|
Zwick Roell Group
The Zwick Roell Group is a manufacturer of static testing machines and systems for materials and components testing used to evaluate the mechanical and physical properties and performance of materials and components. Core static tests carried out with this equipment includes tensile, compression, flexure (also referred to as bend), and cycling. The company operates in 56 countries, has manufacturing facilities in Germany and the UK, and strategic headquarters in the USA and Singapore. As of 2014 the Group employs 1250 staff in its international operations. It generates revenues of approximately 210 million euros. Zwick manufactures a range of testing systems for research and routine testing of materials and components. It has developed materials testing software, digital contact and non contact extensometry and pioneered robotic materials testing systems. History Roell & Korthaus have been involved in materials testing since 1920. Zwick began building machines and instru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Materials Testing
Materials testing is used to assess product quality, functionality, safety, reliability and toxicity of both materials and electronic devices. Some applications of materials testing include defect detection, failure analysis, material development, basic materials science research, and the verification of material properties for application trials. This is a list of organizations and companies that publish materials testing standards or offer materials testing laboratory services. International organizations for materials testing These organizations create materials testing standards or conduct active research in the fields of materials analysis and reliability testing. * American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists (AATCC) * American National Standards Institute (ANSI) * American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) * American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) * ASTM International * Federal Institute for Materials Research and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Properties
A physical property is any property that is measurable, whose value describes a state of a physical system. The changes in the physical properties of a system can be used to describe its changes between momentary states. Physical properties are often referred to as observables. They are not modal properties. A quantifiable physical property is called physical quantity. Physical properties are often characterized as intensive and extensive properties. An intensive property does not depend on the size or extent of the system, nor on the amount of matter in the object, while an extensive property shows an additive relationship. These classifications are in general only valid in cases when smaller subdivisions of the sample do not interact in some physical or chemical process when combined. Properties may also be classified with respect to the directionality of their nature. For example, isotropic properties do not change with the direction of observation, and anisotropic properti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tension (physics)
In physics, tension is described as the pulling force transmitted axially by the means of a string, a rope, chain, or similar object, or by each end of a rod, truss member, or similar three-dimensional object; tension might also be described as the action-reaction pair of forces acting at each end of said elements. Tension could be the opposite of compression. At the atomic level, when atoms or molecules are pulled apart from each other and gain potential energy with a restoring force still existing, the restoring force might create what is also called tension. Each end of a string or rod under such tension could pull on the object it is attached to, in order to restore the string/rod to its relaxed length. Tension (as a transmitted force, as an action-reaction pair of forces, or as a restoring force) is measured in newtons in the International System of Units (or pounds-force in Imperial units). The ends of a string or other object transmitting tension will exert forces on the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compression (physical)
In mechanics, compression is the application of balanced inward ("pushing") forces to different points on a material or structure, that is, forces with no net sum or torque directed so as to reduce its size in one or more directions.Ferdinand Pierre Beer, Elwood Russell Johnston, John T. DeWolf (1992), "Mechanics of Materials". (Book) McGraw-Hill Professional, It is contrasted with tension or traction, the application of balanced outward ("pulling") forces; and with shearing forces, directed so as to displace layers of the material parallel to each other. The compressive strength of materials and structures is an important engineering consideration. In uniaxial compression, the forces are directed along one direction only, so that they act towards decreasing the object's length along that direction. The compressive forces may also be applied in multiple directions; for example inwards along the edges of a plate or all over the side surface of a cylinder, so as to reduce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bending
In applied mechanics, bending (also known as flexure) characterizes the behavior of a slender structural element subjected to an external load applied perpendicularly to a longitudinal axis of the element. The structural element is assumed to be such that at least one of its dimensions is a small fraction, typically 1/10 or less, of the other two.Boresi, A. P. and Schmidt, R. J. and Sidebottom, O. M., 1993, Advanced mechanics of materials, John Wiley and Sons, New York. When the length is considerably longer than the width and the thickness, the element is called a beam. For example, a closet rod sagging under the weight of clothes on clothes hangers is an example of a beam experiencing bending. On the other hand, a shell is a structure of any geometric form where the length and the width are of the same order of magnitude but the thickness of the structure (known as the 'wall') is considerably smaller. A large diameter, but thin-walled, short tube supported at its ends an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensometer
An extensometer is a device that is used to measure changes in the length of an object. It is useful for Stress (physics), stress-Strain (materials science), strain measurements and tensile tests. Its name comes from "extension-meter". It was invented by Charles Huston who described it in an article in the ''Journal of the Franklin Institute'' in 1879. Huston later gave the rights to Fairbanks & Ewing, a major manufacturer of testing machines and scales. Types There are two main types of extensometers: ''contact'' and ''non-contact''. Contact ''Contact extensometers'' have been used for many years and are also subdivided into two further categories. The first type of contact extensometer is called a ''clip-on'' extensometer. These devices are used for applications where high precision strain measurement is required (most ASTM based tests). They come in many configurations and can measure displacements from very small to relatively large (less than a mm to over 100 mm) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robotic
Robotics is an interdisciplinary branch of computer science and engineering. Robotics involves design, construction, operation, and use of robots. The goal of robotics is to design machines that can help and assist humans. Robotics integrates fields of mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, information engineering, mechatronics, electronics, bioengineering, computer engineering, control engineering, software engineering, mathematics, etc. Robotics develops machines that can substitute for humans and replicate human actions. Robots can be used in many situations for many purposes, but today many are used in dangerous environments (including inspection of radioactive materials, bomb detection and deactivation), manufacturing processes, or where humans cannot survive (e.g. in space, underwater, in high heat, and clean up and containment of hazardous materials and radiation). Robots can take any form, but some are made to resemble humans in appearance. This is claimed t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vickers Hardness Test
The Vickers hardness test was developed in 1921 by Robert L. Smith and George E. Sandland at Vickers Ltd as an alternative to the Brinell method to measure the hardness of materials. The Vickers test is often easier to use than other hardness tests since the required calculations are independent of the size of the indenter, and the indenter can be used for all materials irrespective of hardness. The basic principle, as with all common measures of hardness, is to observe a material's ability to resist plastic deformation from a standard source. The Vickers test can be used for all metals and has one of the widest scales among hardness tests. The unit of hardness given by the test is known as the Vickers Pyramid Number (HV) or Diamond Pyramid Hardness (DPH). The hardness number can be converted into units of pascals, but should not be confused with pressure, which uses the same units. The hardness number is determined by the load over the surface area of the indentation and not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
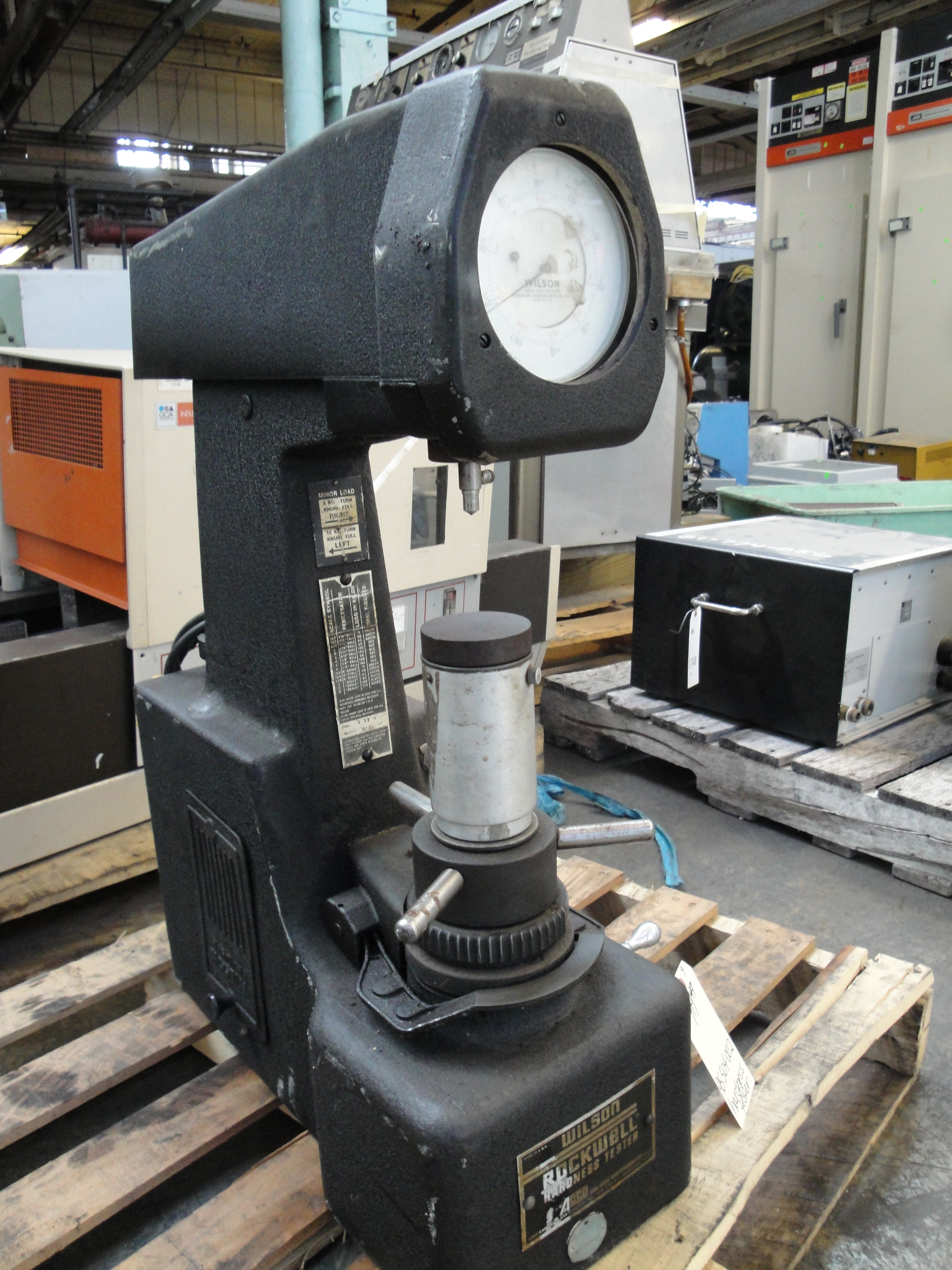
Rockwell Scale
The Rockwell scale is a hardness scale based on indentation hardness of a material. The Rockwell test measures the depth of penetration of an indenter under a large load (major load) compared to the penetration made by a preload (minor load). There are different scales, denoted by a single letter, that use different loads or indenters. The result is a dimensionless number noted as HRA, HRB, HRC, etc., where the last letter is the respective Rockwell scale. When testing metals, indentation hardness correlates linearly with tensile strength. History The differential depth hardness measurement was conceived in 1908 by Viennese professor Paul Ludwik in his book ''Die Kegelprobe'' (crudely, "the cone test"). The differential-depth method subtracted out the errors associated with the mechanical imperfections of the system, such as backlash and surface imperfections. The Brinell hardness test, invented in Sweden, was developed earlier – in 1900 – but it was slow, not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brinell Scale
The Brinell scale characterizes the indentation hardness of materials through the scale of penetration of an indenter, loaded on a material test-piece. It is one of several definitions of hardness in materials science. History Proposed by Swedish engineer Johan August Brinell in 1900, it was the first widely used and standardised hardness test in engineering and metallurgy. The large size of indentation and possible damage to test-piece limits its usefulness. However, it also had the useful feature that the hardness value divided by two gave the approximate UTS in ksi for steels. This feature contributed to its early adoption over competing hardness tests. Test details The typical test uses a diameter steel ball as an indenter with a force. For softer materials, a smaller force is used; for harder materials, a tungsten carbide ball is substituted for the steel ball. The indentation is measured and hardness calculated as: :\operatorname=\frac where: :BHN = Brinell Hard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bending
In applied mechanics, bending (also known as flexure) characterizes the behavior of a slender structural element subjected to an external load applied perpendicularly to a longitudinal axis of the element. The structural element is assumed to be such that at least one of its dimensions is a small fraction, typically 1/10 or less, of the other two.Boresi, A. P. and Schmidt, R. J. and Sidebottom, O. M., 1993, Advanced mechanics of materials, John Wiley and Sons, New York. When the length is considerably longer than the width and the thickness, the element is called a beam. For example, a closet rod sagging under the weight of clothes on clothes hangers is an example of a beam experiencing bending. On the other hand, a shell is a structure of any geometric form where the length and the width are of the same order of magnitude but the thickness of the structure (known as the 'wall') is considerably smaller. A large diameter, but thin-walled, short tube supported at its ends an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charpy Impact Test
In materials science, the Charpy impact test, also known as the Charpy V-notch test, is a standardized high strain rate test which determines the amount of energy absorbed by a material during fracture. Absorbed energy is a measure of the material's notch toughness. It is widely used in industry, since it is easy to prepare and conduct and results can be obtained quickly and cheaply. A disadvantage is that some results are only comparative. The test was pivotal in understanding the fracture problems of ships during World War II. The test was developed around 1900 by S. B. Russell (1898, American) and Georges Charpy (1901, French). The test became known as the Charpy test in the early 1900s due to the technical contributions and standardization efforts by Charpy. History In 1896, S. B. Russell introduced the idea of ''residual fracture energy'' and devised a pendulum fracture test. Russell's initial tests measured un-notched samples. In 1897, Frémont introduced a test to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |