|
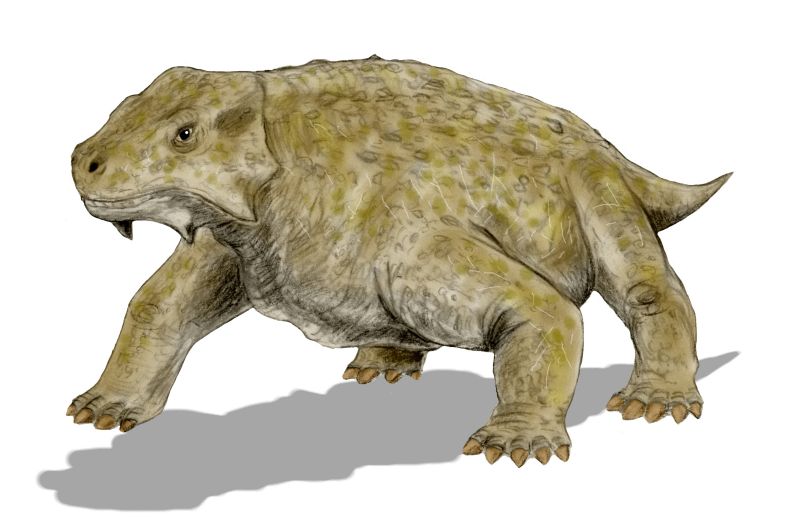
Tapinocephalians
The Tapinocephalia are one of the major groups of dinocephalian therapsids and the major herbivorous group. Tapinocephalia has been found to consist of three clades: Styracocephalidae, Titanosuchidae, and the very successful Tapinocephalidae. Notable tapinocephalians include ''Moschops'', ''Tapinocephalus'', and ''Titanosuchus''. Description Unlike anteosaurs and estemmenosuchids, tapinocephalians are primarily an African group. The estemmenosuchids and pareiasaurs may have occupied this paleo-bovine niche in the north. Only one tapinocephalian, ''Ulemosaurus'', is known from Russia. Earlier tapinocephalians were carnivorous or omnivorous. One such group was Titanosuchidae, which consisted of long-tailed predators that hunted herbivorous therapsids Therapsida is a clade comprising a major group of eupelycosaurian synapsids that includes mammals and their ancestors and close relatives. Many of the traits today seen as unique to mammals had their origin within early therapsids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Permian
The Guadalupian is the second and middle series/epoch of the Permian. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lopingian. It is named after the Guadalupe Mountains of New Mexico and Texas, and dates between 272.95 ± 0.5 – 259.1 ± 0.4 Mya. The series saw the rise of the therapsids, a minor extinction event called Olson's Extinction and a significant mass extinction called the end-Capitanian extinction event. The Guadalupian is also known as the Middle Permian. Name and background The Guadalupian is the second and middle series or epoch of the Permian. Previously called Middle Permian, the name of this epoch is part of a revision of Permian stratigraphy for standard global correlation. The name "Guadalupian" was first proposed in the early 1900s, and approved by the International Subcommission on Permian Stratigraphy in 1996. References to the Middle Permian still exist. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lopingian. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tapinocephalia
The Tapinocephalia are one of the major groups of dinocephalian therapsids and the major herbivorous group. Tapinocephalia has been found to consist of three clades: Styracocephalidae, Titanosuchidae, and the very successful Tapinocephalidae. Notable tapinocephalians include ''Moschops'', ''Tapinocephalus'', and '' Titanosuchus''. Description Unlike anteosaurs and estemmenosuchids, tapinocephalians are primarily an African group. The estemmenosuchids and pareiasaurs may have occupied this paleo-bovine niche in the north. Only one tapinocephalian, ''Ulemosaurus'', is known from Russia. Earlier tapinocephalians were carnivorous or omnivorous. One such group was Titanosuchidae, which consisted of long-tailed predators that hunted herbivorous therapsids Therapsida is a clade comprising a major group of eupelycosaurian synapsids that includes mammals and their ancestors and close relatives. Many of the traits today seen as unique to mammals had their origin within early therap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omnivorous
An omnivore () is an animal that regularly consumes significant quantities of both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nutrients and energy of the sources absorbed. Often, they have the ability to incorporate food sources such as algae, fungi, and bacteria into their diet. Omnivores come from diverse backgrounds that often independently evolved sophisticated consumption capabilities. For instance, dogs evolved from primarily carnivorous organisms ( Carnivora) while pigs evolved from primarily herbivorous organisms (Artiodactyla). Despite this, physical characteristics such as tooth morphology may be reliable indicators of diet in mammals, with such morphological adaptation having been observed in bears. The variety of different animals that are classified as omnivores can be placed into further sub-categories depending on their feeding behaviors. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnivorous
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose nutrition and energy requirements are met by consumption of animal tissues (mainly muscle, fat and other soft tissues) as food, whether through predation or scavenging. Nomenclature Mammal order The technical term for mammals in the order Carnivora is ''carnivoran'', and they are so-named because most member species in the group have a carnivorous diet, but the similarity of the name of the order and the name of the diet causes confusion. Many but not all carnivorans are meat eaters; a few, such as the large and small cats (Felidae) are ''obligate'' carnivores (see below). Other classes of carnivore are highly variable. The ursids (bears), for example: while the Arctic polar bear eats meat almost exclusively (more than 90% of its diet is meat), almost all other bear species are omnivorous, and one species, the gia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders of Russia, land borders with fourteen countries. Russia is the List of European countries by population, most populous country in Europe and the List of countries and dependencies by population, ninth-most populous country in the world. It is a Urbanization by sovereign state, highly urbanised country, with sixteen of its urban areas having more than 1 million inhabitants. Moscow, the List of metropolitan areas in Europe, most populous metropolitan area in Europe, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, while Saint Petersburg is its second-largest city and Society and culture in Saint Petersburg, cultural centre. Human settlement on the territory of modern Russia dates back to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
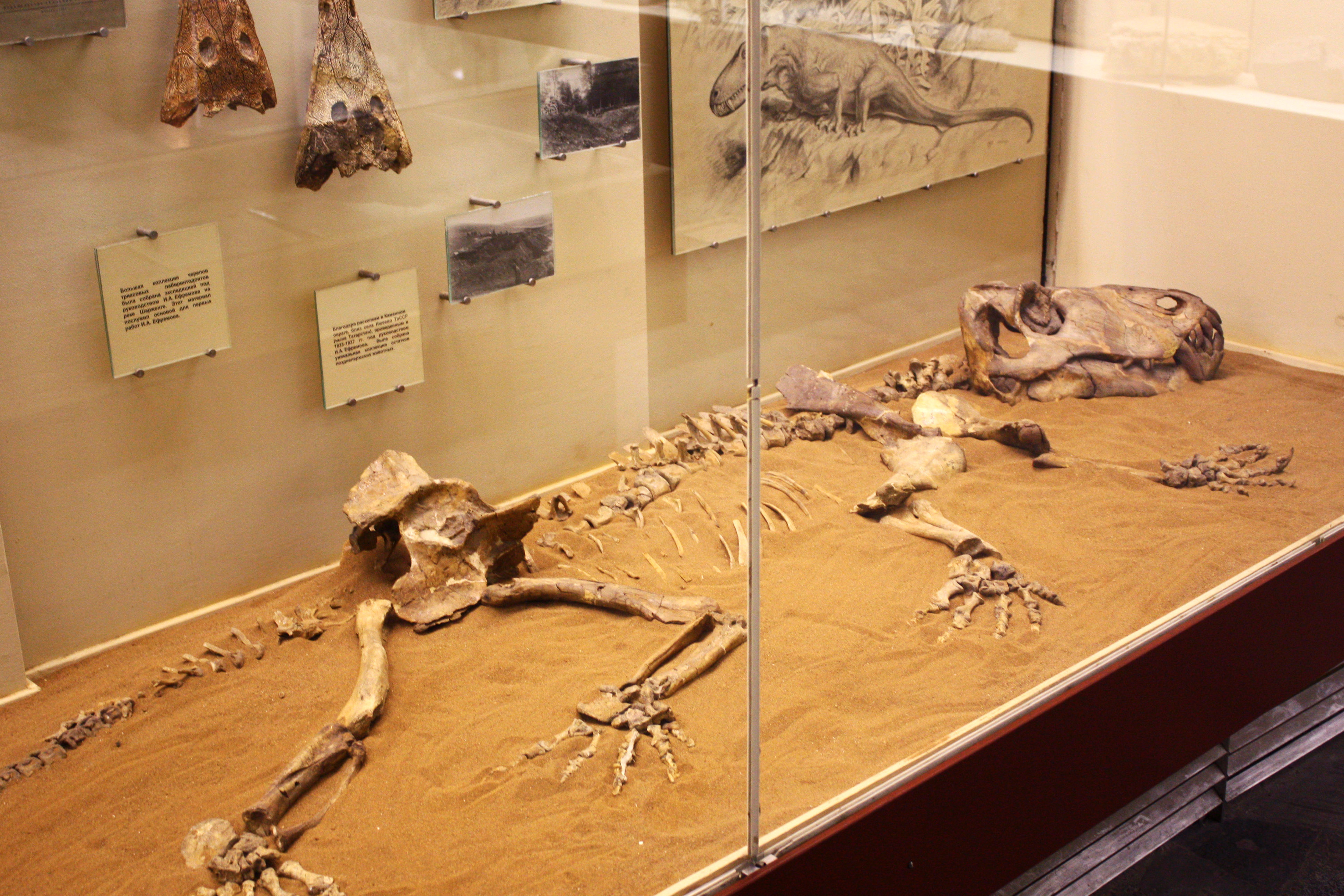
Ulemosaurus
''Ulemosaurus'' is an extinct genus of dinocephalian therapsids that lived 265 to 260 million years ago, at Isheevo in Russian Tatarstan. It was a tapinocephalid, a group of bulky herbivores which flourished in the Middle Permian. ''Ulemosaurus'' and other tapinocephalians disappeared at the end of the Middle Permian. Description Only several partial skeletons and skulls have been found. ''Ulemosaurus'' grew to 4-5 meters in length and weighed up to one ton.https://ar.culture.ru/en/subject/ulemozavr The skull bones are extremely dense: about at its thickest. This thickening is possibly related to head-butting behavior, as some researchers suggest. The species is considered a herbivore, but because the mandible is heavily constructed some palaeontologists consider it a carnivore, with the species being able to use muscle power to cut prey up with its incisors. Classification ''Ulemosaurus'' is a large '' Moschops''-like form from Russia; it is probably similar enough to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pareiasaur
Pareiasaurs (meaning "cheek lizards") are an extinct clade of large, herbivorous parareptiles. Members of the group were armoured with osteoderms which covered large areas of the body. They first appeared in southern Pangea during the Middle Permian, before becoming globally distributed during the Late Permian. Pareiasaurs were the largest reptiles of the Permian, some reaching sizes over , equivalent to the largest contemporary therapsids. Pareiasaurs became extinct in the end-Permian mass extinction event. Description Pareiasaurs ranged in size from long, with some species estimated to exceed in body mass. The limbs of many parieasaurs were extremely robust, likely to account for the increased stress on their limbs caused by their typically sprawling posture. The cow-sized '' Bunostegos'' differed from other pareiasaurs by having a more upright limb posture, being amongst the first amniotes to develop this trait. Pareiasaurs were protected by bony scutes called osteoderms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estemmenosuchid
Estemmenosuchidae is an extinct Family (biology), family of large, very early herbivore, herbivorous therapsids that flourished during the Guadalupian period. They are distinguished by horn-like structures, probably for Animal communication, display or agonistic behavior. Apart from the best known genus, ''Estemmenosuchus'', the group is poorly known. To date, their fossils are known only from the Perm, Russia, Perm region of Russia (a region referred to by Russian paleontologists as the Cis-Urals). Description Estemmenosuchids are among the most distinctive of the Permian tetrapods. The high and massive skull is equipped with a number of horns projecting both upwards and outwards, which were probably used for intra-specific display. The incisors and canine teeth are large, but those at the side are reduced, with a serrated apex, and may have helped to break up plant material, although they were too small to be of much use. The body is large and bulky, indicating a large digestive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anteosaur
Anteosaurs are a group of large, primitive carnivorous dinocephalian therapsids with large canines and incisors and short limbs, that are known from the Middle Permian of South Africa, Russia, China, and Brazil. Some grew very large, with skulls long, and were the largest predators of their time. They died out at the end of the Middle Permian, possibly as a result of the extinction of the herbivorous Tapinocephalia on which they may have fed. Description The Anteosauria are distinguished from the Tapinocephalia by several features, such as very large canines, cheek teeth with bulbous crowns, and an upturning of the premaxilla, so that the front of mouth curves strongly upwards. There is a tendency especially in more advanced forms such as ''Anteosaurus'' towards thickening of the bones of the top of the skull, indicating head-butting behavior. There is a large canal for the pineal organ (third eye); probably tied in with the animal's diurnal and seasonal cycles. The shoulde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanosuchus
''Titanosuchus ferox'' ("fierce titan crocodile") is an extinct species of dinocephalian therapsids that lived in the Middle Permian epoch in South Africa. Along with its close relatives, ''Jonkeria'' and ''Moschops'', ''Titanosuchus'' inhabited present-day South Africa around 265 million years ago, in the Late Permian. ''Titanosuchus'' is frequently cited as being a carnivore; however, this is based on specimens now assigned to ''Anteosaurus''. Instead, ''Titanosuchus'' was likely an omnivorous or herbivorous animal like the related ''Jonkeria''. ''Titanosuchus'' is known from fragmentary jaw and postcranial material, which can be distinguished from ''Jonkeria'' by the greater length of the limb bones. ''Parascapanodon'' and ''Scapanodon'' were once thought to be distinct genera, but are now considered to be junior synonyms of ''Titanosuchus''.Boonstra, L. D., 1969, The fauna of the Tapinocephalus zone (Beaufort beds of the Karoo): Annals of the South African Museum, v. 56, par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tapinocephalus
''Tapinocephalus'' ("low, depressed head") is an extinct genus of large herbivorous dinocephalians that lived during the Middle Permian Period in what is now South Africa. Only the type species, ''Tapinocephalus atherstonei'' is now considered valid for this genus. Discovery and naming Fossils of ''Tapinocephalus atherstonii'' were collected and donated to the British Museum by William Guybon Atherstone. They were described by Richard Owen, who described and named the species in 1876. He initially considered it a close relative of ''Pareiasaurus'' and classified both as members of Dinosauria. Based on the only remains of the skull known at the time—a poorly-preserved partial snout—he believed it had a low, broad skull similar to labyrinthodonts. Owen accordingly named it ''Tapinocephalus'', from Greek ταπεινός "low, depressed" and κεφαλή "head". Description These stocky, barrel-bodied animals were characterised by a massive bony skull roof and short weak sn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |