes can occur. The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reagent, reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more Product (c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allyl Alcohol
Allyl alcohol (IUPAC name: prop-2-en-1-ol) is an organic compound with the structural formula . Like many alcohols, it is a water-soluble, colourless liquid. It is more toxic than typical small alcohols. Allyl alcohol is used as a precursor to many specialized compounds such as flame-resistant materials, drying oils, and plasticizers. Allyl alcohol is the smallest representative of the allylic alcohols. Production Allyl alcohol is produced commercially by the Olin and Shell corporations through the hydrolysis of allyl chloride: : Allyl alcohol can also be made by the rearrangement of propylene oxide, a reaction that is catalyzed by potassium alum at high temperature. The advantage of this method relative to the allyl chloride route is that it does not generate salt. Also avoiding chloride-containing intermediates is the "acetoxylation" of propylene to allyl acetate: : Hydrolysis of this acetate gives allyl alcohol. In alternative fashion, propylene can be oxidized to acrole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharpless Epoxidation DE
Sharpless is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: *Bevan Sharpless (1904–1950), American solar system astronomer *Christopher Sharpless (born 1945), American 1988 Winter Olympics bobsledder *Isaac Sharpless (1848–1920), American educator *Josh Sharpless (born 1988), American baseball player *Karl Barry Sharpless (born 1941), American chemist and Nobel prize winner * Mattie R. Sharpless (born 1942), American diplomat * Nathan J. Sharpless (1823–1893), American politician from Pennsylvania *Norman Sharpless (born 1966), American oncologist and director of the National Cancer Institute *Stewart Sharpless (1926–2013), American galactic astronomer **Sharpless catalog, a 20th-century astronomical catalog with 313 items *Disappearance of Toni Sharpless (born 1979), American nurse who disappeared in 2009 Fictional characters *A character in Madama Butterfly See also *Sharpless asymmetric dihydroxylation, a chemical reaction *Sharpless epoxidation, a chemical reaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacobsen Epoxidation
The Jacobsen epoxidation, sometimes also referred to as Jacobsen-Katsuki epoxidation is a chemical reaction which allows enantioselective epoxidation of unfunctionalized alkyl- and aryl- substituted alkenes. It is complementary to the Sharpless epoxidation (used to form epoxides from the double bond in allylic alcohols). The Jacobsen epoxidation gains its stereoselectivity from a ''C2'' symmetric manganese(III) salen-like ligand, which is used in catalytic amounts. The manganese atom transfers an oxygen atom from chlorine bleach or similar oxidant. The reaction takes its name from its inventor, Eric Jacobsen, with Tsutomu Katsuki sometimes being included. Chiral-directing catalysts are useful to organic chemists trying to control the stereochemistry of biologically active compounds and develop enantiopure drugs. Several improved procedures have been developed. A general reaction scheme follows: : History In the early 1990s, Jacobsen and Katsuki independently released thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salen Ligand
Salen refers to a tetradentate C2-Symmetric ligands, C2-symmetric ligand synthesized from salicylaldehyde (sal) and ethylenediamine (en). It may also refer to a class of compounds, which are structurally related to the classical salen ligand, primarily bis-Schiff bases. Salen ligands are notable for coordinating a wide range of different metals, which they can often stabilise in various oxidation states. For this reason salen-type compounds are used as metal deactivators. Metal salen complexes also find use as catalysts. Synthesis and complexation H2salen may be synthesized by the condensation reaction, condensation of ethylenediamine and salicylaldehyde. : Complexes of salen with metal cations can often be made in situ, i.e., without isolating the H2salen.{{cite journal , doi = 10.1039/B307853C , journal = Chem. Soc. Rev. , title = Metal-Salen Schiff base complexes in catalysis: Practical aspects , year = 2004 , author = Pier Giorgio Cozzi, volume = 33 , issue = 7 , p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shi Epoxidation
The Shi epoxidation is a chemical reaction described as the asymmetric epoxidation of alkenes with oxone (potassium peroxymonosulfate) and a fructose-derived catalyst (1). This reaction is thought to proceed via a dioxirane intermediate, generated from the catalyst ketone by oxone (potassium peroxymonosulfate). The addition of the sulfate group by the oxone facilitates the formation of the dioxirane by acting as a good leaving group during ring closure. It is notable for its use of a non-metal catalyst and represents an early example of organocatalysis. History The reaction was first reported by Yian Shi (史一安, pinyin: Shǐ Yī-ān) is derived from D-fructose and has a stereogenic center close to the reacting center (ketone)- the rigid six-membered ring structure of the catalyst and adjacent quaternary ring group minimizes epimerization of this stereocenter. Oxidation by the active dioxirane catalyst takes place from the si-face, due to steric hindrance of the opposing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organocatalyst
In organic chemistry, organocatalysis is a form of catalysis in which the rate of a chemical reaction is increased by an Organic compound, organic catalyst. This "organocatalyst" consists of carbon, hydrogen, sulfur and other nonmetal elements found in organic compounds.Special Issue: Because of their similarity in composition and description, they are often mistaken as a misnomer for enzymes due to their comparable effects on reaction rates and forms of catalysis involved. Organocatalysts which display secondary amine functionality can be described as performing either enamine catalysis (by forming catalytic quantities of an active enamine nucleophile) or imine, iminium catalysis (by forming catalytic quantities of an activated iminium electrophile). This mechanism is typical for covalent organocatalysis. Covalent binding of substrate normally requires high catalyst loading (for proline-catalysis typically 20–30 mol%). Noncovalent interactions such as hydrogen-bonding fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
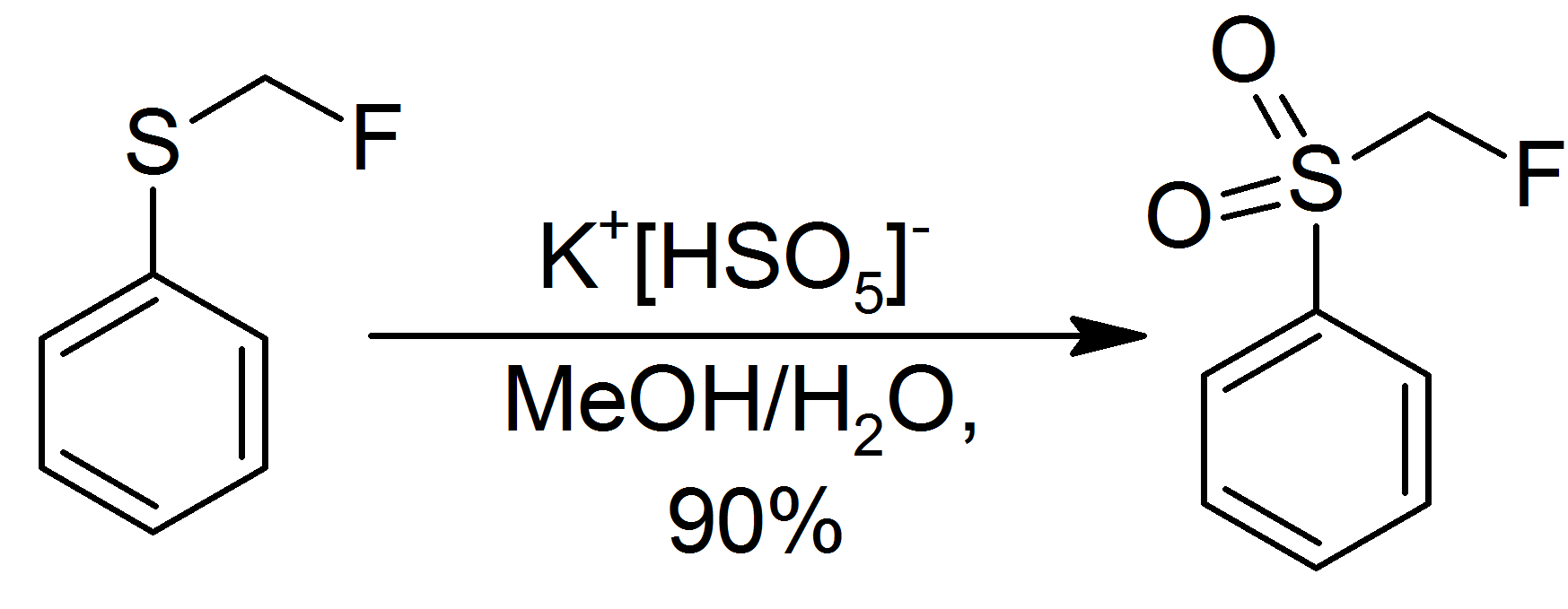
Potassium Peroxymonosulfate
Potassium peroxymonosulfate is widely used as an oxidizing agent, for example, in pools and spas (usually referred to as monopersulfate or "MPS"). It is the potassium salt (chemistry), salt of peroxymonosulfuric acid. Potassium peroxymonosulfate per se is rarely encountered. It is often confused with the triple salt , known as Oxone. The standard electrode potential for potassium peroxymonosulfate is +1.81 V with a half reaction generating the hydrogen sulfate (): : Oxone Potassium peroxymonosulfate per se is a relatively obscure salt, but its derivative called Oxone is of commercial value. Oxone refers to the triple salt . As such about one third by weight is potassium peroxymonosulfate. Oxone has a longer shelf life than does potassium peroxymonosulfate. A white, water-soluble solid, Oxone loses <1% of its oxidizing power per month. Oxone, which is commercially available, is produced from peroxysulfuric acid, which is generated in situ by combining oleum and hydrogen perox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |