|
Geminids
The Geminids are a prolific meteor shower with 3200 Phaethon (which is thought to be an Apollo asteroid with a " rock comet" orbit.) being the parent body. Because of this, it would make this shower, along with the Quadrantids, the only major meteor showers not originating from a comet. The meteors from this shower are slow, they can be seen in December and usually peak around December 4–16, with the date of highest intensity being the morning of December 14. Current showers produce up to 120–160 meteors per hour under optimal conditions, peaking around 2:00 or 3:00. Geminids were first observed in 1862, much later than other showers such as the Perseids (36 AD) and Leonids (902 AD). Based on data from the Parker Solar Probe, a 2023 study suggested that the Geminids may have been formed by the catastrophic breakup of a comet that formed asteroids 2005 UD and 1999 YC in addition to Phaethon. Background The Geminid meteor shower is unique among celestial events as it o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
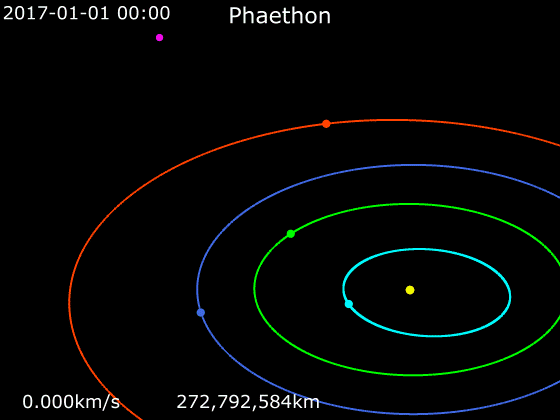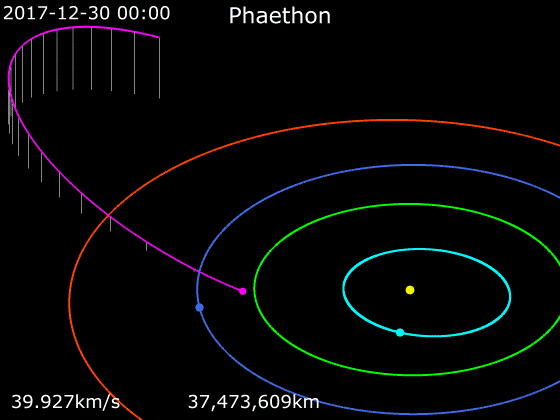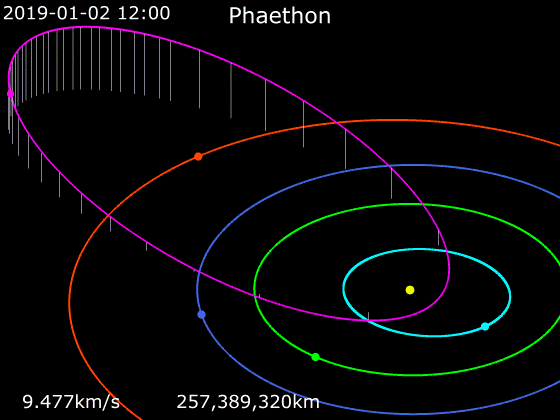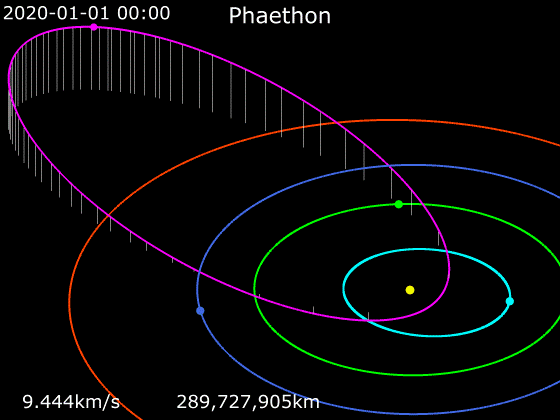
3200 Phaethon
3200 Phaethon (; previously sometimes spelled Phæton), provisionally designated , is an active Apollo asteroid with an orbit that brings it closer to the Sun than any other named asteroid (though there are numerous unnamed asteroids with smaller perihelia, such as ). For this reason, it was named after the Greek Hero, Phaëthon, son of the sun god Helios. It is in diameter and is the parent body of the Geminids meteor shower of mid-December. With an observation arc of 35+ years, it has a very well determined orbit. The 2017 Earth approach distance of about 10 million km was known with an accuracy of ±700 m. Discovery Phaethon was the first asteroid to be discovered using images from a spacecraft. Simon F. Green and John K. Davies discovered it in images from October 11, 1983, while searching Infrared Astronomical Satellite (IRAS) data for moving objects. It was formally announced on October 14 in IAUC 3878 along with optical confirmation by Charles T. Kowal, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waning Gibbous
A lunar phase or Moon phase is the apparent shape of the Moon's directly sunlit portion as viewed from the Earth. Because the Moon is tidally locked with the Earth, the same hemisphere is always facing the Earth. In common usage, the four major phases are the new moon, the first quarter, the full moon and the last quarter; the four minor phases are waxing crescent, waxing gibbous, waning gibbous, and waning crescent. A lunar month is the time between successive recurrences of the same phase: due to the eccentricity of the Moon's orbit, this duration is not perfectly constant but averages about 29.5 days. The appearance of the Moon (its phase) gradually changes over a lunar month as the relative orbital positions of the Moon around Earth, and Earth around the Sun, shift. The visible side of the Moon is sunlit to varying extents, depending on the position of the Moon in its orbit, with the sunlit portion varying from 0% (at new moon) to nearly 100% (at full moon). Phenomenon The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Quarter
A lunar phase or Moon phase is the apparent shape of the Moon's directly sunlit portion as viewed from the Earth. Because the Moon is tidally locked with the Earth, the same hemisphere is always facing the Earth. In common usage, the four major phases are the new moon, the first quarter, the full moon and the last quarter; the four minor phases are waxing crescent, waxing gibbous, waning gibbous, and waning crescent. A lunar month is the time between successive recurrences of the same phase: due to the eccentricity of the Moon's orbit, this duration is not perfectly constant but averages about 29.5 days. The appearance of the Moon (its phase) gradually changes over a lunar month as the relative orbital positions of the Moon around Earth, and Earth around the Sun, shift. The visible side of the Moon is sunlit to varying extents, depending on the position of the Moon in its orbit, with the sunlit portion varying from 0% (at new moon) to nearly 100% (at full moon). Phenomenon T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Moon
In astronomy, the new moon is the first lunar phase, when the Moon and Sun have the same ecliptic longitude. At this phase, the lunar disk is not visible to the naked eye, except when it is silhouetted against the Sun during a solar eclipse. The original meaning of the term 'new moon', which is still sometimes used in calendrical, non-astronomical contexts, is the first visible crescent of the Moon after conjunction with the Sun. This thin waxing crescent is briefly and faintly visible as the Moon gets lower in the western sky after sunset. The precise time and even the date of the appearance of the new moon by this definition will be influenced by the geographical location of the observer. The first crescent marks the beginning of the month in the Islamic calendar and in some lunisolar calendars such as the Hebrew calendar. In the Chinese calendar, the beginning of the month is marked by the last visible crescent of a waning Moon. The astronomical new moon occurs by def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waxing Crescent
A lunar phase or Moon phase is the apparent shape of the Moon's directly sunlit portion as viewed from the Earth. Because the Moon is tidally locked with the Earth, the same hemisphere is always facing the Earth. In common usage, the four major phases are the new moon, the first quarter, the full moon and the last quarter; the four minor phases are waxing crescent, waxing gibbous, waning gibbous, and waning crescent. A lunar month is the time between successive recurrences of the same phase: due to the eccentricity of the Moon's orbit, this duration is not perfectly constant but averages about 29.5 days. The appearance of the Moon (its phase) gradually changes over a lunar month as the relative orbital positions of the Moon around Earth, and Earth around the Sun, shift. The visible side of the Moon is sunlit to varying extents, depending on the position of the Moon in its orbit, with the sunlit portion varying from 0% (at new moon) to nearly 100% (at full moon). Phenomenon The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Meteor Organization
The International Meteor Organization (IMO) was formally founded in 1988 from predecessor gatherings over many years. IMO has several hundred members and was created in response to an ever-growing need for international cooperation on amateur and professional meteor work. The collection of meteor observations by several methods from all around the world ensures the comprehensive study of meteor showers and their relation to comets and interplanetary dust. IMO publishes a bimonthly journal called ''WGN''WGN = "werkgroepnieuws" (Dutch language), in English as "workgroup news". WGN was initially a circular before it became a journal. and holds an annual International Meteor Conference (IMC) in September.IMO website. See also *American Meteor Society The American Meteor Society, Ltd. (AMS) is a non-profit scientific organization established to encourage and support the research activities of both amateur and professional astronomers who are interested in the field of meteor astrono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Phase
A lunar phase or Moon phase is the apparent shape of the Moon's directly sunlit portion as viewed from the Earth. Because the Moon is tidally locked with the Earth, the same hemisphere is always facing the Earth. In common usage, the four major phases are the new moon, the first quarter, the full moon and the last quarter; the four minor phases are waxing crescent, waxing gibbous, waning gibbous, and waning crescent. A lunar month is the time between successive recurrences of the same phase: due to the eccentricity of the Moon's orbit, this duration is not perfectly constant but averages about 29.5 days. The appearance of the Moon (its phase) gradually changes over a lunar month as the relative orbital positions of the Moon around Earth, and Earth around the Sun, shift. The visible side of the Moon is sunlit to varying extents, depending on the position of the Moon in its orbit, with the sunlit portion varying from 0% (at new moon) to nearly 100% (at full moon). Phenomenon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zenithal Hourly Rate
In astronomy, the zenithal hourly rate (ZHR) of a meteor shower is the number of meteors a single observer would see in an hour of peak activity if the radiant was at the zenith, assuming the seeing conditions are perfect (when and where stars with apparent magnitudes up to 6.5 are visible to the naked eye). The rate that can effectively be seen is nearly always lower and decreases the closer the radiant is to the horizon. Calculation The formula to calculate the ZHR is: ZHR = \cfrac where \overline = \cfrac represents the hourly rate of the observer. N is the number of meteors observed, and Teff is the effective observation time of the observer. Example: If the observer detected 12 meteors in 15 minutes, their hourly rate was 48 (12 divided by 0.25 hours). F = \cfrac This represents the field of view The field of view (FOV) is the angle, angular extent of the observable world that is visual perception, seen at any given moment. In the case of optical instrume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meteor Falling Courtesy NASA
A meteor, known colloquially as a shooting star, is a glowing streak of a small body (usually meteoroid) going through Earth's atmosphere, after being heated to incandescence by collisions with air molecules in the upper atmosphere, creating a streak of light via its rapid motion and sometimes also by shedding glowing material in its wake. Although a meteor may seem to be a few thousand feet from the Earth, meteors typically occur in the mesosphere at altitudes from . The root word ''meteor'' comes from the Greek ''meteōros'', meaning "high in the air". Millions of meteors occur in Earth's atmosphere daily. Most meteoroids that cause meteors are about the size of a grain of sand, i.e. they are usually millimeter-sized or smaller. Meteoroid sizes can be calculated from their mass and density which, in turn, can be estimated from the observed meteor trajectory in the upper atmosphere. Meteors may occur in showers, which arise when Earth passes through a stream of debris left by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |