|
Minicomputer
A minicomputer, or colloquially mini, is a type of general-purpose computer mostly developed from the mid-1960s, built significantly smaller and sold at a much lower price than mainframe computers . By 21st century-standards however, a mini is an exceptionally large machine. Minicomputers in the traditional technical sense covered here are only small relative to generally even earlier and much bigger machines. The class formed a distinct group with its own software architectures and operating systems. Minis were designed for control, instrumentation, human interaction, and communication switching, as distinct from calculation and record keeping. Many were sold indirectly to original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) for final end-use application. During the two-decade lifetime of the minicomputer class (1965–1985), almost 100 minicomputer vendor companies formed. Only a half-dozen remained by the mid-1980s. When single-chip CPU microprocessors appeared in the 1970s, the defini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
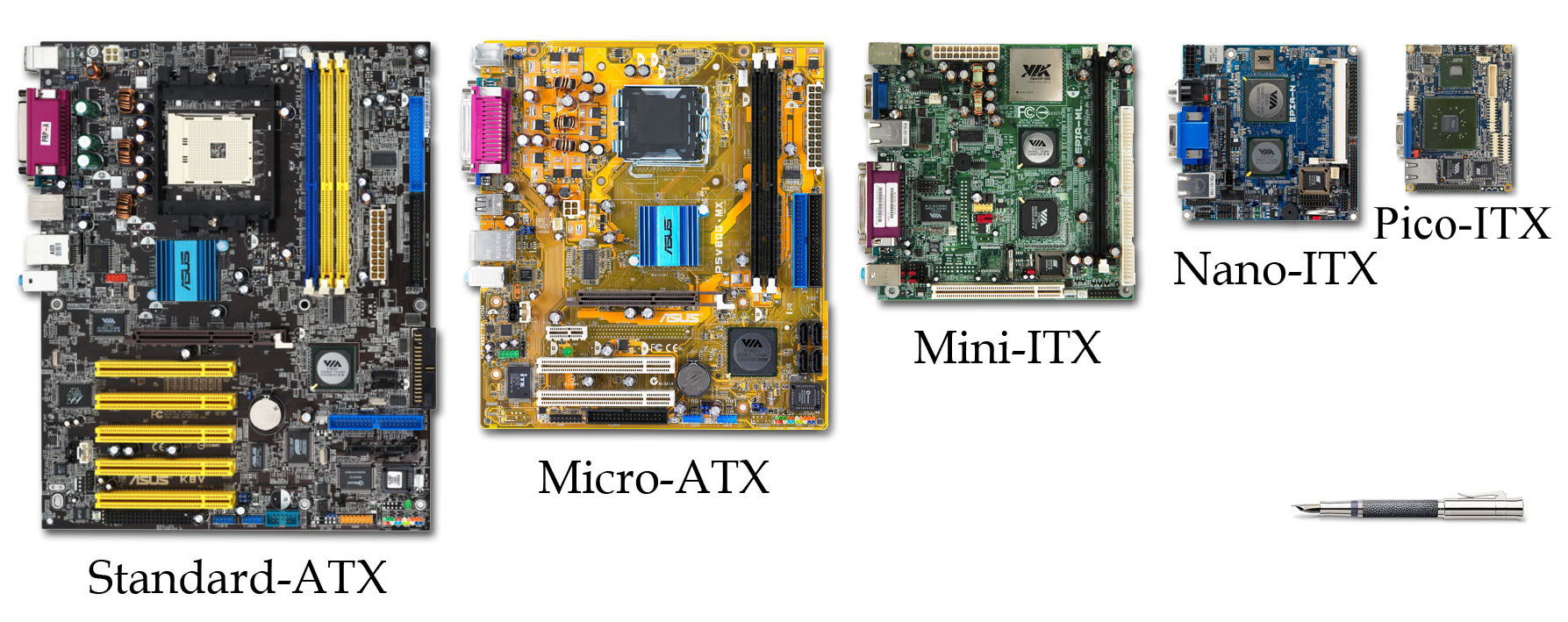
Small Form Factor (desktop And Motherboard)
Small form factor (SFF) is a classification of desktop computers and for some of their components, computer case, chassis and motherboard, to indicate that they are designed in accordance with one of several standardized form factor (design), form factors intended to minimize the volume and footprint of a desktop computer compared to the standard ATX form factor. For comparison purposes, the size of an SFF case is usually measured in litres. SFFs are available in a variety of sizes and shapes, including shoeboxes, cubes, and book-sized PCs. Their smaller and often lighter construction has made them popular as home theater PCs and as gaming computers for attending LAN parties. Manufacturers also emphasize the aesthetic and ergonomic design of SFFs since users are more likely to place them on top of a desk or carry them around. Advancements in technology combined with a reduced size enables a powerful computer to be a smaller size. Small form factor designs do not include computing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teletype Model 33
The Teletype Model 33 is an electromechanical teleprinter designed for light-duty office use. It is less rugged and cost less than earlier Teletype models. The Teletype Corporation introduced the Model 33 as a commercial product in 1963, after it had originally been designed for the United States Navy. The Model 33 was produced in three versions: * Model 33 ASR (Automatic Send and Receive), which has a built-in eight-hole punched tape reader and tape punch; * Model 33 KSR (Keyboard Send and Receive), which lacks the paper tape reader and punch; * Model 33 RO (Receive Only) which has neither a keyboard nor a reader/punch. The Model 33 was one of the first products to employ the newly-standardized ASCII character encoding method, which was first published in 1963. A companion Teletype Model 32 used the older, established five-bit Baudot code. Because of its low price and ASCII compatibility, the Model 33 was widely used, and the large quantity of teleprinters sold strongly influenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CDC 160
The CDC 160 series was a series of minicomputers built by Control Data Corporation. The CDC 160 and CDC 160-A were 12-bit minicomputers built from 1960 to 1965; the CDC 160G was a 13-bit minicomputer, with an extended version of the CDC 160-A instruction set, and a compatibility mode in which it did not use the 13th bit. The 160 was designed by Seymour Cray - reportedly over a long three-day weekend. It fit into the desk where its operator sat. The 160 architecture uses ones' complement arithmetic with end-around carry. NCR joint-marketed the 160-A under its own name for several years in the 1960s. Overview A publishing company that purchased a CDC 160-A described it as "a single user machine with no batch processing capability. Programmers and/or users would go to the computer room, sit at the console, load the paper tape bootstrap and start up a program." The CDC 160-A was a simple piece of hardware, and yet provided a variety of features which were scaled-down capabilitie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferranti Argus
Ferranti's Argus computers were a line of industrial control computers offered from the 1960s into the 1980s. Originally designed for a military role, a re-packaged Argus was the first digital computer to be used to directly control an entire factory. They were widely used in a variety of roles in Europe, particularly in the UK, where a small number continue to serve as monitoring and control systems for nuclear reactors. Original series Blue Envoy, hearing aid computer The original concept for the computer was developed as part of the Blue Envoy missile project. This was a very long-range surface-to-air missile system with a range on the order of . To reach these ranges, the missile was "lofted" in a nearly vertical trajectory at launch, flying as quickly as possible to high altitude where it suffered less drag during the subsequent long cruise toward the target. During the vertical climb, the missile's radar would not be able to see the target, so during this period it was com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
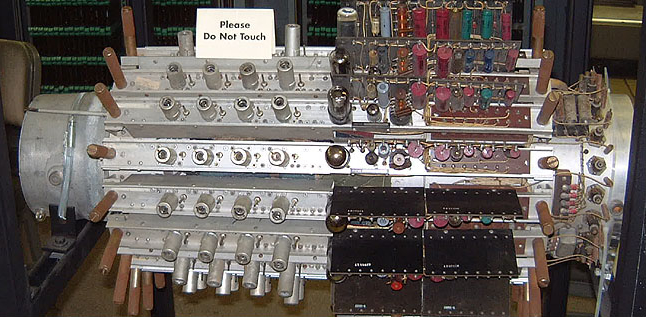
Plugboard
A plugboard or control panel (the term used depends on the application area) is an array of jack (connector), jacks or sockets (often called hubs) into which patch cords can be inserted to complete an electrical circuit. Control panels are sometimes used to direct the operation of unit record equipment, :Cryptographic hardware, cipher machines, and History of computing hardware#Digital computation, early computers. The array of holes is often contained in a flat removable panel that can be inserted into a machine and pressed against an array of contacts. This allows the machine to be quickly switched between different applications. The contacts on the machine are hard wired to the various devices that comprise the machine, such as relays, counters, inputs from each card reader column, outputs to a card punch column or printer position, and so on. The wiring on a plugboard connects these devices to perform a specific function, say reading cards and summing up the numbers punched ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Language
