|
Alexandrite
The mineral or gemstone chrysoberyl is an aluminate of beryllium with the formula Be Al2 O4. The name chrysoberyl is derived from the Greek words χρυσός ''chrysos'' and βήρυλλος ''beryllos'', meaning "a gold-white spar". Despite the similarity of their names, chrysoberyl and beryl are two completely different gemstones, although they both contain beryllium. Chrysoberyl is the third-hardest frequently encountered natural gemstone and lies at 8.5 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, between corundum (9) and topaz (8). An interesting feature of its crystals are the cyclic twins called ''trillings''. These twinned crystals have a hexagonal appearance, but are the result of a triplet of twins with each "twin" oriented at 120° to its neighbors and taking up 120° of the cyclic trilling. If only two of the three possible twin orientations are present, a V-shaped twin results. Ordinary chrysoberyl is yellowish-green and transparent to translucent. When the mineral ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Oxide Minerals
The oxide mineral class includes those minerals in which the oxide anion (O2−) is bonded to one or more metal alloys. The hydroxide-bearing minerals are typically included in the oxide class. Minerals with complex anion groups such as the Silicate mineral, silicates, Sulfate mineral, sulfates, carbonate mineral, carbonates and Phosphate mineral, phosphates are classed separately. Simple oxides *XO form **Periclase group ***Periclase ***Manganosite **Zincite group ***Zincite ***Bromellite ***Tenorite ***Litharge * form **Cuprite **Ice * form **Hematite group ***Corundum ***Hematite ***Ilmenite * form **Rutile group ***Rutile ***Pyrolusite ***Cassiterite **Baddeleyite **Uraninite **Thorianite * form **Spinel group ***Spinel ***Gahnite ***Magnetite ***Franklinite ***Chromite **Chrysoberyl **Columbite *Hydroxide subgroup: **Brucite **Manganite **Romanèchite **Goethite group: ***Diaspore ***Goethite Nickel–Strunz class 4: oxides Internationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Victorian Era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the reign of Queen Victoria, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. Slightly different definitions are sometimes used. The era followed the Georgian era and preceded the Edwardian era, and its later half overlaps with the first part of the ''Belle Époque'' era of continental Europe. Various liberalising political reforms took place in the UK, including expanding the electoral franchise. The Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine caused mass death in Ireland early in the period. The British Empire had relatively peaceful relations with the other great powers. It participated in various military conflicts mainly against minor powers. The British Empire expanded during this period and was the predominant power in the world. Victorian society valued a high standard of personal conduct across all sections of society. The Victorian morality, emphasis on morality gave impetus to soc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pegmatitic
A pegmatite is an igneous rock showing a very coarse texture, with large interlocking crystals usually greater in size than and sometimes greater than . Most pegmatites are composed of quartz, feldspar, and mica, having a similar silicic composition to granite. However, rarer intermediate composition and mafic pegmatites are known. Many of the world's largest crystals are found within pegmatites. These include crystals of microcline, quartz, mica, spodumene, beryl, and tourmaline. Some individual crystals are over long. Most pegmatites are thought to form from the last fluid fraction of a large crystallizing magma body. This residual fluid is highly enriched in volatiles and trace elements, and its very low viscosity allows components to migrate rapidly to join an existing crystal rather than coming together to form new crystals. This allows a few very large crystals to form. While most pegmatites have a simple composition of minerals common in ordinary igneous ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cabochon
A cabochon (; ) is a gemstone that has been shaped and polished, as opposed to faceted. The resulting form is usually a convex (rounded) obverse with a flat reverse. Cabochon was the default method of preparing gemstones before gemstone cutting developed. Application Cutting ''en cabochon'' (French: "in the manner of a cabochon") is usually applied to opaque gems, while faceting is usually used for transparent stones. Hardness is also taken into account as softer gemstones with a hardness lower than 7 on the Mohs hardness scale are easily scratched, mainly by silicon dioxide in dust and grit. This would quickly make translucent gems unattractive—instead they are polished as cabochons, making the scratches less evident. In asteriated stones such as star sapphires and chatoyant stones such as cat's eye chrysoberyl, a domed cabochon cut can show the star or eye, which would not be visible in a faceted cut. The usual shape for cutting cabochons is an ellipse, because the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cat Senses
Cat senses are adaptations that allow cats to be highly efficient predators. Cats are good at detecting movement in low light, have an acute sense of hearing and smell, and their sense of touch is enhanced by long whiskers that protrude from their heads and bodies. These senses evolved to allow cats to hunt effectively at dawn and dusk. Sight Cats have a ''tapetum lucidum'', which is a reflective layer behind the retina that sends light that passes through the retina back into the eye. They also have a high number of Rod cell, rods in their retina that are sensitive to dim light. While these improve the ability to see in darkness and enable cats to see using roughly one-sixth the amount of light that humans need, they appear to reduce net visual acuity, thus detracting when light is abundant. A cat's visual acuity is anywhere from 20/100 to 20/200, which means a cat has to be at 6 metres to see what an average human can see at 20 or 30 metres. Cats seem to be nearsighted, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Chatoyancy
In gemology, chatoyancy ( ), also called chatoyance or the cat's eye effect, is an optical phenomenon, optical reflectance effect seen in certain gemstones. (Historically, the term has applied specifically to gems; in woods and other materials the effect is more broadly known as "figure" or iridescence.) Coined from the French , meaning cat's eye, the chatoyant effect is typically characterized by one or more well-defined bands of reflected light, reminiscent of a cat's eye, which appear to glide across a gem's surface as the object is moved, or when the observer moves while viewing it. Chatoyancy is caused by the presence of fibrous structures within the material, such as in tiger's eye quartz, or by fibrous inclusions and cavities, as seen in cat's eye chrysoberyl, in which the effect is caused by the presence of titanium dioxide, which aligns perpendicularly to produce the effect. Description Chatoyancy in the gemstone chrysoberyl is induced by the presence of the minera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Incandescent Light
An incandescent light bulb, also known as an incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe, is an electric light that produces illumination by Joule heating a #Filament, filament until it incandescence, glows. The filament is enclosed in a glass bulb that is either vacuum, evacuated or filled with inert gas to protect the filament from oxidation. Electric current is supplied to the filament by terminals or wires embedded in the glass. A bulb socket provides mechanical support and electrical connections. Incandescent bulbs are manufactured in a wide range of sizes, light output, and voltage ratings, from 1.5 volts to about 300 volts. They require no external Regulator (automatic control), regulating equipment, have low manufacturing costs, and work equally well on either alternating current or direct current. As a result, the incandescent bulb became widely used in household and commercial lighting, for portable lighting such as table lamps, car headlamps, and flashlights, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Color Temperature
Color temperature is a parameter describing the color of a visible light source by comparing it to the color of light emitted by an idealized opaque, non-reflective body. The temperature of the ideal emitter that matches the color most closely is defined as the color temperature of the original visible light source. The color temperature scale describes only the ''color'' of light emitted by a light source, which may actually be at a different (and often much lower) temperature. Color temperature has applications in lighting, photography, videography, publishing, manufacturing, astrophysics, and other fields. In practice, color temperature is most meaningful for light sources that correspond somewhat closely to the color of some black body, i.e., light in a range going from red to orange to yellow to white to bluish white. Although the concept of correlated color temperature extends the definition to any visible light, the color temperature of a green or a purple light rar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats. In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves), phase'' on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, troughs, or zero crossings. Wavelength is a characteristic of both traveling waves and standing waves, as well as other spatial wave patterns. The multiplicative inverse, inverse of the wavelength is called the ''spatial frequency''. Wavelength is commonly designated by the Greek letter lambda (''λ''). For a modulated wave, ''wavelength'' may refer to the carrier wavelength of the signal. The term ''wavelength'' may also apply to the repeating envelope (mathematics), envelope of modulated waves or waves formed by Interference (wave propagation), interference of several sinusoids. Assuming a sinusoidal wave moving at a fixed phase velocity, wave speed, wavelength is inversely proportion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Polarization (waves)
, or , is a property of transverse waves which specifies the geometrical orientation of the oscillations. In a transverse wave, the direction of the oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the wave. One example of a polarized transverse wave is vibrations traveling along a taut string, for example, in a musical instrument like a guitar string. Depending on how the string is plucked, the vibrations can be in a vertical direction, horizontal direction, or at any angle perpendicular to the string. In contrast, in longitudinal waves, such as sound waves in a liquid or gas, the displacement of the particles in the oscillation is always in the direction of propagation, so these waves do not exhibit polarization. Transverse waves that exhibit polarization include electromagnetic waves such as light and radio waves, gravitational waves, and transverse sound waves ( shear waves) in solids. An electromagnetic wave such as light consists of a coupled oscillating el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
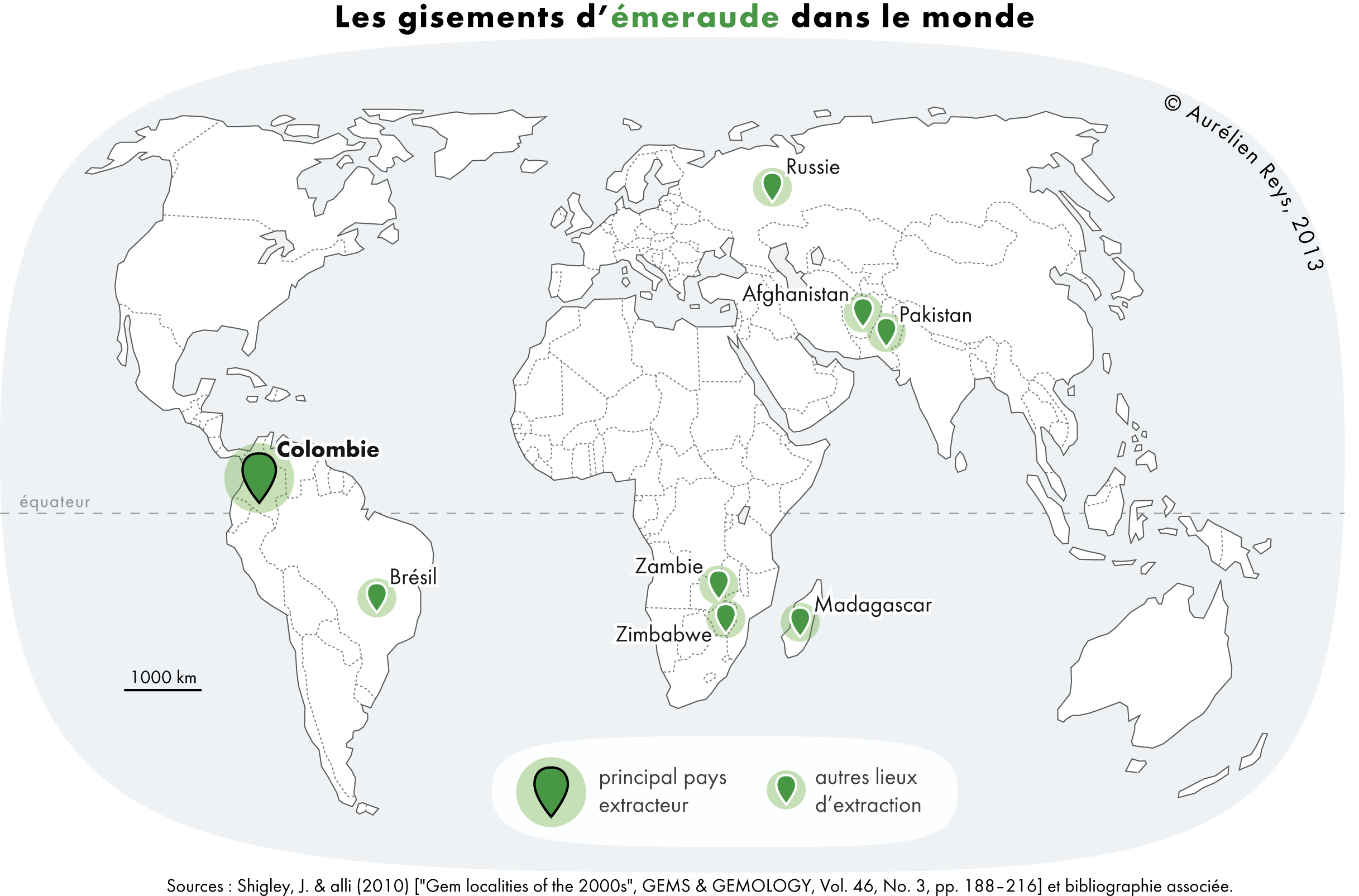
Emerald
Emerald is a gemstone and a variety of the mineral beryl (Be3Al2(SiO3)6) colored green by trace amounts of chromium or sometimes vanadium.Hurlbut, Cornelius S. Jr., and Kammerling, Robert C. (1991). ''Gemology'', John Wiley & Sons, New York, p. 203, . Beryl has a hardness of 7.5–8 on the Mohs scale. Most emeralds have many inclusions, so their toughness (resistance to breakage) is classified as generally poor. Emerald is a cyclosilicate. Etymology The word "emerald" is derived (via and ), from Vulgar Latin: ''esmaralda/esmaraldus'', a variant of Latin ''smaragdus'', which was via (smáragdos; "green gem"). The Greek word may have a Semitic, Sanskrit or Persian origin. According to ''Webster's Dictionary'' the term emerald was first used in the 14th century. Properties determining value Emeralds, like all colored gemstones, are graded using four basic parameters known as "the four ''C''s": ''color'', ''clarity,'' ''cut'' and ''carat weight''. Normally, in grading ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pleochroic
Pleochroism is an optical phenomenon in which a substance has different colors when observed at different angles, especially with polarized light. Etymology The roots of the word are from Greek (). It was first made compound in the German term ''Pleochroismus'' by mineralogist Wilhelm Haidinger in 1854, in the journal ''Annalen der Physik und Chemie''. Its first known English usage is by geologist James Dana in 1854. Background Anisotropic crystals will have optical properties that vary with the direction of light. The direction of the electric field determines the polarization of light, and crystals will respond in different ways if this angle is changed. These kinds of crystals have one or two optical axes. If absorption of light varies with the angle relative to the optical axis in a crystal then pleochroism results. Anisotropic crystals have double refraction of light where light of different polarizations is bent different amounts by the crystal, and therefore follows ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |