|
Zwicken
Zwicken is an old Austrian and Germany, German card game for 4 to 6 players, which is usually played for small stakes and makes a good party game. It is one of the Rams group of card games characterised by allowing players to drop out of the current game if they think they will be unable to win any tricks or a minimum number of tricks. King (playing card), King > Ober (playing card), Ober/Queen (playing card), Queen > Unter (playing card), Unter/Jack (playing card), Jack > Ten > Nine > Eight > Seven. However, as the permanent, second highest trump – the 7/7 – outranks all cards except for the Trump Sow. Description Zwicken is a very common Austrian and German gambling game that is usually played for small stakes and makes a good party game. It is like a more intense version of the German game of Tippen – the general rules and mode of play are much the same – but there are significant differences, especially its permanent trump, the 7, and its 'hop and jump' (''Hupf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tippen
Tippen, also known as Dreiblatt, Dreikart, Drei Karten, Dreekort, Kleinpréférence or Labet, is an historical Germany, German 3-card, plain-trick game which was popular as a gambling game for three or more players. The Danish version of the game was known as Trekort and more elaborate Swedish variants include Knack (card game), Knack and Köpknack. It appears to be related to the English game of Three-Card Loo. It was banned as a gambling game in some places. History and etymology The game was described in 19th century anthologies and encyclopedias but appears related to 3-card Lanterloo, Loo, which was already described in the 18th century. In some locations the game was illegal. Dreiblatt is recorded as early as 1807 as a gambling game in which players received three cards, and Tippen is mentioned in 1790 as a gambling game similar to Grobhäusern and Trischak. In 1810 it is briefly described as follows: "Tippen... each of the participants in the game is deal (cards), dealt 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mauscheln
Mauscheln, also Maus or Vierblatt, is a gambling card game that resembles Tippen, which is commonly played in Germany and the countries of the old Austro-Hungarian Empire. Background Origin of the name The name Mauscheln means something like "(secretive) talk". According to ''Meyers Konversationslexikon'' of 1885 to 1892 the word ''Mauschel'' is derived from the Hebrew word ''moscheh'' "Moses", in Ashkenazi Hebrew ''Mausche, Mousche,'' and was a nickname for Jews; in Old German ''mauscheln'' means something like "speak with a Jewish accent" or haggle". The word first surfaced in the 17th century.Isabel Enzenbach: ''Mauscheln.'' In: Wolfgang Benz (ed.): ''Handbuch des Antisemitismus.'' Vol. 3: ''Begriffe, Ideologien, Theorien.'' De Gruyter Saur, Berlin 2008, ISBN 978-3-598-24074-4, p. 205 (retrieved via De Gruyter Online). Today ''mauscheln'' is a synonym for "scheme", "wheel and deal", "wangle" or "diddle". Other names for the game include Anschlagen (in Tyrol and Lower Austr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mistigri (card Game)
Mistigri, historically Pamphile, is an old, French, trick-taking card game for three or four players that has elements reminiscent of poker. It is a member of the Rams family of games and, although it is a gambling game, often played for small stakes, it is also suitable as a party game or as a family game with children from the age of 12 upwards. Name Mistigri is a variant of Mouche (card game), ''Mouche'' or ''Lenterlu'' and a cousin of the English Lanterloo. It is known in Germany as Mönch ("monk"), possibly a corruption of the French ''Mouche'' as ''Monche'' was the old German for monk. Meyer certainly equates it to ''Mouche'', ''Lenturla'' and ''Pamphile'', while Grupp also states that it is known as ''trente et un'' ("thirty-one") in French, but Méry's research shows that Mistigri was derived from ''Mouche'' (which was also called ''Lenturlu'') and was first named ''Pamphile''. It is related to the historical card game of Tippen. The game is named after the "mistigri" (F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contra (card Game)
Kontraspiel, also called Contra, is a German 5-card plain-trick game for four individual players using 24 cards. Eldest hand has the first right to accept or make trumps. The Unters of Acorns and Leaves (the equivalent of the two black Jacks) are permanent highest trumps, the ''Wenzels''. Kontraspiel is similar to the Scandinavian game Polskpas and is recorded as early as 1811. History The earliest mention of Contra appears in a list of games in a 1755 poem. In 1773 it is described as one of the games played with "German cards" i.e. a 32-card German-suited pack, and, in 1786 it was reported that, along with Trischaken, it was a very popular game among the peasants in German-speaking lands.Cella, Johann Jakob''Freymüthige Aufsätze'' Vol. 3. Anspach: Benedikt Friedrich Haueisens, p. 161 The earliest rules appeared in the same 1773 source under a separate entry, but the first comprehensive account is given in Hammer's 1811 edition of ''Die deutschen Kartenspiele''. and then re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
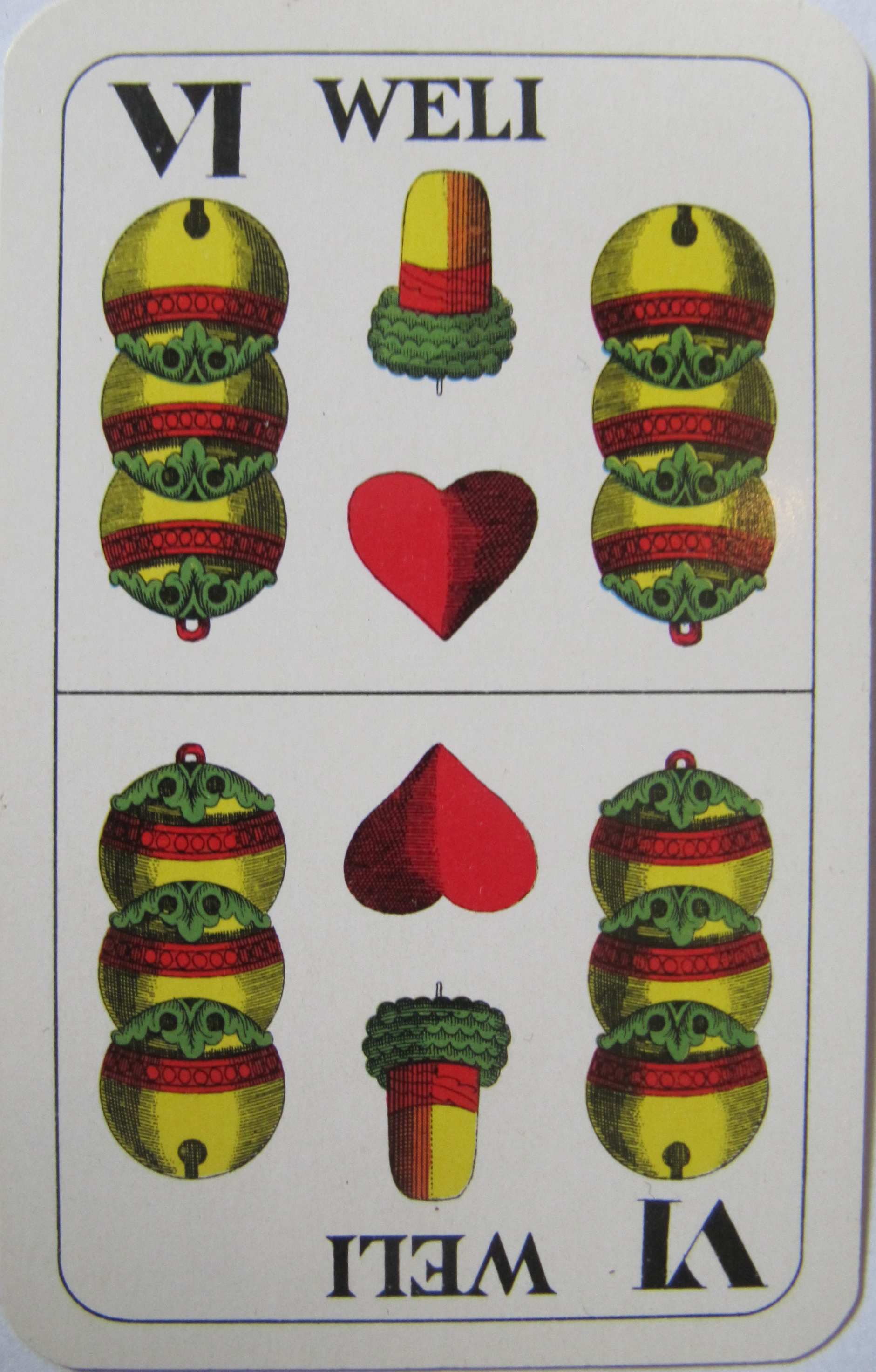
Kratzen
Kratzen is an Austrian card game for three to six players that is played for small stakes usually using a 33-card William Tell pack. It is a member of the Rams group of card games characterised by allowing players to drop out of the current game if they think they will be unable to win any tricks or a minimum number of tricks. Unter > Ten > Nine > Eight > Seven. In the trump suit, the ''Weli'' is just below the Trump Sow. Playing The following rules are taken from kartenspiele.net, the source recommended by Geiser. The game is in two phases. In the first phase, players may not drop out and they contribute an ante to the pot. In the second phase, the aim is to win the contents of the pot, but players may drop out for an individual hand if they think they are unlikely to take the minimum number of tricks. First phase – ''Muss'' The first deal is a 'force' or ''Muss'' i.e. everyone has to participate; there is no option to 'drop out'. Each player pays an ante into the pot; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lupfen (card Game)
Lupfen is a card game for 3–5 players that is played mainly in west Austria and south Germany, but also in Liechtenstein. The rules vary slightly from region to region, but the basic game in each variation is identical. It is one of the Rams group of card games characterised by allowing players to drop out of the current game if they think they will be unable to win any tricks or a minimum number of tricks.''Card Games: Rams Group'' at www.pagat.com. Retrieved 16 Oct 2018Geiser, Remigius (2004). "100 Kartenspiele des Landes Salzburg" in ''Talon'', Issue 13, p. 38. History In many ways, Lupfen res ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ober (playing Card)
The Ober, formerly Obermann, in Austrian also called the Manderl, is the court card in the German and Swiss styles of playing cards that corresponds in rank to the Queen in French packs. The name ''Ober'' (lit.: "over") is an abbreviation of the former name for these cards, ''Obermann'', which meant something like 'superior' or 'lord'. Van der Linde argues that the King, Ober and Unter in a pack of German cards represented the military ranks of general, officer (''Oberofficier'') and sergeant (''Unterofficier''), while the pip cards represented the common soldier. The figure depicted on an Ober is usually a nobleman or officer. It is distinguished from the lowest court card, the Unter (lit. "under", formerly ''Untermann'' or "vassal", "subject", "subordinate"), by the figure's suit sign located in the upper range of the card. In the Württemberg pattern the Ober appears on horseback, as they were inspired by Cego packs whose face cards included a Knight or Cavalier as we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Bavaria
The Kingdom of Bavaria ( ; ; spelled ''Baiern'' until 1825) was a German state that succeeded the former Electorate of Bavaria in 1806 and continued to exist until 1918. With the unification of Germany into the German Empire in 1871, the kingdom became a federated state of the new empire and was second in size, power, and wealth only to the leading state, the Kingdom of Prussia. The polity's foundation dates back to the ascension of Elector Maximilian IV Joseph of the House of Wittelsbach as King of Bavaria in 1806. The crown continued to be held by the Wittelsbachs until the kingdom came to an end in 1918. Most of the border of modern Germany's Free State of Bavaria was established after 1814 with the Treaty of Paris, in which the Kingdom of Bavaria ceded Tyrol and Vorarlberg to the Austrian Empire while receiving Aschaffenburg and Würzburg. In 1918, Bavaria became a republic after the German Revolution, and the kingdom was thus succeeded by the current Free State of Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sow (playing Card)
The deuce (, plural: ''Däuser'') is the playing card with the highest value in German card games. It may have derived its name from dice games in which the face of the die with two pips is also called a ''Daus'' in German.''Games played with German suited cards'' at www.pagat.com. Retrieved 26 May 2018. Unlike the , with which it may be confused, the ''deuce'' represents the 2, which is why two hearts, bells, etc. are depicted on the card. In many regions it is not only equated to the ace, but is also, incorrectly, called an ace. In the south German area it has been historically called the sow (''Sau'') and still is today, because of the appearance of a |
King (playing Card)
The king is a playing card with a picture of a king displayed on it. The king is usually the highest-ranking face card. In the French version of playing cards and tarot decks, the king immediately outranks the queen. In Italian and Spanish playing cards, the king immediately outranks the knight. In German and Swiss playing cards, the king immediately outranks the '' Ober''. In some games, the king is the highest-ranked card; in others, the Ace is higher. Aces began outranking kings around 1500 with Trappola being the earliest known game in which the aces were highest in all four suits. In the ace–ten family of games such as pinochle and Schnapsen, both the ace and the 10 rank higher than the king. History The king card is the oldest and most universal court card. It most likely originated in Persian Ganjifeh where kings are depicted as seated on thrones and outranking the viceroy cards which are mounted on horses. Playing cards were transmitted to Italy and Spain via ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plain-trick
A trick-taking game is a card game, card- or tile-based game in which play of a ''Hand (card games), hand'' centers on a series of finite rounds or units of play, called ''tricks'', which are each evaluated to determine a winner or ''taker'' of that trick. The object of such games then may be closely tied to the number of tricks taken, as in plain-trick games such as contract bridge, whist, and Spades (card game), spades, or to the value of the cards contained in taken tricks, as in point-trick games such as pinochle, the Tarot card games, tarot family, briscola, and most evasion games like Hearts (card game), hearts. Trick-and-draw games are trick-taking games in which the players can fill up their hands after each trick. In most variants, players are free to play any card into a trick in the first phase of the game, but must ''follow suit'' as soon as the stock is depleted. Trick-avoidance games like reversis or Polignac (card game), polignac are those in which the aim is to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |