|
Adelospondyl
Adelospondyli is an order of elongated, presumably aquatic, Carboniferous amphibians (''sensu lato''). They have a robust skull roofed with solid bone, and orbits located towards the front of the skull. The limbs were almost certainly absent, although some historical sources reported them to be present. Despite the likely absence of limbs, adelospondyls retained a large part of the bony shoulder girdle. Adelospondyls have been assigned to a variety of groups in the past. They have traditionally been seen as members of the subclass Lepospondyli, related to other unusual early tetrapods such as " microsaurs", " nectrideans", and aïstopods. Analyses such as Ruta & Coates (2007) have offered an alternate classification scheme, arguing that adelospondyls were actually far removed from other lepospondyls, instead being stem-tetrapod stegocephalians closely related to the family Colosteidae. Most adelospondyls belong to the family Adelogyrinidae, and prior to 2003 the order and family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acherontiscus Skeletal
''Acherontiscus'' is an extinct genus of stegocephalians that lived in the Early Carboniferous (Mississippian era) of Scotland. The type and only species is ''Acherontiscus caledoniae'', named by paleontologist Robert Carroll in 1969. Members of this genus have an unusual combination of features which makes their placement within amphibian-grade tetrapods uncertain. They possess multi-bone vertebrae similar to those of embolomeres, but also a skull similar to lepospondyls. The only known specimen of ''Acherontiscus'' possessed an elongated body similar to that of a snake or eel. No limbs were preserved, and evidence for their presence in close relatives of ''Acherontiscus'' is dubious at best. Phylogenetic analyses created by Marcello Ruta and other paleontologists in the 2000s indicate that ''Acherontiscus'' is part of Adelospondyli, closely related to other snake-like animals such as '' Adelogyrinus'' and '' Dolichopareias''. Adelospondyls are traditionally placed within the gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
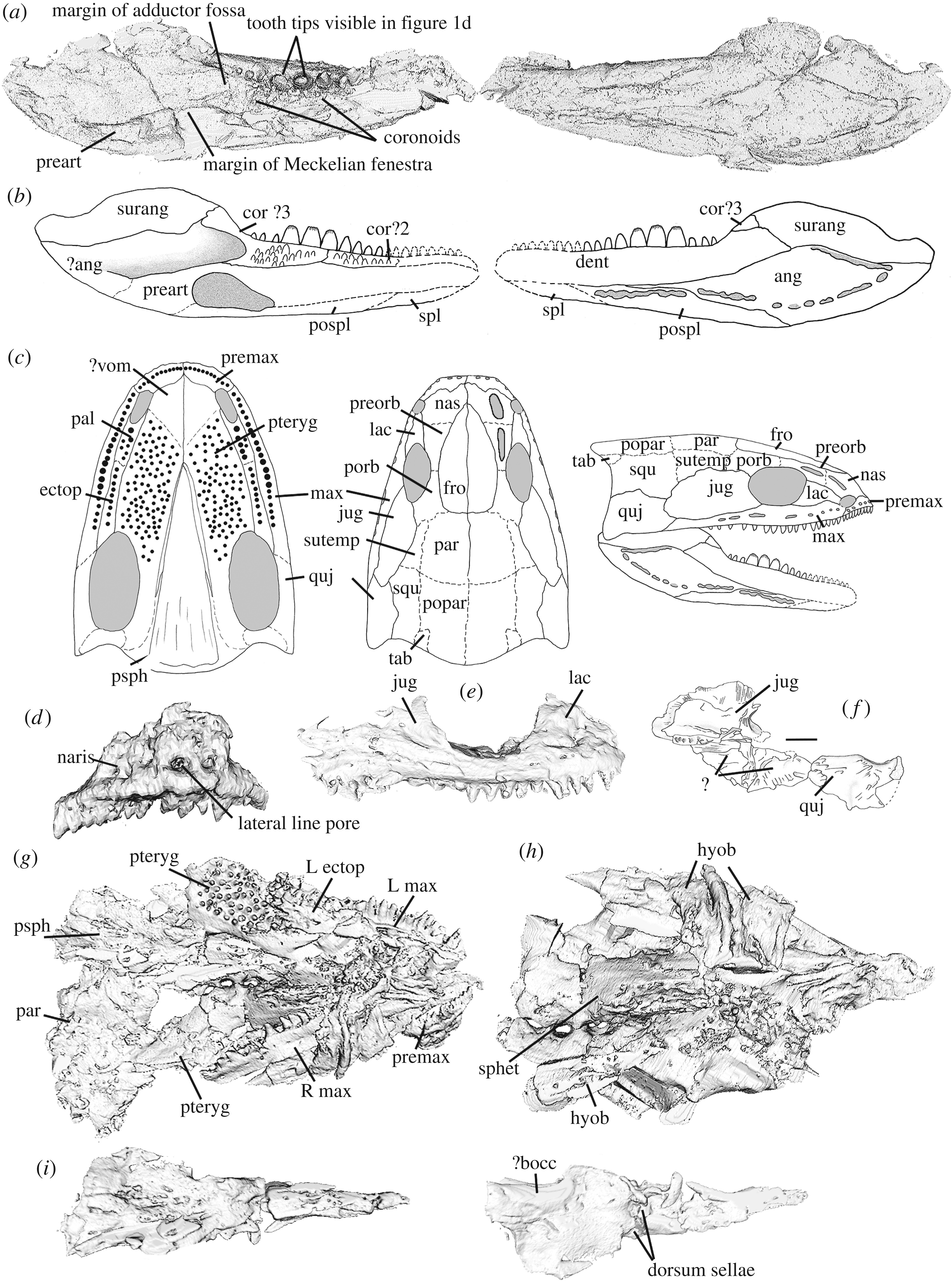
Adelogyrinidae
Adelospondyli is an Order (biology), order of elongated, presumably aquatic, Carboniferous amphibians (''Sensu, sensu lato''). They have a robust skull roofed with solid bone, and Orbit (anatomy), orbits located towards the front of the skull. The limbs were almost certainly absent, although some historical sources reported them to be present. Despite the likely absence of limbs, adelospondyls retained a large part of the bony shoulder girdle. Adelospondyls have been assigned to a variety of groups in the past. They have traditionally been seen as members of the subclass Lepospondyli, related to other unusual early Tetrapod, tetrapods such as "Microsauria, microsaurs", "Nectridea, nectrideans", and Aistopoda, aïstopods. Analyses such as Ruta & Coates (2007) have offered an alternate classification scheme, arguing that adelospondyls were actually far removed from other lepospondyls, instead being Crown group#Stem groups, stem-tetrapod Stegocephalia, stegocephalians closely related ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepospondyli
Lepospondyli is a diverse clade of early tetrapods. With the exception of one late-surviving lepospondyl from the Late Permian of Morocco ('' Diplocaulus minimus''), lepospondyls lived from the Visean stage of the Early Carboniferous to the Early Permian and were geographically restricted to what is now Europe and North America. Five major groups of lepospondyls are known: Adelospondyli; Aïstopoda; Lysorophia; Microsauria; and Nectridea. Lepospondyls have a diverse range of body forms and include species with newt-like, eel- or snake-like, and lizard-like forms. Various species were aquatic, semiaquatic, or terrestrial. None were large (the biggest genus, the diplocaulid '' Diplocaulus'', reached a meter in length, but most were much smaller), and they are assumed to have lived in specialized ecological niches not taken by the more numerous temnospondyl amphibians that coexisted with them in the Paleozoic. Lepospondyli was named in 1888 by Karl Alfred von Zittel, who coi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adelospondylus
''Adelospondylus'' is an extinct adelospondyl tetrapodomorph from the Carboniferous of what is now Scotland Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac .... References External links2D, stereoscopic, and 3D imagery of the type specimen of Adelospondylus watsoni Adelospondyli Mississippian sarcopterygians of Europe [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adelogyrinus
''Adelogyrinus'' is an extinct genus of adelospondyl tetrapodomorph Tetrapodomorpha (also known as Choanata) is a clade of vertebrates consisting of tetrapods (four-limbed vertebrates) and their closest sarcopterygian relatives that are more closely related to living tetrapods than to living lungfish. Advanced for ..., fossils of which were found in the Dunnet Shale of Scotland. References Adelospondyli Mississippian sarcopterygians of Europe Carboniferous Scotland Fossils of Scotland Fossil taxa described in 1928 Taxa named by D. M. S. Watson {{paleo-tetrapodomorph-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolichopareias
''Dolichopareias'' is an extinct genus of adelospondyl tetrapodomorph. See also * Prehistoric amphibian * List of prehistoric amphibians This list of prehistoric amphibians is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera from the fossil record that have ever been considered to be amphibians, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted gen ... References External links 2D, stereoscopic, and 3D imagery of the type specimen of Dolichopareias disjectus Adelospondyli Mississippian sarcopterygians of Europe [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeomolgophis
''Palaeomolgophis'' is an extinct genus of eel-like adelospondyl tetrapodomorph Tetrapodomorpha (also known as Choanata) is a clade of vertebrates consisting of tetrapods (four-limbed vertebrates) and their closest sarcopterygian relatives that are more closely related to living tetrapods than to living lungfish. Advanced for ...s containing a single species—''Palaeomolgophis scoticus''. Their limbs are much reduced, and they were probably fully aquatic. References External links 2D, stereoscopic, and 3D imagery of the type specimen of ''Palaeomolgophis scoticus'' Adelospondyli Mississippian sarcopterygians of Europe Fossils of Scotland Fossil taxa described in 1967 {{paleo-tetrapodomorph-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Classification
image:Hierarchical clustering diagram.png, 280px, Generalized scheme of taxonomy Taxonomy is a practice and science concerned with classification or categorization. Typically, there are two parts to it: the development of an underlying scheme of classes (a taxonomy) and the allocation of things to the classes (classification). Originally, taxonomy referred only to the Taxonomy (biology), classification of organisms on the basis of shared characteristics. Today it also has a more general sense. It may refer to the classification of things or concepts, as well as to the principles underlying such work. Thus a taxonomy can be used to organize species, documents, videos or anything else. A taxonomy organizes taxonomic units known as "taxa" (singular "taxon"). Many are hierarchy, hierarchies. One function of a taxonomy is to help users more easily find what they are searching for. This may be effected in ways that include a library classification system and a Taxonomy for search e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stegocephalia