In computer programming, machine code is computer code consisting of machine language instructions, which are used to control a computer's central processing unit (CPU). For conventional binary computers, machine code is the binaryOn nonbinary machines it is, e.g., a decimal representation. representation of a computer program that is actually read and interpreted by the computer. A program in machine code consists of a sequence of machine instructions (possibly interspersed with data). Each machine code instruction causes the CPU to perform a specific task. Examples of such tasks include: # Load a word from memory to a CPU register # Execute an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) operation on one or more registers or memory locations # Jump or skip to an instruction that is not the next one In general, each architecture family (e.g., x86, ARM) has its own instruction set architecture (ISA), and hence its own specific machine code language. There are exceptions, such as the V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
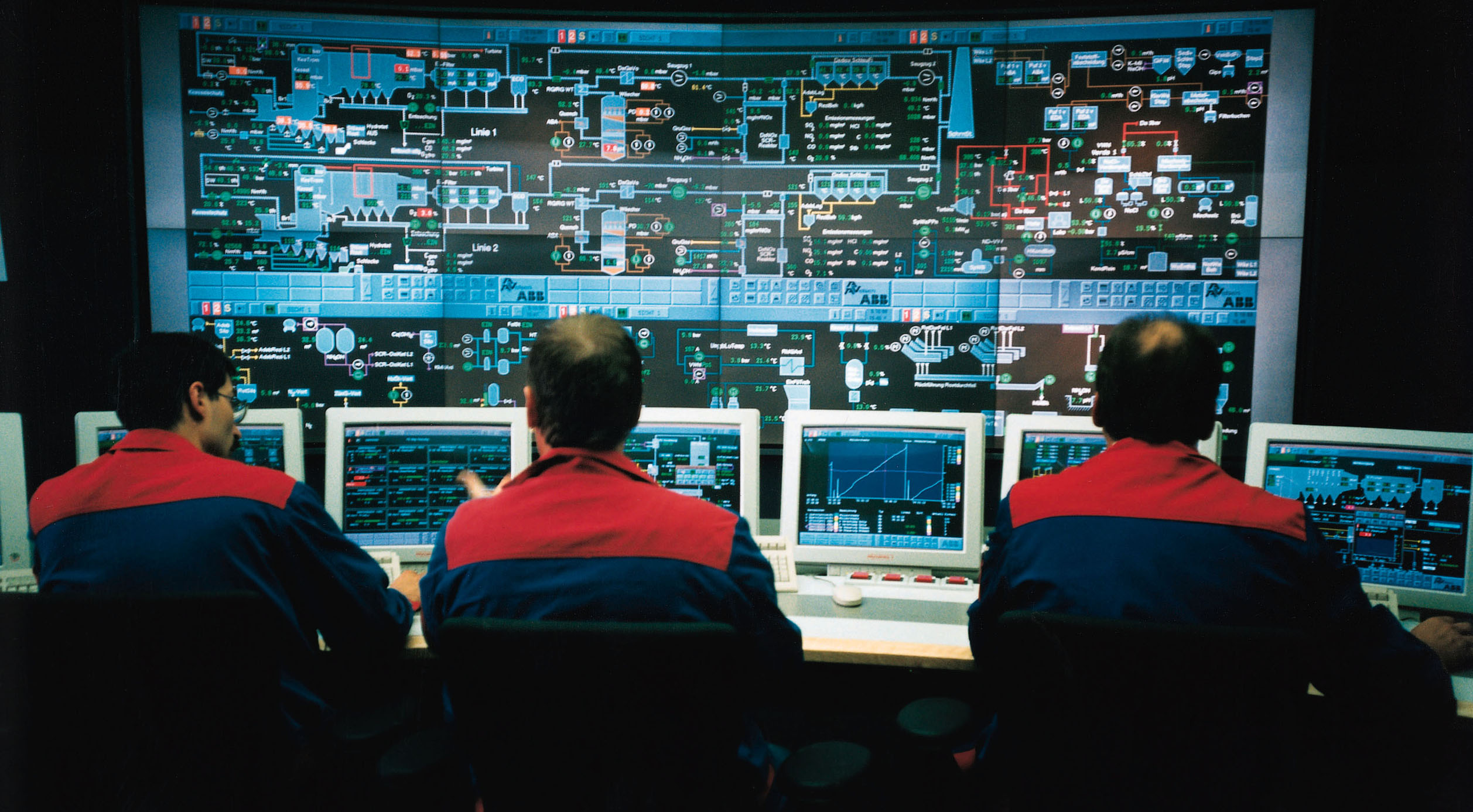
Process Control
Industrial process control (IPC) or simply process control is a system used in modern manufacturing which uses the principles of control theory and physical industrial control systems to monitor, control and optimize continuous Industrial processes, industrial production processes using control algorithms. This ensures that the industrial machines run smoothly and safely in factories and efficiently use energy to transform raw materials into high-quality finished products with reliable consistency while reducing Efficient energy use#Industry, energy waste and economic costs, something which could not be achieved purely by human manual control. In IPC, control theory provides the theoretical framework to understand system dynamics, predict outcomes and design control strategies to ensure predetermined objectives, utilizing concepts like feedback loops, stability analysis and controller design. On the other hand, the physical apparatus of IPC, based on automation technologies, cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delay-line Memory
Delay-line memory is a form of computer memory, mostly obsolete, that was used on some of the earliest Digital data, digital computers, and is reappearing in the form of #Optical_delay_lines, optical delay lines. Like many modern forms of electronic computer memory, delay-line memory was a memory refresh, refreshable memory, but as opposed to modern random-access memory, delay-line memory was Sequential access, sequential-access. Analog delay line technology had been used since the 1920s to delay the propagation of analog signals. When a delay line is used as a memory device, an amplifier and a pulse shaping, pulse shaper are connected between the output of the delay line and the input. These devices recirculate the signals from the output back into the input, creating a loop that maintains the signal as long as power is applied. The shaper ensures the pulses remain well-formed, removing any degradation due to losses in the medium. The memory capacity equals the time to transmit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGP-30
The LGP-30, standing for Librascope General Purpose and then Librascope General Precision, is an early off-the-shelf computer. It was manufactured by the Librascope company of Glendale, California (a division of General Precision Inc.), and sold and serviced by the Royal Precision Electronic Computer Company, a joint venture with the Royal McBee division of the Royal Typewriter Company. The LGP-30 was first manufactured in 1956, at a retail price of $47,000, . The LGP-30 was commonly referred to as a desk computer. Its height, width, and depth, excluding the typewriter shelf, was . It weighed about , and was mounted on sturdy casters which facilitated moving the unit. Design The primary design consultant for the Librascope computer was Stan Frankel, a Manhattan Project veteran and one of the first programmers of ENIAC, assisted by James Cass, at the time a graduate student at Caltech. They designed a usable computer with a minimal amount of hardware. The single addre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bendix G-15
The Bendix G-15 is a computer introduced in 1956 by the Bendix Corporation, Computer Division, Los Angeles, California. It is about and weighs about . The G-15 has a drum memory of 2,160 29-bit words, along with 20 words used for special purposes and rapid-access storage. The base system, without peripherals, cost $49,500. A working model cost around $60,000 (). It could also be rented for $1,485 per month. It was meant for scientific and industrial markets. The series was gradually discontinued when Control Data Corporation took over the Bendix computer division in 1963. The chief designer of the G-15 was Harry Huskey, who had worked with Alan Turing on the Automatic Computing Engine (ACE) in the United Kingdom and on the SWAC (computer), Standards Western Automatic Computer (SWAC) in the 1950s. He made most of the design while working as a professor at University of California, Berkeley (where his graduate students included Niklaus Wirth), and other universities. David C. Evan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNIVAC 1101
The ERA 1101, later renamed UNIVAC 1101, was a computer system designed and built by Engineering Research Associates (ERA) in the early 1950s and continued to be sold by the Remington Rand corporation after that company later purchased ERA. Its (initial) military model, the ERA Atlas, was the first stored-program computer that was moved from its site of manufacture and successfully installed at a distant site. Remington Rand used the 1101's architecture as the basis for a series of machines into the 1960s. History Codebreaking ERA was formed from a group of code-breakers working for the United States Navy during World War II. The team had built a number of code-breaking machines, similar to the more famous Colossus computer in England, but designed to attack World War II cryptography#Japan, Japanese codes. After the war the Navy was interested in keeping the team together even though they had to formally be turned out of Navy service. The result was ERA, which formed in St. Paul, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drum Memory
Drum memory was a magnetic data storage device invented by Gustav Tauschek in 1932 in Austria. Drums were widely used in the 1950s and into the 1960s as computer memory. Many early computers, called drum computers or drum machines, used drum memory as the main working memory of the computer. Some drums were also used as Auxiliary memory, secondary storage as for example various IBM_drum_storage, IBM drum storage drives and the UNIVAC FASTRAND series of drums. Drums were displaced as primary computer memory by magnetic core memory, which offered a better balance of size, speed, cost, reliability and potential for further improvements. Drums were then replaced by hard disk drives for secondary storage, which were both less expensive and offered denser storage. The manufacturing of drums ceased in the 1970s. Technical design A drum memory or drum storage unit contained a large metal cylinder, coated on the outside surface with a ferromagnetic recording material. It could be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |