|
Assassination Of Empress Myeongseong
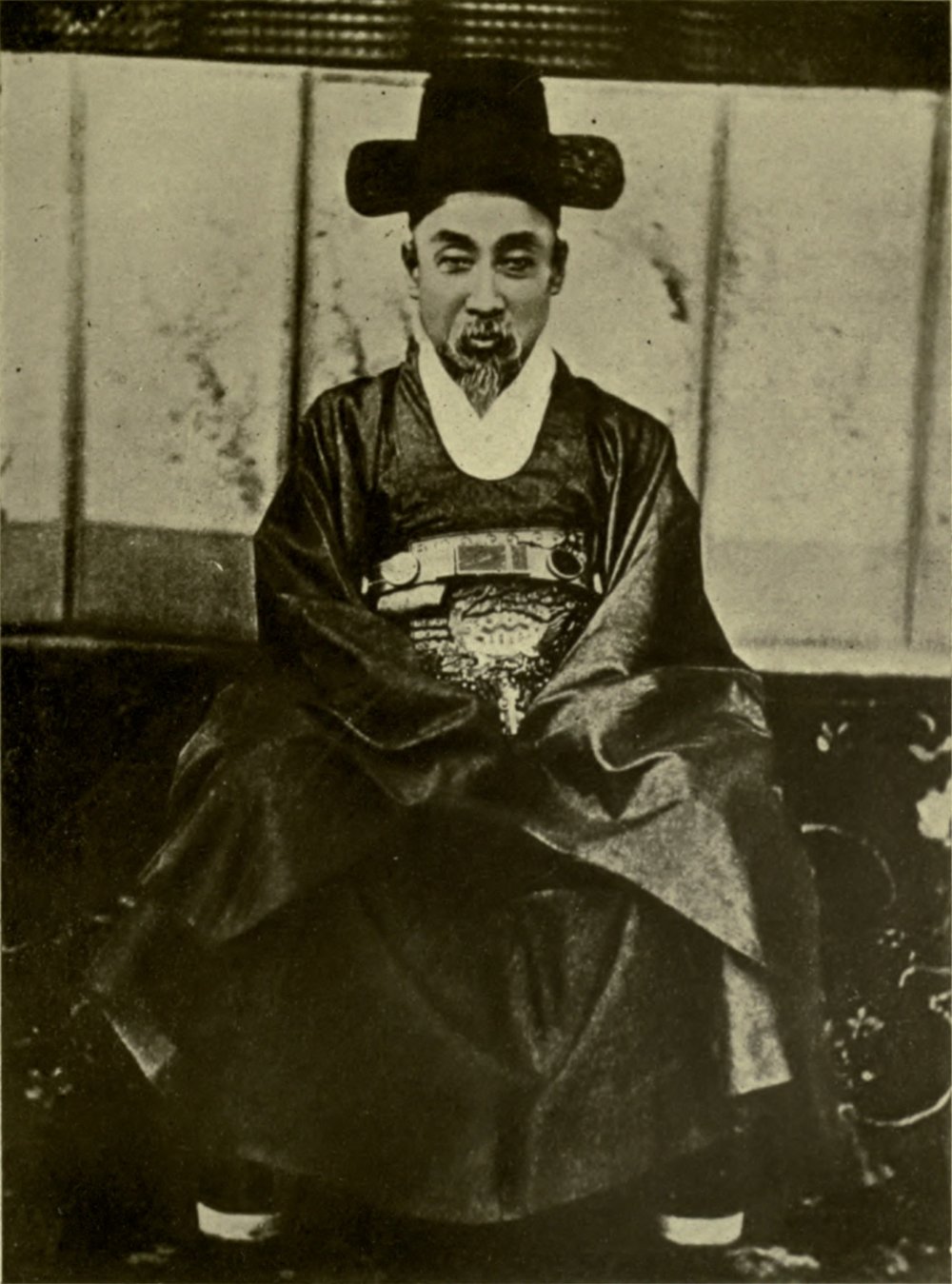
Around 6a.m. on 8 October 1895, Empress Myeongseong, Queen Min, the consort of the Korean monarch Gojong of Korea, Gojong, was assassinated by a group of Japanese agents under Miura Gorō. After her death, she was posthumously given the title of "Empress Myeongseong". The attack happened at the royal palace Gyeongbokgung in Seoul, Joseon. This incident is known in Korea as the Eulmi Incident. By the time of her death, the queen had acquired arguably more political power than even her husband. Through this process, she made many enemies and escaped a number of assassination attempts. Among her opponents were the king's father the Heungseon Daewongun, the pro-Japanese ministers of the court, and the Korean army regiment that had been trained by Japan: the Hullyŏndae. Weeks before her death, Japan replaced their emissary to Korea with a new one: Miura Gorō. Miura was a former military man who professed to being inexperienced in diplomacy, and reportedly found dealing with the powerf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korea Under Japanese Rule
From 1910 to 1945, Korea was ruled by the Empire of Japan under the name Chōsen (), the Japanese reading of "Joseon". Japan first took Korea into its sphere of influence during the late 1800s. Both Korea (Joseon) and Japan had been under policies of isolationism, with Joseon being a Tributary system of China, tributary state of Qing China. However, in 1854, Perry Expedition, Japan was forcibly opened by the United States. It then rapidly modernized under the Meiji Restoration, while Joseon continued to resist foreign attempts to open it up. Japan eventually succeeded in opening Joseon with the unequal Japan–Korea Treaty of 1876. Afterwards, Japan embarked on a decades-long process of defeating its local rivals, securing alliances with Western powers, and asserting its influence in Korea. Japan Assassination of Empress Myeongseong, assassinated the defiant Korean queen and intervened in the Donghak Peasant Revolution.Donald Keene, ''Emperor of Japan: Meiji and his World, 1852� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JoongAng Ilbo
''The JoongAng'', formerly known as ''JoongAng Ilbo'' (), is a South Korean daily newspaper published in Seoul, South Korea. It is one of the three biggest newspapers in South Korea, and a newspaper of record for South Korea. The paper also publishes an English edition, ''Korea JoongAng Daily'', in alliance with the ''International New York Times''. It is often regarded as the holding company of JoongAng Group ''chaebol'' (a spin-off from Samsung) as it is owner of various affiliates, such as the broadcast station and drama producing company JTBC, and movie theatres chain Megabox. History It was first published on September 22, 1965, by Lee Byung-chul, the founder of Samsung Group which once owned the Tongyang Broadcasting Company (TBC). In 1980, ''JoongAng Ilbo'' gave up TBC and TBC merged with KBS. ''JoongAng Ilbo'' is the pioneer in South Korea for the use of horizontal copy layout, topical sections, and specialist reporters with investigative reporting teams. Since Apri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empire Of Japan
The Empire of Japan, also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was the Japanese nation state that existed from the Meiji Restoration on January 3, 1868, until the Constitution of Japan took effect on May 3, 1947. From Japan–Korea Treaty of 1910, 1910 to Japanese Instrument of Surrender, 1945, it included the Japanese archipelago, the Kuril Islands, Kurils, Karafuto Prefecture, Karafuto, Korea under Japanese rule, Korea, and Taiwan under Japanese rule, Taiwan. The South Seas Mandate and Foreign concessions in China#List of concessions, concessions such as the Kwantung Leased Territory were ''de jure'' not internal parts of the empire but dependent territories. In the closing stages of World War II, with Japan defeated alongside the rest of the Axis powers, the Japanese Instrument of Surrender, formalized surrender was issued on September 2, 1945, in compliance with the Potsdam Declaration of the Allies of World War II, Allies, and the empire's territory subsequent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan–Korea Treaty Of 1876
The Japan–Korea Treaty of 1876 (also known as the Japan–Korea Treaty of Amity in Japan and the Treaty of Ganghwa Island in Korea) was made between representatives of the Empire of Japan and the Joseon, Kingdom of Joseon in 1876.Chung, Young-lob (2005). . "...the initial opening of Korea's borders to the outside world came in the form of the Korea-Japan Treaty of Amity (the so-called Ganghwa Treaty)." Negotiations were concluded on February 26, 1876.Korean Mission to the Conference on the Limitation of Armament, Washington, D.C., 1921–1922 (1922). ; "Treaty between Japan and Korea, dated February 26, 1876." In Korea, Heungseon Daewongun, who instituted a policy of increased isolationism against the European powers, was forced into retirement by his son Gojong of Korea, King Gojong and Gojong's wife, Empress Myeongseong. Second French Empire, France and the United States had already made several unsuccessful attempts to begin commerce with the Joseon dynasty during the Daewo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Komura Jutarō
was a Japanese statesman and diplomat."The Marquess Komura; A Notable Career," ''The Times'' (London). November 25, 1911. ...
|
Sadatsuchi Uchida
was a Japanese diplomat. Assigned to postings in the United States and Brazil, Uchida was instrumental in facilitating improved Japanese trade relations and emigration to both countries. Uchida also served as the first consul in Korea. Early life and diplomatic career A law graduate of the Tokyo Imperial University, Uchida joined the Japanese Ministry of Foreign Affairs in 1889. He was appointed as an Eleve-Consul to Shanghai in 1890, Consul to Seoul in 1893 and in 1902 was reassigned to serve as Consul General in New York City. Rice cultivation in Southeast Texas In 1902, Uchida toured the Gulf Coast region of the United States. At the time, overpopulation and the limited usable land for farming was affecting Japan. In the United States, rice farming was still in its infancy, and local rice production was falling short of its full potential. Consul General Uchida met with officials from the Texas Governor’s office, business owners in Houston, and other community leaders who ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academy Of Korean Studies
The Academy of Korean Studies (AKS; ) is a South Korean research and educational institute focusing on Korean studies. It was established on June 22, 1978, by the Ministry of Education & Science Technology. Works Journals *'' Korea Journal'' *''Review of Korean Studies'' *''Korean Studies Quarterly'' The following journals are not published by the AKS, but are often incorrectly assumed to be: *'' Korean Studies'', Hawaii *'' The Journal of Korean Studies'', Seattle *'' Encyclopedia of Korean Culture'' *'' Acta Koreana'' See also * List of national universities in South Korea * List of universities and colleges in South Korea * Education in Korea References External links * * Introducing research institutesat the Korean History On-line (한국역사정보통합시스템) (archived) Bundang 1978 establishments in South Korea Universities and colleges in Gyeonggi Province Research institutes in South Korea Social science research institutes Educational instit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopedia Of Korean Culture
The ''Encyclopedia of Korean Culture'' () is a Korean-language encyclopedia published by the Academy of Korean Studies and DongBang Media Co. It was originally published as physical books from 1991 to 2001. There is now an online version of the encyclopedia that continues to be updated. Overview On September 25, 1979, a presidential order (No. 9628; ) was issued to begin work on compiling a national encyclopedia. Work began on compiling the encyclopedia on March 18, 1980. It began publishing books in 1991. The encyclopedia's first version was completed, with 28 volumes, in 1995. It continued to be revised beginning in 1996. In 2001, the digital edition EncyKorea was published on CD-ROM A CD-ROM (, compact disc read-only memory) is a type of read-only memory consisting of a pre-pressed optical compact disc that contains computer data storage, data computers can read, but not write or erase. Some CDs, called enhanced CDs, hold b ... and DVD. It launched an online version in 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
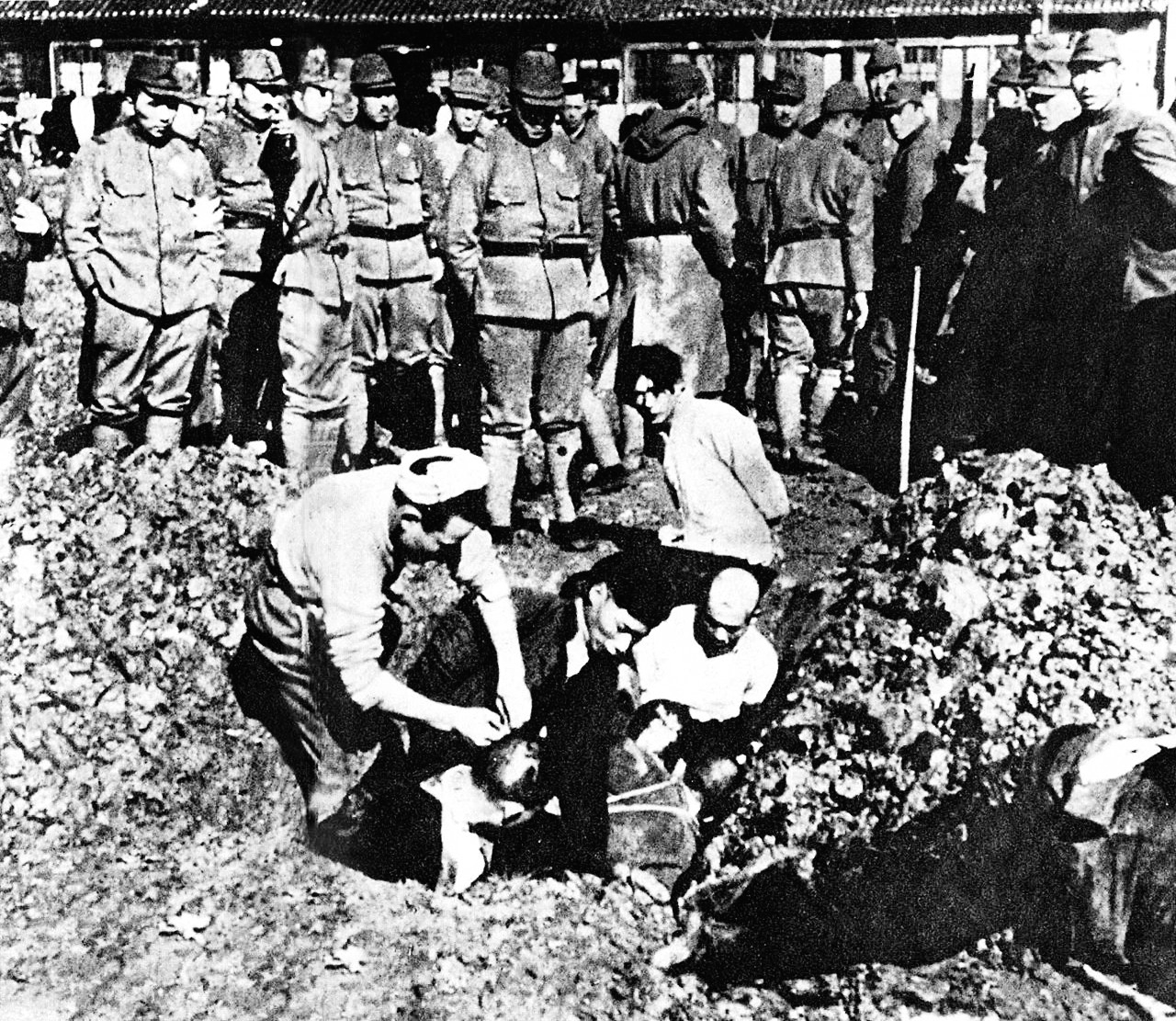
Japanese War Crimes
During its imperial era, Empire of Japan, Japan committed numerous war crimes and crimes against humanity across various Asian-Pacific nations, notably during the Second Sino-Japanese War, Second Sino-Japanese and Pacific Wars. These incidents have been referred to as "the Asian The Holocaust, Holocaust" and "Japan's Holocaust", and also as the "Rape of Asia". The crimes occurred during the early part of the Shōwa era, under Hirohito's reign. The Imperial Japanese Army (IJA) and the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) were responsible for a multitude of war crimes leading to millions of deaths. War crimes ranged from sexual slavery and massacres to human experimentation, torture, starvation, and forced labor, all either directly committed or condoned by the Japanese military and government. Evidence of these crimes, including oral testimonies and written records such as diaries and war journals, has been provided by Japanese veterans. The Japanese political and military leadership kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Righteous Armies
Righteous armies (), sometimes translated as irregular armies or militias, were informal civilian militias that appeared several times in Korean history, when the national armies were in need of assistance. The first righteous armies emerged during the Khitan invasions of Korea and the Mongol invasions of Korea. They subsequently rose up during the Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–1598), the first and second Manchu invasions, and during the Japanese occupation and preceding events. During the long period of Japanese intervention and annexation from 1890 to 1945, the disbanded imperial guard, and Confucian scholars, as well as farmers, formed over 60 successive righteous armies to fight for Korean freedom on the Korean peninsula. These were preceded by the Donghak movement, and succeeded by various Korean independence movements in the 1920s and beyond, which declared Korean independence from Japanese occupation. Japanese invasions of Korea The righteous armies were an irre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gojong's Internal Exile To The Russian Legation
King Gojong's internal exile to the Russian legation, also called the Agwan Pacheon incident (), occurred in 1896 in Korea when King Gojong and his crown prince left the Gyeongbokgung palace to take refuge at the Russian legation in Hanseong (Seoul). The incident resulted in a temporary decline of Japan's influence in Korea and corresponding rise in Russia's influence. Context The incident occurred after the First Sino-Japanese War during a period of factional confrontation within the Korean royal court. King Gojong of the Joseon dynasty and his crown prince took refuge from the Gyeongbok Palace at the Russian legation in Seoul, from which they controlled the Korean government for about one year from February 11, 1896, to February 20, 1897. Their escape took place in secrecy; it was arranged by the pro-Russian official Yi Bum-jin, the Russian consul Karl Ivanovich Weber, and others. The event, which was triggered in part by the king's fear of a coup d'état and his reaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Yi
The House of Yi, also called the Yi dynasty (also transcribed as the Lee dynasty), was the royal family of the Joseon dynasty and later the imperial family of the Korean Empire, descended from the Joseon founder Yi Seong-gye. All of his descendants are members of the Jeonju Yi clan. After the Japan–Korea Treaty of 1910, in which the Empire of Japan annexed the Korean Peninsula, some members of the Jeonju Yi clan were incorporated into the Imperial House of Japan and the Japanese peerage by the Japanese government. This lasted until 1947, just before the Constitution of Japan was promulgated. The treaty was nullified in the Treaty on Basic Relations between Japan and the Republic of Korea. With the Constitution succeeding to the Provisional Government, the descendants of the Imperial Family continue to be given preference and constitute a favored symbol in South Korea. The July 2005 funeral of Yi Ku, former head of the royal household, attracted considerable media coverage. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |