|
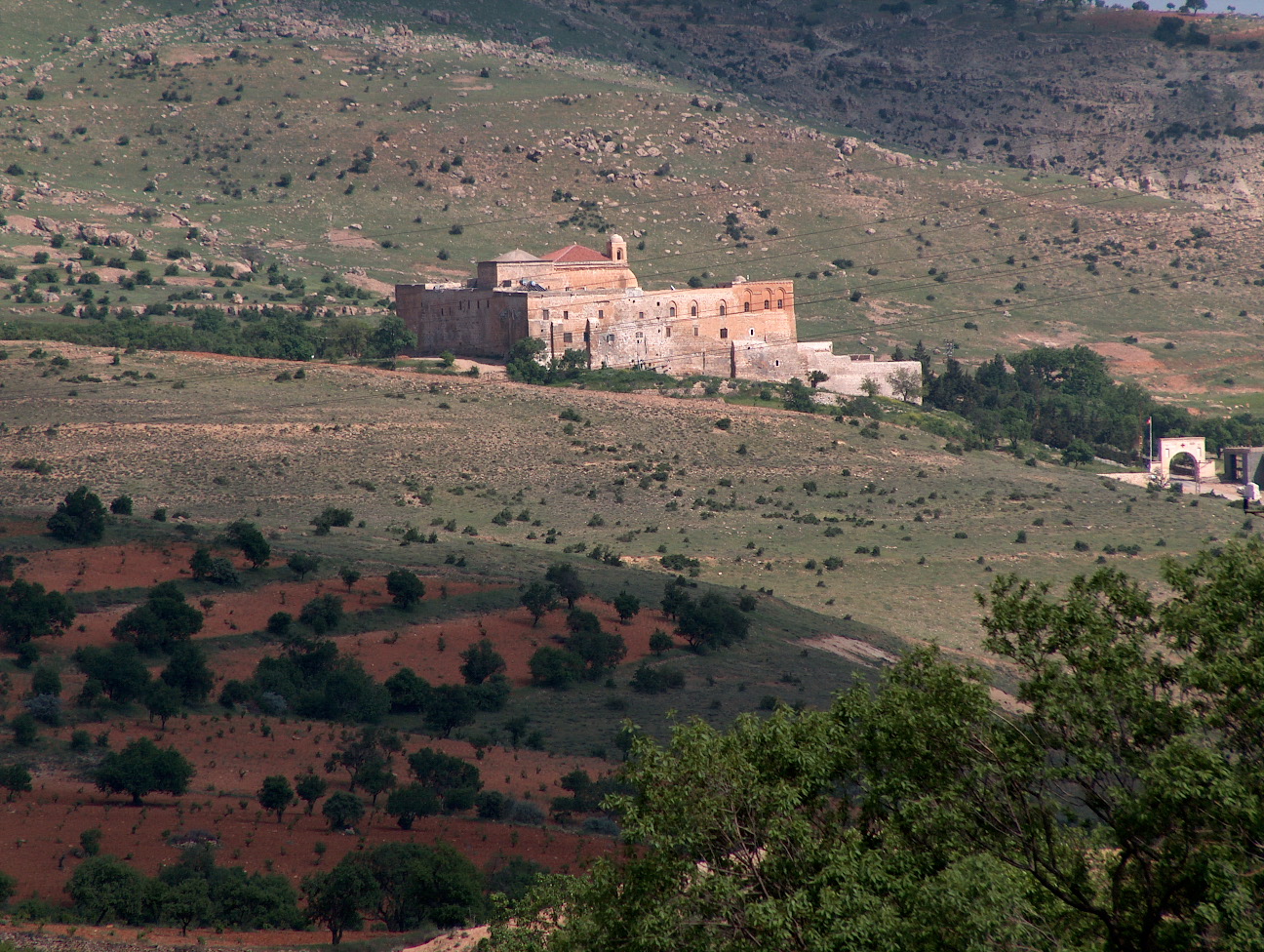
Sisauranon
Sisauranon, Sisauronon (), Sisaurana, or Sarbane was a Sasanian fortress city in the province of Arbayistan, located to the east of Nisibis at the edge of the north Syrian plain. It was situated near the border with the Byzantine Empire. History Sisauranon is mentioned by Procopius in the 6th century. On linguistic grounds, it is identified with the way-station Sarbane in the 5th-century ''Tabula Peutingeriana'', and with the modern site of Sirvan on the Turkish–Syrian border, whose name probably derives from the ancient settlement. The site is also variously mentioned as Sarbanon (τὸ Σαρβανῶν) in Theophanes the Confessor, Sisarbanon (τὸ Σισαρβάνων) in Theophylact Simocatta, and Sisara in Ammianus Marcellinus, as well as the variant forms of Sisaurion (Σισαύριον), Sisabranon (Σισαβράνων), Isauranon (Ἰσαυρανῶν) in various manuscripts of Procopius. The locality of Sambure in the ''Ravenna Cosmography'' may also refer to the sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lazic War
The Lazic War, also known as the Colchidian War or in Georgian historiography as the Great War of Egrisi, was fought between the Byzantine Empire and the Sasanian Empire for control of the ancient Georgia (country), Georgian region of Lazica. The Lazic War lasted for twenty years, from 541 to 562, and ended with the Fifty-Year Peace Treaty, which obligated the Byzantine Empire to pay tribute to Persia each year for the recognition of Lazica as a Byzantine vassal state by Persians. The Lazic War is narrated in detail in the works of Procopius and Agathias. Lazica Lazica, situated on the eastern shore of the Black Sea, and controlling important mountain passes across the Caucasus and to the Caspian Sea, had a key strategic importance for both empires. For Byzantines, it was a barrier against a Persian advance through Kingdom of Iberia (antiquity), Iberia to the coasts of the Black Sea. Persians on the other side hoped to gain access to the sea, and control a territory from which Iber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Populated Places In Turkey
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being used in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose cone to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forts
A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ("strong") and ("to make"). From very early history to modern times, defensive walls have often been necessary for cities to survive in an ever-changing world of invasion and conquest. Some settlements in the Indus Valley Civilization were the first small cities to be fortified. In ancient Greece, large cyclopean stone walls fitted without mortar had been built in Mycenaean Greece, such as the ancient site of Mycenae. A Greek '' phrourion'' was a fortified collection of buildings used as a military garrison, and is the equivalent of the Roman castellum or fortress. These constructions mainly served the purpose of a watch tower, to guard certain roads, passes, and borders. Though smaller than a real fortress, they acted a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sassanian Fortifications
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranian peoples, Iranians"), was an List of monarchs of Iran, Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, the length of the Sasanian dynasty's reign over ancient Iran was second only to the directly preceding Arsacid dynasty of Parthia. Founded by Ardashir I, whose rise coincided with the decline of Arsacid influence in the face of both internal and external strife, the House of Sasan was highly determined to restore the legacy of the Achaemenid Empire by expanding and consolidating the Iranian nation's dominions. Most notably, after defeating Artabanus IV of Parthia during the Battle of Hormozdgan in 224, it began competing far more zealously with the neighbouring Roman Empire than the Arsacids had, thus sparking a new phase of the Roman–Iranian Wars. This effort by Ardashir's dynasty ultimately re-established Iran as a major power of late an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhabdion
Rhabdion () was a Late Antique fortress of the Roman Empire, located on the Tur Abdin plateau to the northeast of Nisibis on the border with the Sasanian Empire. The fortress was later known as ''Qalʿat Haytham'' and is now identified with Hatem Tai, a fortification () in south-eastern Turkey. History It was probably built, along with Amida (Diyarbakır) and Cepha (Hasankeyf), by the emperor Constantius II (). According to the ''Life of Simeon of the Olives'', a certain Demetrius was ordered to build the castle in 350/351 AD and hence the fortress was also known as Demetrius' castle.After the cession by the emperor Jovian () of the five Transtigritine provinces and some border forts to the Sasanian Empire under Shapur II () as a result of the Persians' victory in Julian's Persian War, Rhabdion became the easternmost Roman frontier outpost, perhaps even ''de facto'' exclave in Persian territory, since the only road to it appears to have been from the south, passing across the pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Izla
Mount Izla ( ''Ṭūr Īzlā' ''),Thomas A. Carlson et al., “Izla — ܛܘܪܐ ܕܐܝܙܠܐ ” in The Syriac Gazetteer last modified January 14, 2014, http://syriaca.org/place/100. also Mountain of Nisibis or briefly in the 9th century Mount Kashyari, is a low mountain or ridge near Nisibis in what once a part of Assyria, then Sassanid Persian province of Asoristan, but is now southeastern Turkey, along the border with Syria. The ridge is the location of dozens of ancient monasteries which were built by the Assyrian Church of the East and Syriac Orthodox Church in the early centuries of Eastern Rite Christianity. In modern times, all of the monasteries are in ruins except for that of Mar Melke reconsecrated in the 1930s, Mor Yakub Monastery, founded in Dibek in 2012–2013, and the Monastery of Mor Augin which was refounded in 2008 after being abandoned in the 70's. Geography Though called a mountain, it is actually a ridge running from east to west, with a plateau o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Roads
Roman roads ( ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. They provided efficient means for the overland movement of Military history of ancient Rome, armies, officials, civilians, inland carriage of official communications, and Roman commerce, trade goods. Roman roads were of several kinds, ranging from small local roads to broad, long-distance highways built to connect cities, major towns and military bases. These major roads were often stone-paved and metaled, cambered for drainage, and were flanked by footpaths, Bridle path, bridleways and drainage ditches. They were laid along accurately surveyed courses, and some were cut through hills or conducted over rivers and ravines on bridgework. Sections could be supported over marshy ground on rafted or piled foundations.Corbishley, Mike: "The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of the three-age system, following the Stone Age and preceding the Iron Age. Conceived as a global era, the Bronze Age follows the Neolithic, with a transition period between the two known as the Chalcolithic. The final decades of the Bronze Age in the Mediterranean basin are often characterised as a period of widespread societal collapse known as the Late Bronze Age collapse (), although its severity and scope are debated among scholars. An ancient civilisation is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age if it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from producing areas elsewhere. Bronze Age cultures were the first to History of writing, develop writin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudo-Zacharias Rhetor
Pseudo-Zacharias Rhetor is the designation used by modern scholarship for the anonymous 6th-century author who compiled a twelve-part history in the Syriac language around 569. It contains portions of the otherwise lost ''Ecclesiastical History'' of the real Zacharias Rhetor. The history of Pseudo-Zacharias is found a single manuscript, on vellum, now British Library The British Library is the national library of the United Kingdom. Based in London, it is one of the largest libraries in the world, with an estimated collection of between 170 and 200 million items from multiple countries. As a legal deposit li ... Add MS 17202, dated to around 600. The title of the history as it appears in the manuscript is ''A Volume of Records of Events Which Have Happened in the World''. In addition to Zacharias Rhetor's ''Ecclesiastical History'', British Library Add MS 17202 also contains: *A work by Sylvester, bishop of Rome, on the conversion of the Emperor Constantine. *The finding of tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simeon Of The Olives
Simeon of the Olives (''Shimʿun Zaytuni'', 624–734) was a Syriac Orthodox bishop of Harran from Ḥabsenus in the eight century. He is attributed to have built or rebuilt several churches and monasteries in the region around Nisibis, such as the Mor Loʿozor Monastery. Biography According to his vita, Simeon was born in the village of Ḥabsenus in the Tur Abdin in 624/5, though others date his birth later to 657. He first learned how to read and write at his village church and was then sent to the monastic school at the Qartmin Abbey at the age of ten. At the age of fifteen he became a monk and at twenty-five, a priest. While still a youth, he was trampled to death at the feast of Mor Gabriel (possibly Gabriel's funeral) and miraculously revived upon being placed on the saint's tomb. Simeon also lived as a stylite for some time in the Monastery of the Column in Sīrwān close to Nisibis and finally became abbot of the Qartmin Abbey. At some point, his nephew David came up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comentiolus
Comentiolus (, ''Komentiolos''; died 602) was a prominent Eastern Roman (Byzantine) general at the close of the 6th century during the reign of Emperor Maurice (). He played a major role in Maurice's Balkan campaigns, and fought also in the East against the Sassanid Persians. Comentiolus was ultimately executed in 602 after the Byzantine army rebelled against Maurice and Emperor Phocas () usurped the throne. Biography Nothing is known of Comentiolus's early life, except that he hailed from Thrace. He first appears in 583, as an officer (''scribon'') in the '' Excubitores'', the imperial bodyguard, when he accompanied a Byzantine embassy to Bayan I (), the khagan of the Avars. According to the historian Theophylact Simocatta, he enraged the khagan with an outspoken statement, and was briefly imprisoned. It is likely that the close trust he shared with Maurice dates from the latter's time as commander of the ''Excubitores'', before his ascension to the throne. Throughout his c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |