|
Arab Gas Pipeline
The Arab Gas Pipeline is a natural gas pipeline in the Middle East. It originates near Arish in the Sinai Peninsula and was built to export Egyptian natural gas to Jordan, Syria, and Lebanon, with branch underwater and overland pipelines to and from Israel. It has a total length of , constructed at a cost of US$1.2 billion. History The pipeline has been used intermittently since its inauguration. Egyptian gas exports were reduced dramatically in 2011 – initially due to sabotage (mostly to its feeder pipeline in Sinai), followed by natural gas shortages in Egypt which forced it to discontinue gas exports by the mid-2010s. Sections of the pipeline continued to operate in Jordan to facilitate domestic transport of gas. The pipeline was reversed to flow gas from Jordan to Egypt from 2015 to 2018 (fed by imported LNG through Jordan's Aqaba LNG reception terminal). The recovery in Egyptian gas production has enabled gas to flow to Jordan through the link from 2018. In 2020 the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Gas
Natural gas (also fossil gas, methane gas, and gas) is a naturally occurring compound of gaseous hydrocarbons, primarily methane (95%), small amounts of higher alkanes, and traces of carbon dioxide and nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide and helium. Methane is a colorless and odorless gas, and, after carbon dioxide, is the second-greatest greenhouse gas that contributes to global climate change. Because natural gas is odorless, a commercial odorizer, such as Methanethiol (mercaptan brand), that smells of hydrogen sulfide (rotten eggs) is added to the gas for the ready detection of gas leaks. Natural gas is a fossil fuel that is formed when layers of organic matter (primarily marine microorganisms) are thermally decomposed under oxygen-free conditions, subjected to intense heat and pressure underground over millions of years. The energy that the decayed organisms originally obtained from the sun via photosynthesis is stored as chemical energy within the molecules of methane and other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amman
Amman ( , ; , ) is the capital and the largest city of Jordan, and the country's economic, political, and cultural center. With a population of four million as of 2021, Amman is Jordan's primate city and is the largest city in the Levant region, the fifth-largest city in the Arab world, and the tenth-largest metropolitan area in the Middle East. The earliest evidence of settlement in Amman dates to the 8th millennium BC in 'Ain Ghazal, home to the world's oldest statues of the human form. During the Iron Age, the city was known as ''Rabat Aman'', the capital of the Ammonite Kingdom. In the 3rd century BC, the city was renamed ''Philadelphia'' and became one of the ten Greco-Roman cities of the Decapolis. Later, in the 7th century AD, the Rashidun Caliphate renamed the city Amman. Throughout most of the Islamic era, the city alternated between periods of devastation and periods of relative prosperity. Amman was largely abandoned during the Ottoman period from the 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neve Ur
Neve Ur () is a kibbutz in northern Israel. Located in the Beit She'an Valley on the Jordan River and to the south of the Sea of Galilee, it falls under the jurisdiction of Valley of Springs Regional Council. In it had a population of . Etymology The kibbutz is named after the Biblical town of Ur of the Chaldees, Ur Kasdim (Ur of the Chaldees) in Mesopotamia, where Abraham lived before he left for the land of Canaan, the future land of Israel (). Historical and archaeological sites Prehistory Mesolithic, including Late Mesolithic Natufian remains were excavated in Neve Ur, as well as Pre-Pottery Neolithic A stone and bone tools. Belvoir Fortress On the west side of Highway 90 and some 500 meters above, overlooking Neve Ur's hillside citrus groves, is the most completely preserved Kingdom of Jerusalem , Crusader fortress in Israel, the Belvoir Fortress (Israel), Belvoir Fortress. Its Hebrew name is Kokhav HaYarden (lit. ''Star of the Jordan''), for the nearby ancient Jewish vil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
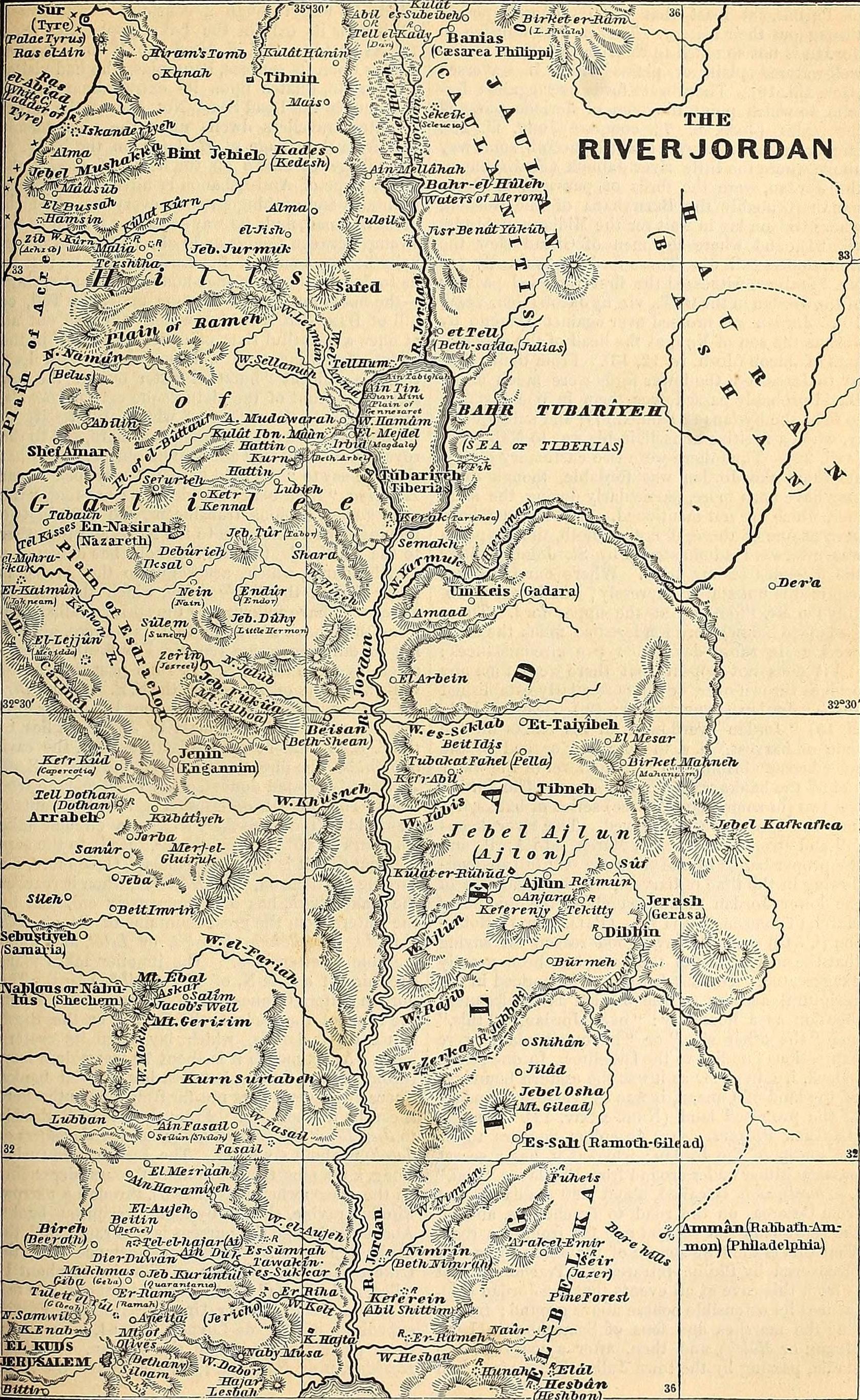
Jordan River
The Jordan River or River Jordan (, ''Nahr al-ʾUrdunn''; , ''Nəhar hayYardēn''), also known as ''Nahr Al-Sharieat'' (), is a endorheic river in the Levant that flows roughly north to south through the Sea of Galilee and drains to the Dead Sea. The river passes by or through Jordan, Syria, Israel, and the Palestinian territories. Jordan and the Israeli-occupied Golan Heights border the river to the east, while Israel and the Israeli-occupied West Bank lie to its west. Both Jordan and the West Bank derive their names in relation to the river. The river holds major significance in Judaism and Christianity. According to the Bible, the Israelites crossed it into the Promised Land and Jesus of Nazareth was baptized by John the Baptist in it. Etymology Several hypotheses for the origin of most of the river's names in modern languages (e.g., Jordan, Yarden, Urdunn), one is that it comes from Semitic 'Yard, on' 'flow down' <√ירד reflecting the river's declivity, possibly a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aqaba Thermal Power Plant
The Aqaba Thermal Power Station is the largest power station in Jordan. It has a total generation capacity of 656 MW, which consists of five steam turbines units (5 x 130 MW), and two hydraulic turbines (2 x 3 MW). The power station is fueled by natural gas and by fuel oil. It is operated by the Central Electricity Generating Company of Jordan. The Aqaba Thermal Power Station was established in 1986 as an oil-fueled power station. After construction of the Arab Gas Pipeline The Arab Gas Pipeline is a natural gas pipeline in the Middle East. It originates near Arish in the Sinai Peninsula and was built to export Egyptian natural gas to Jordan, Syria, and Lebanon, with branch underwater and overland pipelines to and ..., the power station was switched to use natural gas. References Aqaba Oil-fired power stations in Jordan Natural gas-fired power stations in Jordan {{jordan-struct-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Sea
The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez—leading to the Suez Canal. It is underlain by the Red Sea Rift, which is part of the Great Rift Valley. The Red Sea has a surface area of roughly , is about long, and wide at its widest point. It has an average depth of , and in the central Suakin Trough, it reaches its maximum depth of . Approximately 40% of the Red Sea is quite shallow at less than deep and about 25% is less than deep. The extensive shallow shelves are noted for their marine life and corals. More than 1,000 invertebrate species and 200 types of soft and hard coral live in the sea. The Red Sea is the world's northernmost tropical sea and has been designated a Global 200 ecoregion. Extent The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taba (Egypt)
Taba ( ', ) is a town in the South Sinai Governorate, South Sinai of Egypt, near the northern tip of the Gulf of Aqaba. Taba is the location of one of Egypt's busiest Taba Border Crossing, border crossings. It is the northernmost resort of Egypt's Red Sea Riviera. History In 1906, Taba became the center of a territorial dispute between the British Empire and the Ottoman Empire, known as the "Taba Crisis." Although the Sinai Peninsula was nominally Ottoman, it had been largely administered by Egypt, except for the Aqaba region, which had been officially under Ottoman administration since 1892. When the Ottomans began plans to extend the Hejaz railway to the Gulf of Aqaba, potentially challenging British influence in the Red Sea via the Suez Canal, Britain dispatched Lieutenant Bramly with a small Egyptian force to establish police stations in the region. Upon encountering Ottoman troops already positioned in Taba — territory the British claimed as Egyptian — they demanded t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinai Peninsula
The Sinai Peninsula, or simply Sinai ( ; ; ; ), is a peninsula in Egypt, and the only part of the country located in Asia. It is between the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Red Sea to the south, and is a land bridge between Asia and Africa. Sinai has a land area of about (6 percent of Egypt's total area) and a population of approximately 600,000 people. Administratively, the vast majority of the area of the Sinai Peninsula is divided into two Governorates of Egypt, governorates: the South Sinai Governorate and the North Sinai Governorate. Three other governorates span the Suez Canal, crossing into African Egypt: Suez Governorate on the southern end of the Suez Canal, Ismailia Governorate in the center, and Port Said Governorate in the north. In the classical era, the region was known as Arabia Petraea. The peninsula acquired the name ''Sinai'' in modern times due to the assumption that a mountain near Saint Catherine's Monastery is the Biblical Mount Sinai. Mount Sinai i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq. The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western European nations in the early 20th century as a replacement of the term Near East (both were in contrast to the Far East). The term "Middle East" has led to some confusion over its changing definitions. Since the late 20th century, it has been criticized as being too Eurocentrism, Eurocentric. The region includes the vast majority of the territories included in the closely associated definition of West Asia, but without the South Caucasus. It also includes all of Egypt (not just the Sinai Peninsula, Sinai) and all of Turkey (including East Thrace). Most Middle Eastern countries (13 out of 18) are part of the Arab world. The list of Middle Eastern countries by population, most populous countries in the region are Egypt, Turkey, and Iran, whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleppo
Aleppo is a city in Syria, which serves as the capital of the Aleppo Governorate, the most populous Governorates of Syria, governorate of Syria. With an estimated population of 2,098,000 residents it is Syria's largest city by urban area, and was the largest by population until it was surpassed by Damascus, the capital of Syria. Aleppo is also the largest city in Syria's Governorates of Syria, northern governorates and one of the List of largest cities in the Levant region by population, largest cities in the Levant region. Aleppo is one of List of cities by time of continuous habitation#West Asia, the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world; it may have been inhabited since the sixth millennium BC. Excavations at Tell as-Sawda and Tell al-Ansari, just south of the old city of Aleppo, show that the area was occupied by Amorites by the latter part of the third millennium BC. That is also the time at which Aleppo is first mentioned in cuneiform tablets unearthed in Ebl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baniyas
Baniyas ( ') is a Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coastal city in Tartous Governorate, western Syria, located south of Latakia and north of Tartous. It is known for its citrus fruit orchards and its export of wood. North of the city is an Baniyas Refinery, oil refinery, the largest in Syria, and a power station. The oil refinery is connected with Iraq by the Kirkuk–Baniyas pipeline (now defunct). On a nearby hill stands the Crusader castle of Margat (Qalaat el-Marqab), a huge Knights Hospitaller fortress built with black basalt stone. History Ancient In Phoenician and Hellenistic times, it was an important seaport. Some have identified it with the Hellenistic city of Leucas (from colonists from the island Lefkada), in Greece, mentioned by Stephanus of Byzantium. It was a colony of Arwad, Aradus,Strabo, ''Geographica'', 16.2.12Greek sourcean and was placed by Stephanus in the late Roman province of Phoenice (Roman province), Phoenicia, though it belonged rather to the prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |