|
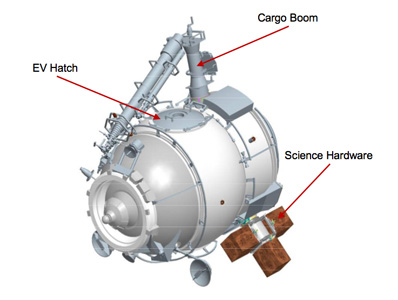
Zvezda (ISS Module)
''Zvezda'' (), also known as the ''Zvezda'' Service Module, is a module of the International Space Station (ISS). It was the third module launched to the station, and provided all of the station's life support systems, some of which are supplemented in the US Orbital Segment (USOS), as well as living quarters for two crew members. It is the structural and functional center of the Russian Orbital Segment (ROS), which is the Russian part of the ISS. Crew assemble here to deal with emergencies on the station. The module was manufactured in the USSR by Energia, with major sub-contracting work by GKNPTs Khrunichev. ''Zvezda'' was launched on a Proton launch vehicle on 12 July 2000, and docked with the ''Zarya'' module on 26 July 2000 at 01:45 UTC. It is a descendant of the ''Salyut'' programme's DOS spacecraft, leading to the alternate name, DOS-8. Origins The basic structural frame of ''Zvezda'', known as "DOS-8", was initially built in the mid-1980s to be the core ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-106
STS-106 was a 2000 Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) flown by Space Shuttle '' Atlantis''. Crew Spacewalks * '' Lu and Malenchenko '' – EVA 1 *EVA 1 Start: 11 September 2000 – 04:47 UTC *EVA 1 End: 11 September 2000 – 11:01 UTC *Duration: 6 hours, 14 minutes Mission highlights Space Station assembly flight ISS-2A.2b utilized the SPACEHAB Double Module and the Integrated Cargo Carrier (ICC) to bring supplies to the station. The mission also included one spacewalk. Veteran Astronaut Terrence Wilcutt (Col., USMC) led the seven-man crew, commanding his second Shuttle flight and making his fourth trip into space. During the planned 11-day mission, Wilcutt and his crew mates spent a week inside the ISS unloading supplies from both a double SPACEHAB cargo module in the rear of ''Atlantiss cargo bay and from a Russian Progress M-1 resupply craft docked to the aft end of the ''Zvezda'' Service Module. ''Zvezda'', which linked up to the ISS on 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salyut
The ''Salyut'' programme (russian: Салют, , meaning "salute" or "fireworks") was the first space station programme, undertaken by the Soviet Union. It involved a series of four crewed scientific research space stations and two crewed military reconnaissance space stations over a period of 15 years, from 1971 to 1986. Two other ''Salyut'' launches failed. In one respect, ''Salyut'' had the task of carrying out long-term research into the problems of living in space and a variety of astronomical, biological and Earth-resources experiments, and on the other hand the USSR used this civilian programme as a cover for the highly secretive military '' Almaz'' stations, which flew under the ''Salyut'' designation. ''Salyut'' 1, the first station in the programme, became the world's first crewed space station. ''Salyut'' flights broke several spaceflight records, including several mission-duration records, and achieved the first orbital handover of a space station from one cre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nauka (ISS Module)
''Nauka'' ( rus, Наука, p=nɐˈukə, litt. ''Science''), also known as the Multipurpose Laboratory Module-Upgrade (MLM-U; Russian: Многоцелевой лабораторный модуль, усоверше́нствованный, or ''МЛМ-У'') or simply Multipurpose Laboratory Module (MLM), is a module of the International Space Station (ISS). The MLM-U is funded by Roscosmos. In the original ISS plans, ''Nauka'' was to use the location of the Docking and Storage Module (DSM). Later, the DSM was replaced by the '' Rassvet'' module and ''Nauka'' was moved from '' Zarya''s nadir port to ''Zvezda''s nadir port. The launch of ''Nauka'', initially planned for 2007, was repeatedly delayed. By May 2020, ''Nauka'' was reported to be planned for launch in the second quarter of 2021, after which the manufacturer's warranties of some of ''Nauka''s components, such as engines, would have expired. ''Nauka'' was finally launched on 21 July 2021, 14:58 UTC, along with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poisk (ISS Module)
''Poisk'' (russian: Поиск, , Search), also known as the Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM 2), , or ''МИМ 2'', is a docking module of the International Space Station. Its original name was Docking Module 2 (, SO-2), as it is almost identical to the ''Pirs'' Docking Compartment. Added in 2009, ''Poisk'' was the first major Russian addition to the International Space Station since 2001. ''Poisk'' is overall the same design as the docking module ''Pirs''. Whereas ''Pirs'' had been attached to the nadir ("bottom") port of ''Zvezda'', ''Poisk'' is attached to the zenith ("top"); ''Pirs'' was closer to the Earth with the ISS in its usual orientation, and ''Poisk'' is on the other side. ''Poisk'' is Russian for ''explore'' or ''search''. ''Poisk'' combines various docking, EVA, and science capabilities. It has two egress hatches for EVAs in addition to the two spacecraft docking ports. Although ''Poisk'' is designated as Mini-Research Module 2, it arrived before Mini-Research Modu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pirs (ISS Module)
''Pirs'' ''(russian: Пирс'', meaning "pier Seaside pleasure pier in England.html" ;"title="Brighton, England">Brighton, England. The first seaside piers were built in England in the early 19th century. A pier is a raised structure that rises above a body of water and usually juts out ...") – also called Stykovochny Otsek 1 (SO-1; russian: Стыковочный отсек, "docking module") and DC-1 (Docking Compartment 1) – was a Russian module on the International Space Station (ISS). ''Pirs'' was launched on 14 September 2001, and was located on the ''Zvezda (ISS module), Zvezda'' module of the station. It provided the ISS with one Spacecraft docking and berthing mechanisms, docking port for Soyuz (spacecraft), Soyuz and Progress (spacecraft), Progress spacecraft, and allowed egress and ingress for Extra-vehicular activity, spacewalks by Astronaut, cosmonauts using Russian Orlan space suits. ''Pirs'' was docked to ''Zvezda'' for almost 20 years, until 26 July ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nadir
The nadir (, ; ar, نظير, naẓīr, counterpart) is the direction pointing directly ''below'' a particular location; that is, it is one of two vertical directions at a specified location, orthogonal to a horizontal flat surface. The direction opposite of the nadir is the zenith. Definitions Space science Since the concept of ''being below'' is itself somewhat vague, scientists define the nadir in more rigorous terms. Specifically, in astronomy, geophysics and related sciences (e.g., meteorology), the nadir at a given point is the local vertical direction pointing in the direction of the force of gravity at that location. The term can also be used to represent the lowest point that a celestial object reaches along its apparent daily path around a given point of observation (i.e. the object's ''lower culmination''). This can be used to describe the position of the Sun, but it is only technically accurate for one latitude at a time and only possible at the low latitudes. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James S
James is a common English language surname and given name: *James (name), the typically masculine first name James * James (surname), various people with the last name James James or James City may also refer to: People * King James (other), various kings named James * Saint James (other) * James (musician) * James, brother of Jesus Places Canada * James Bay, a large body of water * James, Ontario United Kingdom * James College, a college of the University of York United States * James, Georgia, an unincorporated community * James, Iowa, an unincorporated community * James City, North Carolina * James City County, Virginia ** James City (Virginia Company) ** James City Shire * James City, Pennsylvania * St. James City, Florida Arts, entertainment, and media * ''James'' (2005 film), a Bollywood film * ''James'' (2008 film), an Irish short film * ''James'' (2022 film), an Indian Kannada-language film * James the Red Engine, a character in ''Thom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yury Usachov
Yury Vladimirovich Usachov (russian: Юрий Владимирович Усачёв; born October 9, 1957) is a former cosmonaut who resides in Star City, Moscow. Usachov is a veteran of four spaceflights, including two long duration missions on board the '' Mir'' Space Station and another on board the International Space Station. During his career, he also conducted seven spacewalks before his retirement on April 5, 2004. Personal Married to Vera Sergeevna Usachova (née Nazarova) from the Kaliningrad. They have one daughter, Zhenya. His mother, Anna Grigorevna Usachova resides in Donetsk. His father is deceased. He has a brother, five years older, and a twin sister, five minutes older. He enjoys photography and video production. Education Usachov graduated from the Donetsk Public School in 1975. In 1985, he graduated from the Moscow Aviation Institute with an engineering diploma. Experience Upon graduation from the Aviation Institute, he went to work for Energia, participating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expedition 2
Expedition 2 (also called ISS EO-2) was the second long-duration spaceflight aboard the International Space Station, immediately following Expedition 1. Its three-person crew stayed aboard the station from March to August 2001. In addition to station maintenance, the crew assisted in several station assembly missions, welcomed the first space tourist Dennis Tito, and conducted some scientific experiments. The crew consisted of one Russian, Commander Yury Usachev, and two American flight engineers Susan Helms and James Voss. The three had been to the station briefly in the previous year, during the 10-day mission STS-101 in May 2000. The Expedition 2 crew was brought to the station aboard Space Shuttle ''Discovery'' during mission STS-102. The Expedition's increment began when ''Discovery'' docked on 10 March 2001, bringing Expedition 1 to an end. In addition to the Space Shuttle flights which brought the crew to and from the station, there were two visiting Space Shuttle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orlan Space Suit
270px, Cosmonaut Maksim Surayev next to two Orlan-MK models on the International Space Station image:Sharipov one.jpg, 270px, Cosmonaut Salizhan Sharipov, next to the Orlan-M spacesuit. The Orlan space suit (russian: Орлан, lit=Sea eagle (bird), sea eagle) is a series of semi-rigid one-piece space suit models designed and built by NPP Zvezda. They have been used for spacewalks (EVAs) in the Russian space program, the successor to the Soviet space program, and by space programs of other countries, including NASA. History The first spacewalk using an Orlan suit took place on December 20, 1977, on the Soviet space station Salyut 6, during the Soyuz 26 mission. Yuri Romanenko and Georgi Grechko tested the Orlan-D space suit. The Orlan-DM was used for the first time on August 2, 1985, by the cosmonauts Vladimir Dzhanibekov and Viktor Savinykh of Salyut 7. The Orlan space suits were used for spacewalks on the Salyut stations, but for Mir they were replaced by the Orlan-DM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universal Docking Module
The Universal Docking Module (UDM) (russian: Универсальный стыковочный модуль), was a planned Russian docking module for the International Space Station, to be jointly built by RKK Energia and Khrunichev. The ''Prichal'' nodal addition to the ''Nauka'' laboratory, the eventual form of the FGB-2 design upon which the UDM was based, grew out of this proposal. History The original design resembled ''Zarya'' but was larger. It would be docked to the nadir (Earth-facing) '' Zvezda'' service module docking port, and have four docking ports to accommodate the two Russian Research Module The Russian Research Module (RM) was to be a Russian component of the International Space Station (ISS) that provided facilities for Russian science experiments and research. History The original designs of ISS featured two research modules shape ...s and the SO2 docking compartment, later named '' Poisk''. Because one Russian Research Module was cancelled due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_(cropped).jpg)