|
Andachtsbild
''Andachtsbilder'' (singular ''Andachtsbild'', German for devotional image) is a German term often used in English in art history for Christian devotional images designed as aids for prayer or contemplation. The images "generally show holy figures extracted from a narrative context to form a highly focused, and often very emotionally powerful, vignette". The term is especially used of Northern Gothic art around the 14th and 15th centuries, when new subjects such as the ''Pietà'', ''Pensive Christ'', '' Man of Sorrows'', '' Arma Christi'', ''Veil of Veronica'', the severed head of John the Baptist, and the ''Virgin of Sorrows'' became extremely popular. Subjects and genres Traditional subjects from the narrative of the Passion of Christ such as the '' Ecce Homo'' and the ''Crucifixion of Jesus'' were also treated in the same way. Though the ''Crucifix'' had been treated as an intense, isolated image for centuries, at least as far back as the 10th century '' Gero Cross'' i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arma Christi
Arma Christi ("weapons of Christ"), or the Instruments of the Passion, are the objects associated with the Passion of Jesus Christ in Christian symbolism and art. They are seen as arms in the sense of heraldry, and also as the weapons Christ used to achieve his conquest over Satan. There is a group, at a maximum of about 20 items, which are frequently used in Christian art, especially in the Late Middle Ages. Typically they surround either a cross or a figure of Christ of the Man of Sorrows type, either placed around the composition, or held by angels. History The prime member, the Cross, had been introduced to Christian art in the 4th century as the ''crux invicta'', a symbol of victory. As a group they have a long tradition in iconography, dating back to the 9th century; the Utrecht Psalter of 830 is an example, though the only one from the Early Middle Ages known to Gertrud Schiller. This reflected an increase in theological interest in the sufferings of Christ at the ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pensive Christ
The Pensive Christ (german: Christus im Elend – 'Christ in Distress' or ''Christus in der Rast''; pl, Chrystus Frasobliwy – 'Worried Christ'; lt, Rūpintojėlis) is a subject in Christian iconography depicting a contemplating Jesus, sitting with his head supported by his hand with the Crown of Thorns and marks of his flagellation. It is, therefore, a picture of Jesus shortly before his crucifixion, although more an andachtsbild or devotional subject than intended to show an actual moment in the narrative of the Passion of Christ. The Pensive Christ is much more common in sculpture than in painting, where the similar Man of Sorrows is more often depicted (in this Jesus is shown with the wounds of the crucifixion). Development of the image Similar images are known from Neolithic sculptures in Europe, dating several thousand years before Christ. The first known depictions of the Pensive Christ occur in northern German sculptures from the latter half of the 14th century, tak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veronicas Svetteduk Av Domenico Fetti
The Veronicas is an Australian pop duo from Brisbane. The group was formed in 2004 by identical twin sisters Lisa and Jessica Origliasso. In 2005, the Veronicas released their debut studio album, titled '' The Secret Life of...'', which peaked at number two on the Australian Album Chart and was certified 4× platinum by Australian Recording Industry Association (ARIA) for selling over 280,000 copies. The album spawned five singles, led by " 4ever", three of which were top ten singles in Australia. In 2007, the duo released their second studio album, ''Hook Me Up'', which also peaked at number two in Australia and was certified 2× platinum for selling over 140,000 copies. The album garnered four Australian top ten singles. The album's title track, "Hook Me Up", was the Veronicas' first number one single in Australia, while " Untouched" was an international top-ten hit. Following a lengthy hiatus (broken only by the July 2012 release of the Australian top-40 single "Lolita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crucifix
A crucifix (from Latin ''cruci fixus'' meaning "(one) fixed to a cross") is a cross with an image of Jesus on it, as distinct from a bare cross. The representation of Jesus himself on the cross is referred to in English as the ''corpus'' (Latin for "body"). The crucifix is a principal symbol for many groups of Christians, and one of the most common forms of the Crucifixion in the arts. It is especially important in the Roman Rite of the Roman Catholic Church, but is also used in the Eastern Orthodox Church, most Oriental Orthodox Churches (except the Armenian & Syriac Church), and the Eastern Catholic Churches, as well as by the Lutheran, Moravian and Anglican Churches. The symbol is less common in churches of other Protestant denominations, and in the Assyrian Church of the East and Armenian Apostolic Church, which prefer to use a cross without the figure of Jesus (the ''corpus''). The crucifix emphasizes Jesus' sacrifice—his death by crucifixion, which Christians believ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic States
The Baltic states, et, Balti riigid or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, and the OECD. The three sovereign states on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea are sometimes referred to as the "Baltic nations", less often and in historical circumstances also as the "Baltic republics", the "Baltic lands", or simply the Baltics. All three Baltic countries are classified as high-income economies by the World Bank and maintain a very high Human Development Index. The three governments engage in intergovernmental and parliamentary cooperation. There is also frequent cooperation in foreign and security policy, defence, energy, and transportation. The term "Baltic states" ("countries", "nations", or similar) cannot be used unambiguously in the context of cultural areas, national identity, or language. While the majori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchy Of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Lithuanians, who were at the time a polytheistic nation born from several united Baltic tribes from Aukštaitija. The Grand Duchy expanded to include large portions of the former Kievan Rus' and other neighbouring states, including what is now Lithuania, Belarus and parts of Ukraine, Latvia, Poland, Russia and Moldova. At its greatest extent, in the 15th century, it was the largest state in Europe. It was a multi-ethnic and multiconfessional state, with great diversity in languages, religion, and cultural heritage. The consolidation of the Lithuanian lands began in the late 13th century. Mindaugas, the first ruler of the Grand Duchy, was crowned as Catholic King of Lithuania in 1253. The pagan state was targeted in a religious crusad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars. From the accession of Otto I in 962 until the twelfth century, the Empire was the most powerful monarchy in Europe. Andrew Holt characterizes it as "perhaps the most powerful European state of the Middle Ages". The functioning of government depended on the harmonic cooperation (dubbed ''consensual rulership'' by Bernd Schneidmüller) between monarch and vassals but this harmony was disturbed during the Salian period. The empire reached the apex of territorial expansion and power under the House of Hohenstaufen in the mid-thirteenth century, but overextending led to partial collapse. On 25 December 800, Pope Leo III crowned the Frankish king Charlemagne as emperor, reviving the title in Western Europe, more than three centuries after the fall of the earlier ancient West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
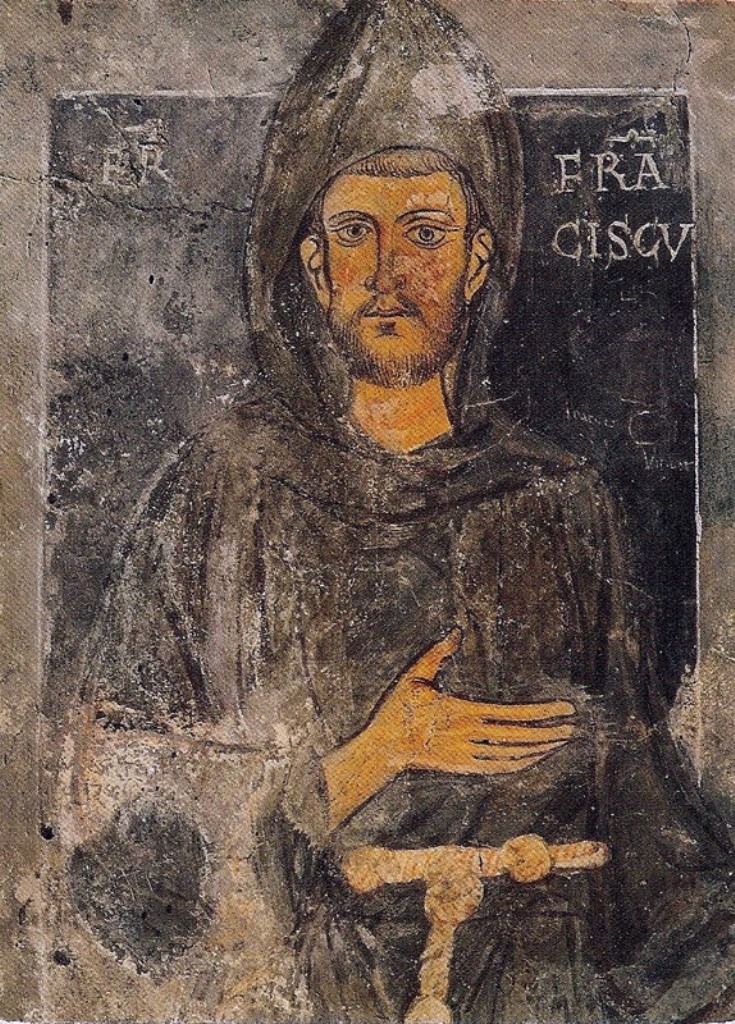
Affective Meditation
Affective meditation is a Christian spiritual practice originating in Medieval Europe by which a pilgrim, worshipper, or other follower of Christ seeks to imagine the sights, sounds, tastes, smells, movement, and tactility of specific scenes from canonical Gospels and their characters, with particular emphasis on empathising with the compassion and suffering of Jesus and the joys and sorrows of the Virgin Mary, leading to the authentic and spontaneous expression of emotion. History Middle Ages Affective meditation is the spiritual practice around which the tradition and philosophy of affective piety revolves, and was initiated by Saint Anselm of Canterbury, subsequently by Bernard of Clairvaux, and latterly by Francis of Assisi, who are credited with spawning an expressive form of worship through which members of the clergy, monastic orders, and laity visualized and envisioned scenes from the life of Christ with which they empathized to such degree that their compassio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Renaissance). Around 1300, centuries of prosperity and growth in Europe came to a halt. A series of famines and plagues, including the Great Famine of 1315–1317 and the Black Death, reduced the population to around half of what it had been before the calamities. Along with depopulation came social unrest and endemic warfare. France and England experienced serious peasant uprisings, such as the Jacquerie and the Peasants' Revolt, as well as over a century of intermittent conflict, the Hundred Years' War. To add to the many problems of the period, the unity of the Catholic Church was temporarily shattered by the Western Schism. Collectively, those events are sometimes called the Crisis of the Late Middle Ages. Despite the crises, the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Mysticism
The Friends of God (German: Gottesfreunde; or gotesvriunde) was a medieval mystical group of both ecclesiastical and lay persons within the Catholic Church (though it nearly became a separate sect) and a center of German mysticism. It was founded between 1339 and 1343 during the Avignon Papacy of the Western Schism, a time of great turmoil for the Catholic Church. The Friends of God were originally centered in Basel, Switzerland and were also fairly important in Strasbourg and Cologne. Some late-nineteenth century writers made large claims for the movement, seeing it both as influential in fourteenth-century mysticism and as a precursor of the Protestant Reformation. Modern studies of the movement have emphasised the derivative and often second-rate character of its mystical literature, and its limited impact on medieval literature in Germany. Some of the movement's ideas still prefigured the Protestant reformation. Name The name "Friends of God" may have been influenced by var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devotio Moderna
Devotio Moderna (Latin; lit., Modern Devotion) was a movement for religious reform, calling for apostolic renewal through the rediscovery of genuine pious practices such as humility, obedience, and simplicity of life. It began in the late 14th-century, largely through the work of Gerard Groote,''Devotio Moderna'' by John H. Van Engen 1988 pages 7-12''The Westminster Dictionary of Christian Spirituality'' by Gordon S. Wakefield 1983 ISBN pages 113-114 and flourished in the Low Countries and Germany in the 15th century, but came to an end with the Protestant Reformation. It is most known today through its influence on Thomas à Kempis, the author of ''The Imitation of Christ'', a book which has proved highly influential for centuries. The Devotio Moderna wrote in IJssellands, a written language which stood in between Middle Dutch and Middle Low German. Origins The origins of the movement likely stem from the Congregation of Windesheim, though it has so far proved elusive to locate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franciscan
, image = FrancescoCoA PioM.svg , image_size = 200px , caption = A cross, Christ's arm and Saint Francis's arm, a universal symbol of the Franciscans , abbreviation = OFM , predecessor = , merged = , formation = , founder = Francis of Assisi , founding_location = , extinction = , merger = , type = Mendicant Order of Pontifical Right for men , status = , purpose = , headquarters = Via S. Maria Mediatrice 25, 00165 Rome, Italy , location = , coords = , region = , services = , membership = 12,476 members (8,512 priests) as of 2020 , language = , sec_gen = , leader_title = Motto , leader_name = ''Pax et bonum'' ''Peace and llgood'' , leader_title2 = Minister General , leader_name2 = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |