|
Ascarid
The Ascarididae are a family of the large intestinal roundworms. Members of the family are intestinal parasites, infecting all classes of vertebrates. It includes a number of genera,Anderson RC (2000)''Nematode Parasites of Vertebrates. Their Development and Transmission, 2nd ed.''CAB International, Wallingford, Oxon, UK, pp. 245-315. the most well known of which are: *'' Amplicaecum'' *'' Angusticaecum'' *''Ascaris'' *†'' Ascarites'' (fossil)Poinar Jr, G. and Boucot, A. J. (2006) Evidence of intestinal parasites of dinosaurs. ''Parasitology'', 133: 245-249. *''Baylisascaris'' *'' Crossophorus'' *'' Dujardinascaris'' *''Hexametra'' *'' Lagochilascaris'' *'' Ophidascaris'' *''Parascaris'' *'' Polydelphis'' *'' Seuratascaris'' *''Toxascaris'' *''Toxocara'' *'' Travassoascaris'' ''Ascaris lumbricoides'' is the main ascarid parasite of humans, causing ascariasis Ascariasis is a disease caused by the parasitic roundworm ''Ascaris lumbricoides''. Infections have no sympto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascaris
''Ascaris'' is a genus of parasitic nematode worms known as the "small intestinal roundworms", which is a type of parasitic worm. One species, ''Ascaris lumbricoides'', affects humans and causes the disease ascariasis. Another species, ''Ascaris suum'', typically infects pigs. ''Parascaris equorum'', the equine roundworm, is also commonly called an "ascarid". Their eggs are deposited in feces and soil. Plants with the eggs on them infect any organism that consumes them. ''A. lumbricoides'' is the largest intestinal roundworm and is the most common helminth infection of humans worldwide. Infestation can cause morbidity by compromising nutritional status, affecting cognitive processes, inducing tissue reactions such as granuloma to larval stages, and by causing intestinal obstruction, which can be fatal. Morphology * Adult: cylindrical shape, creamy white or pinkish in color * Male: average 15–30 cm (6–12 inches); more slender than the female * Female: average 20–35&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
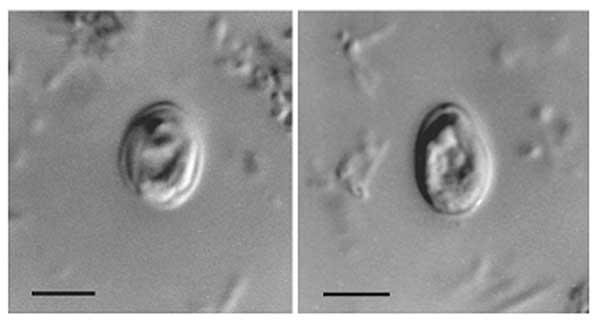
Toxocara Cati
''Toxocara cati'', also known as the feline roundworm, is a parasite of cats and other felids. It is one of the most common nematodes of cats, infecting both wild and domestic felids worldwide. Adult worms are localised in the gut of the host. In adult cats, the infection – which is called toxocariasis – is usually asymptomatic. However, massive infection in juvenile cats can be fatal. Feline roundworms are brownish-yellow to cream-colored to pink and may be up to 10 cm in length. Adults have short, wide cervical alae giving their anterior ends the distinct appearance of an arrow (hence their name, ''toxo'', meaning arrow, and ''cara,'' meaning head). Eggs are pitted ovals with a width of 65 μm and a length of about 75 μm making them invisible to the human eye. The larvae are so small that they are easily transmitted from an adult female to her nursing kittens through her milk. Transmission Wild felids can become infected from a variety of sources; the pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascariasis
Ascariasis is a disease caused by the parasitic roundworm '' Ascaris lumbricoides''. Infections have no symptoms in more than 85% of cases, especially if the number of worms is small. Symptoms increase with the number of worms present and may include shortness of breath and fever in the beginning of the disease. These may be followed by symptoms of abdominal swelling, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Children are most commonly affected, and in this age group the infection may also cause poor weight gain, malnutrition, and learning problems. Infection occurs by ingestion of food or drink contaminated with ''Ascaris'' eggs from feces. The eggs hatch in the intestines, the larvae burrow through the gut wall, and migrate to the lungs via the blood. There they break into the alveoli and pass up the trachea, where they are coughed up and may be swallowed. The larvae then pass through the stomach for a second time into the intestine, where they become adult worms. It is a type of soil- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxascaris
''Toxascaris leonina'' is a common parasitic roundworm found in dogs, cats, foxes, and related host species. ''T. leonina'' is an ascarid nematode, a worldwide distributed helminth parasite which is in a division of eukaryotic parasites that, unlike external parasites such as lice and fleas, live inside their host. The definitive hosts of ''T. leonina'' include canids (dogs, foxes, etc.) and felines (cats), while the intermediate hosts are usually rodents, such as mice or rats. Infection occurs in the definitive host when the animal eats an infected rodent. While ''T. leonina'' can occur in either dogs or cats, it is far more frequent in cats. A coprolite containing ''T. leonina'' eggs was excavated in Argentina's Catamarca Province and dated to 17002–16573 years old. This finding indicates that ''T. leonina'' has existed in South America since at least the Late Pleistocene. Life cycle The life cycle of ''T. leonina'' is fairly simple. Eggs are ingested and hatch in the sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nematoda
The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant-parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a broad range of environments. Less formally, they are categorized as Helminths, but are taxonomically classified along with arthropods, tardigrades and other moulting animals in the clade Ecdysozoa, and unlike flatworms, have tubular digestive systems with openings at both ends. Like tardigrades, they have a reduced number of Hox genes, but their sister phylum Nematomorpha has kept the ancestral protostome Hox genotype, which shows that the reduction has occurred within the nematode phylum. Nematode species can be difficult to distinguish from one another. Consequently, estimates of the number of nematode species described to date vary by author and may change rapidly over time. A 2013 survey of animal biodiversity published in the mega jou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baylisascaris
''Baylisascaris'' is a genus of roundworms that infect more than fifty animal species. Life cycle ''Baylisascaris'' eggs are passed in feces and become active within a month. They can remain viable in the environment for years, withstanding heat and cold. Animals become infested either by swallowing the eggs or eating another animal infested with ''Baylisascaris.'' Disease progression After an animal swallows the eggs, the microscopic larvae hatch in the intestine and invade the intestinal wall. If they are in their definitive host they develop for several weeks, then enter the intestinal lumen, mature, mate, and produce eggs, which are carried out in the fecal stream. If the larvae are in a paratenic host, they break into the bloodstream and enter various organs, particularly the central nervous system. A great deal of damage occurs wherever the larva try to make a home. In response to the attack, the body attempts to destroy it by walling it off or killing it. The larva moves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nematode Families
The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant-parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a broad range of environments. Less formally, they are categorized as Helminths, but are taxonomically classified along with arthropods, tardigrades and other moulting animals in the clade Ecdysozoa, and unlike flatworms, have tubular digestive systems with openings at both ends. Like tardigrades, they have a reduced number of Hox genes, but their sister phylum Nematomorpha has kept the ancestral protostome Hox genotype, which shows that the reduction has occurred within the nematode phylum. Nematode species can be difficult to distinguish from one another. Consequently, estimates of the number of nematode species described to date vary by author and may change rapidly over time. A 2013 survey of animal biodiversity published in the mega jou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitic Nematodes Of Vertebrates
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the broomrapes. There are six major parasitic strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), vector-transmitted parasitism, parasitoidism, and micropredation. One major axis of classification concerns invasiveness: an endoparasite lives inside the host' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intestinal Parasites
An intestinal parasite infection is a condition in which a parasite infects the gastro-intestinal tract of humans and other animals. Such parasites can live anywhere in the body, but most prefer the intestinal wall. Routes of exposure and infection include ingestion of undercooked meat, drinking infected water, fecal-oral transmission and skin absorption. Some types of helminths and protozoa are classified as intestinal parasites that cause infection—those that reside in the intestines. These infections can damage or sicken the host (humans or other animals). If the intestinal parasite infection is caused by helminths, the infection is called helminthiasis. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms depend on the type of infection. Intestinal parasites produce a variety of symptoms in those affected, most of which manifest themselves in gastrointestinal complications and general weakness. Gastrointestinal conditions include inflammation of the small and/or large intestine, diar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascaris Lumbricoides
''Ascaris lumbricoides'' is a large parasitic worm that causes ascariasis in humans. A roundworm of genus '' Ascaris'', it is the most common parasitic worm in humans. An estimated one-sixth of the human population is at some point infected by a roundworm such as ''A. lumbricoides''; people living in tropical and subtropical countries are at greater risk of infection. It has been proposed that ''Ascaris lumbricoides'' and '' Ascaris suum'' (pig roundworm) are the same species. Lifecycle ''Ascaris lumbricoides'', a roundworm, infects humans via the fecal-oral route. Eggs released by adult females are shed in feces. Unfertilized eggs are often observed in fecal samples but never become infective. Fertilized eggs embryonate and become infectious after 18 days to several weeks in soil, depending on the environmental conditions (optimum: moist, warm, shaded soil).Parasites - Ascariasis. (14 February 2018). Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/ascariasis/biology.html Infect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)