Stegocephali (often spelled Stegocephalia, from Greek , lit. "roofed head") is a clade of vertebrate animals containing all fully limbed tetrapodomorphs. It is equivalent to a broad definition of the superclass Tetrapoda: under this broad definition, the term "tetrapod" applies to any animal descended from the first vertebrate with four limbs each with digits in the extremity ( pentadactyly), rather than fins of their sarcopterygian relatives. Stegocephalians include both the modern lineage of limbed vertebrates (the crown group tetrapods, including modern amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals) as well as a portion of the stem group, the earliest limbed tetrapodomorphs such as '' Ichthyostega'' and '' Acanthostega'', which evolved in the Devonian period long before the origin of the crown group. Many paleontologists prefer a stricter definition of Tetrapoda which applies solely to the crown group, excluding earlier types of limbed tetrapodomorphs. Stegocephali was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colosteidae
Colosteidae is a Family (biology), family of stegocephalians (stem-group tetrapod, tetrapods) that lived in the Carboniferous period. They possessed a variety of characteristics from different tetrapod or stem-tetrapod groups, which made them historically difficult to classify. They are now considered to be part of a lineage intermediate between the earliest Devonian terrestrial vertebrates (such as ''Ichthyostega''), and the different groups ancestral to all modern tetrapods, such as temnospondyls (probably ancestral to modern amphibians) and reptiliomorphs (ancestral to amniotes such as mammals, reptiles, and birds). Description Colosteids had elongated bodies, with an estimated 40 vertebrae, not including the tail. The skull is relatively flat and composed of many separate bones, like that of other stegocephalians. Colosteids lacked Otic notch, otic notches at the back of the head, unlike temnospondyls and other "labyrinthodonts". However, they did possess large mandibular an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysorophia
Lysorophia is an order (biology), order of fossorial Carboniferous and Permian Tetrapod, tetrapods within the Recumbirostra. Lysorophians resembled small snakes, as their bodies are extremely elongate. There is a single family (biology), family, the Molgophidae (previously known as Lysorophidae). Currently there are around five genus, genera included within Lysorophia, although many may not be valid. Description The skull is heavily built but with large lateral openings to accommodate jaw musculature, with small Orbit (anatomy), orbits restricted to the anterior edge of the large Fenestra (anatomy), fenestrae. The intertemporal, supratemporal, postfrontal, and jugal bones of the skull have disappeared. The mandibles are short and robust with a small number of large triangular teeth. Although it was initially thought that the maxilla and premaxilla were freely movable, detailed anatomical studies show that this is not the case. The braincase is extremely robust, suggesting that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |