|
Lok Sabha
The Lok Sabha, also known as the House of the People, is the lower house of India's bicameral Parliament, with the upper house being the Rajya Sabha. Members of the Lok Sabha are elected by an adult universal suffrage and a first-past-the-post system to represent their respective constituencies, and they hold their seats for five years or until the body is dissolved by the President on the advice of the council of ministers. The house meets in the Lok Sabha Chambers of the Parliament House, New Delhi. The maximum membership of the House allotted by the Constitution of India is 552 (Initially, in 1950, it was 500.) Currently, the house has 543 seats which are filled by the election of up to 543 elected members. Between 1952 and 2020, two additional members of the Anglo-Indian community were also nominated by the President of India on the advice of the Government of India, which was abolished in January 2020 by the 104th Constitutional Amendment Act, 2019. The new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th Lok Sabha
General elections are expected to be held in India between April and May 2024 to elect 543 members of the Lok Sabha. Background The tenure of the 17th Lok Sabha is scheduled to end on 16 June 2024. The previous general elections were held in April–May 2019. After the election, National Democratic Alliance, led by Bharatiya Janata Party, formed the union government, with Narendra Modi continuing as Prime Minister. Electoral system All 543 elected MPs are elected from single-member constituencies using first-past-the-post voting. The 104th amendment to the constitution abolished the two seats that were reserved for the Anglo-Indian community. Eligible voters must be Indian citizens, 18 years or older, an ordinary resident of the polling area of the constituency and registered to vote (name included in the electoral rolls), possess a valid voter identification card issued by the Election Commission of India or equivalent. Some people convicted of electoral or other offe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leader Of The Opposition In Lok Sabha
The Leader of the Opposition in Lok Sabha ( IAST: ) is an elected Member of Lok Sabha who leads the official opposition in the Lower House of the Parliament of India. The Leader of the Opposition is the parliamentary chairperson of the largest political party in the Lok Sabha that is not in government (provided that said political party has at least 10% of the seats in the Lok Sabha). The post is vacant since 26 May 2014, as no opposition party has 10% Seats. History In Lok Sabha until 1969, there was de facto opposition leader with no formal recognition, status or privilege. Later, the leader of the opposition was given official recognition and their salary and allowances was extended by the Act, 1977. Since then, the leader in the Lok Sabha should satisfy three conditions, namely, # he should be a member of the House # of the party in opposition to the Government having the greatest numerical strength and # be recognised by the Speaker of the Lok Sabha In December 1969, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower House
A lower house is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the upper house. Despite its official position "below" the upper house, in many legislatures worldwide, the lower house has come to wield more power or otherwise exert significant political influence. The lower house, typically, is the larger of the two chambers, meaning its members are more numerous. Common attributes In comparison with the upper house, lower houses frequently display certain characteristics (though they vary per jurisdiction). ;Powers: * In a parliamentary system, the lower house: **In the modern era, has much more power, usually based on restrictions against the upper house. **Is able to override the upper house in some ways. **Can vote a motion of no confidence against the government, as well as vote for or against any proposed candidate for head of government at the beginning of the parliamentary term. **Exceptions are Australia, where the Senate has considerable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitution Of India
The Constitution of India (IAST: ) is the supreme law of India. The document lays down the framework that demarcates fundamental political code, structure, procedures, powers, and duties of government institutions and sets out fundamental rights, directive principles, and the duties of citizens. It is the longest written national constitution in the world. It imparts constitutional supremacy (not parliamentary supremacy, since it was created by a constituent assembly rather than Parliament) and was adopted by its people with a declaration in its preamble. Parliament cannot override the constitution. It was adopted by the Constituent Assembly of India on 26 November 1949 and became effective on 26 January 1950. The constitution replaced the Government of India Act 1935 as the country's fundamental governing document, and the Dominion of India became the Republic of India. To ensure constitutional autochthony, its framers repealed prior acts of the British parliam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Delhi
New Delhi (, , ''Naī Dillī'') is the Capital city, capital of India and a part of the NCT Delhi, National Capital Territory of Delhi (NCT). New Delhi is the seat of all three branches of the government of India, hosting the Rashtrapati Bhavan, Parliament House (India), Parliament House, and the Supreme Court of India. New Delhi is a Municipal governance in India, municipality within the NCT, administered by the New Delhi Municipal Council, NDMC, which covers mostly Lutyens' Delhi and a few adjacent areas. The municipal area is part of a larger List of districts in India, administrative district, the New Delhi district. Although colloquially ''Delhi'' and ''New Delhi'' are used interchangeably to refer to the National Capital Territory of Delhi, both are distinct entities, with both the municipality and the New Delhi district forming a relatively small part of the megacity of Delhi. The National Capital Region (India), National Capital Region is a much larger entity compri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sansad Bhavan
The Parliament House ( IAST: ) in New Delhi is the seat of the Parliament of India. Its houses the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha which represent lower and upper houses respectively in India's bicameral parliament. At a distance of 750 meters from the Rashtrapati Bhavan, it is located on Sansad Marg which crosses the Central Vista and is surrounded by the Vijay Chowk, India Gate(All India War Memorial), National War Memorial (India), Vice President's House, Hyderabad House, Secretariat Building, Prime minister's office and residence, ministerial buildings and other administrative units of Indian government. The building was designed by the British architects Edwin Lutyens and Herbert Baker and was constructed between 1921 and 1927. It was opened in January 1927 as the seat of the Imperial Legislative Council. Following the end of British rule in India, it was taken over by the Constituent Assembly, and then by the Indian Parliament once India's Constitution came into for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Next Indian General Election
General elections are expected to be held in India by May 2024 to elect the members of the 18th Lok Sabha. Background The tenure of Lok Sabha is scheduled to end on 16 June 2024. The previous general elections were held in April–May 2019. After the election, National Democratic Alliance, led by Bharatiya Janata Party, formed the union government, with Narendra Modi continuing as Prime Minister. Electoral system All 543 elected MPs are elected from single-member constituencies using first-past-the-post voting. The 104th amendment to the constitution effectively abolished the two seats that were reserved for the Anglo-Indian community. Eligible voters must be Indian citizens, 18 years or older, an ordinary resident of the polling area of the constituency and registered to vote (name included in the electoral rolls), possess a valid voter identification card issued by the Election Commission of India or equivalent. Some people convicted of electoral or other off ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First-past-the-post Voting
In a first-past-the-post electoral system (FPTP or FPP), formally called single-member plurality voting (SMP) when used in single-member districts or informally choose-one voting in contrast to ranked voting, or score voting, voters cast their vote for a candidate of their choice, and the candidate who receives the most votes wins even if the top candidate gets less than 50%, which can happen when there are more than two popular candidates. As a winner-take-all method, FPTP often produces disproportional results (when electing members of an assembly, such as a parliament) in the sense that political parties do not get representation according to their share of the popular vote. This usually favours the largest party and parties with strong regional support to the detriment of smaller parties without a geographically concentrated base. Supporters of electoral reform are generally highly critical of FPTP because of this and point out other flaws, such as FPTP's vulnerability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of India
The Government of India ( ISO: ; often abbreviated as GoI), known as the Union Government or Central Government but often simply as the Centre, is the national government of the Republic of India, a federal democracy located in South Asia, consisting of 28 union states and eight union territories. Under the Constitution, there are three primary branches of government: the legislative, the executive and the judiciary, whose powers are vested in a bicameral Parliament, President, aided by the Council of Ministers, and the Supreme Court respectively. Through judicial evolution, the Parliament has lost its sovereignty as its amendments to the Constitution are subject to judicial intervention. Judicial appointments in India are unique in that the executive or legislature have negligible say. Etymology and history The Government of India Act 1833, passed by the British parliament, is the first such act of law with the epithet "Government of India". Basic structure The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
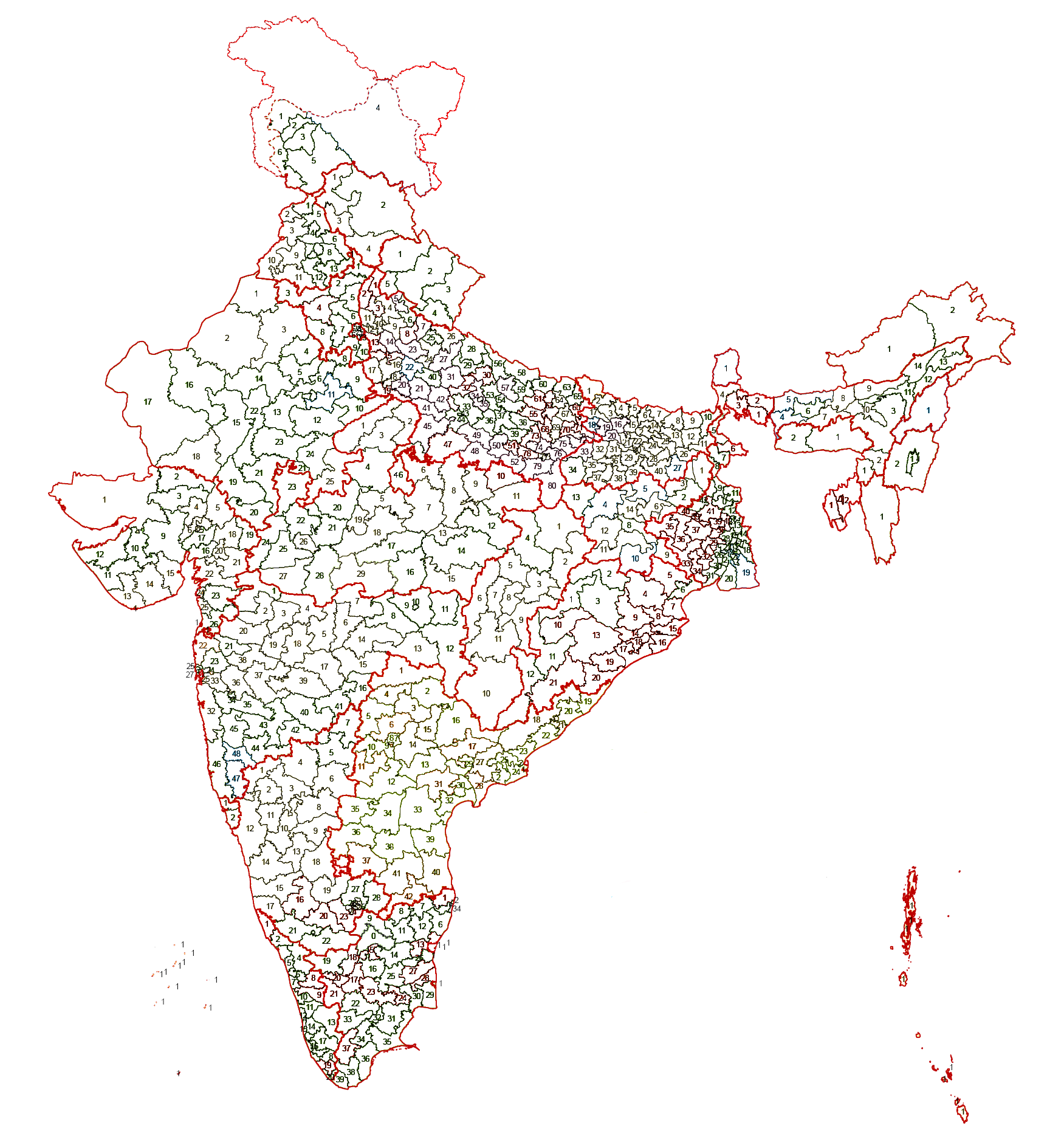
List Of Constituencies Of The Lok Sabha
The Lok Sabha, the lower house of the Parliament of India, is made up of Members of Parliament (MPs). Each MP, represents a single geographic constituency. There are currently 543 constituencies while maximum seats will fill up to 550 (after article 331- 2 seats reserved for Anglo Indian but by 104th Constitution Amendment article 331 is null by parliament , before this amendment maximum seat will 552) The maximum size of the Lok Sabha as outlined in the Constitution of India is 552 members, made up of up to 524 members representing people of 28 states and 19 members representing people of 8 Union territories on the basis of their population. Delimitation of constituencies Under the Delimitation Act of 2002, the Delimitation Commission of India has redefined the list of parliamentary constituencies, their constituent assembly segments and reservation status (whether reserved for Scheduled castes (SC) candidates or Scheduled tribes (ST) candidates or unreserved). 2008 Karnat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utpal Kumar Singh
Utpal Kumar Singh (born 29 July 1960) is a 1986–batch retired Indian Administrative Service (IAS) officer of Uttarakhand cadre who is currently serving as the Secretary General of the Lok Sabha since 30 November 2020. Early life Singh was born to Braj Kishore Singh and Annapurna singh in 1960. Personal life Singh was married to Nipunika Singh and his family have 1 children. Education Singh completed his master's degree in B.A (hons), M.A (History) from Delhi University and International Institute of Social Studies. He subsequently received a M.A in Public Policy and Management from a university in The Hague, Netherlands. Career Mr. Singh has also held several important positions at the center, including Additional Secretary, Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Singh, Utpal Kumar Indian Administrative Service officers People from Jamui district 1960 births Academic staff of Delhi University Living people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.png)