|
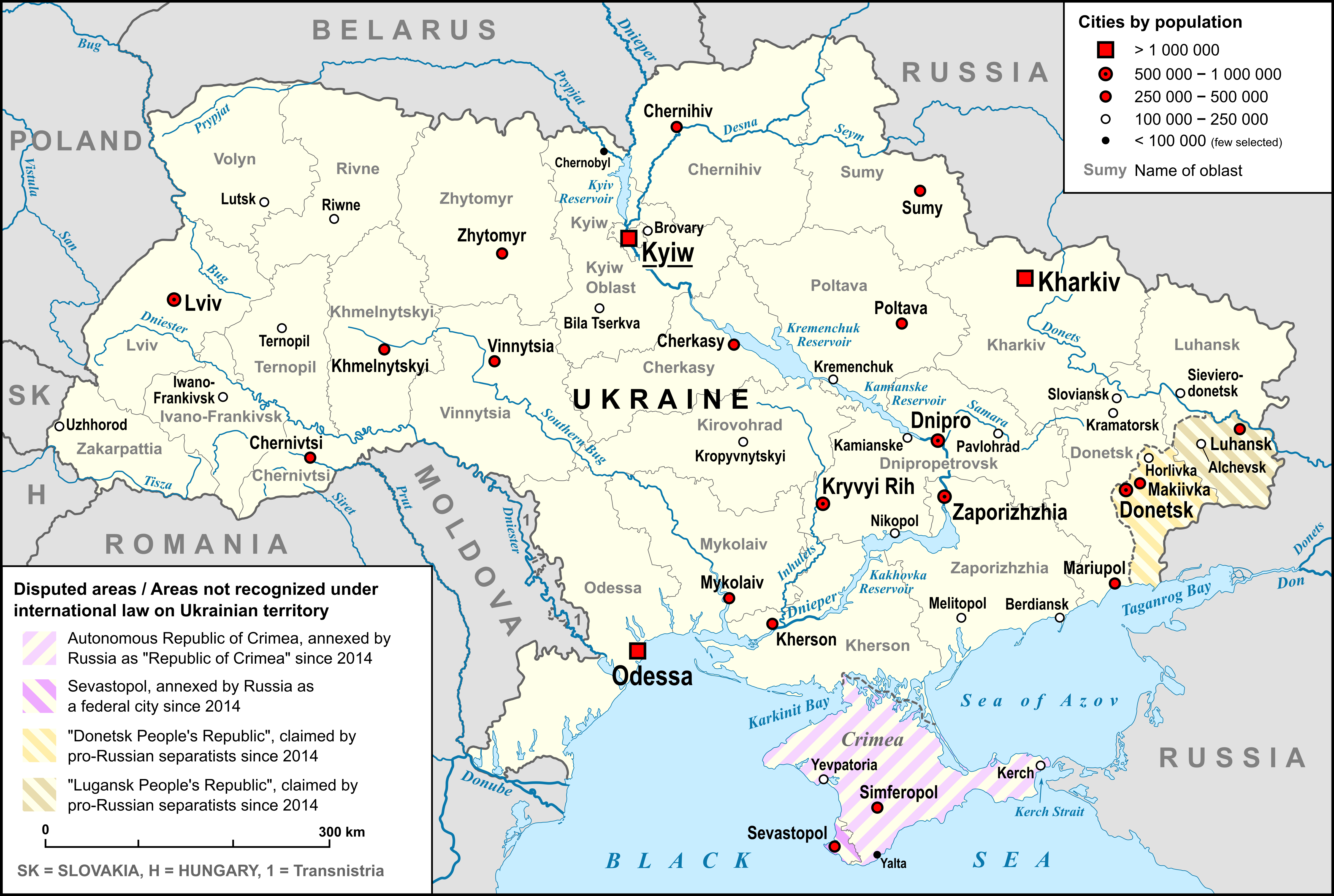
Zinkiv, Poltava Oblast
Zinkiv (, ; ) is a city on the Tashan River in the Poltava Oblast in central Ukraine. The city was previously the administrative center of the Zinkiv Raion until 2020, when it became part of the Poltava Raion. It hosts the administration of , one of the hromadas of Ukraine. The city's estimated population in 2022 was History The first recorded mention of Zinkiv was in 1604. The city was greatly affected by the Khmelnytsky Uprising, a Cossak rebellion between 1648 and 1657, which was accompanied by mass atrocities that destroyed the Jewish community in Zinkov. The city's importance grew during the 17th century Cossack Hetmanate. After the Polish–Cossack–Tatar War in the late 1660s, the city became an important fortification in the Poltava Regiment. By the mid-18th century, Hetman Kirill Razumovski had been granted jurisdiction of the city by Empress Elizabeth of Russia. By the 19th century, Zinkiv had flourishing manufacturing and trading industries. Population Languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cities In Ukraine
There are 463 populated places in Ukraine, populated places in Ukraine that have been officially granted city status () by the Verkhovna Rada, the country's parliament, as of 23 April 2025. Settlements with more than 10,000 people are eligible for city status although the status is typically also granted to settlements of historical or regional importance. Smaller settlements are Populated places in Ukraine#Rural settlements, rural settlements () and villages (). Historically, there were systems of city rights, granted by the territorial lords, which defined the status of a place as a ''misto'' or ''selo''. In the past, cities were self-governing and had several privileges. The list of cities is roughly ordered by population and the 2022 estimates are compared to the 2001 Ukrainian census, except for Chernobyl for which the population is an unofficial estimate. The City with special status, cities with special status are shown in ''italic''. The average population size is 62,000. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cossak
The Cossacks are a predominantly East Slavic Eastern Christian people originating in the Pontic–Caspian steppe of eastern Ukraine and southern Russia. Cossacks played an important role in defending the southern borders of Ukraine and Russia, countering the Crimean-Nogai raids, alongside economically developing steppe regions north of the Black Sea and around the Azov Sea. Historically, they were a semi-nomadic and semi-militarized people, who, while under the nominal suzerainty of various Eastern European states at the time, were allowed a great degree of self-governance in exchange for military service. Although numerous linguistic and religious groups came together to form the Cossacks, most of them coalesced and became East Slavic–speaking Orthodox Christians. The rulers of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Russian Empire endowed Cossacks with certain special privileges in return for the military duty to serve in the irregular troops: Zaporozhian Cossacks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau ( ; ; ), Jugendstil and Sezessionstil in German, is an international style of art, architecture, and applied art, especially the decorative arts. It was often inspired by natural forms such as the sinuous curves of plants and flowers. Other characteristics of Art Nouveau were a sense of dynamism and movement, often given by asymmetry or whiplash lines, and the use of modern materials, particularly iron, glass, ceramics and later concrete, to create unusual forms and larger open spaces.Sembach, Klaus-Jürgen, ''L'Art Nouveau'' (2013), pp. 8–30 It was popular between 1890 and 1910 during the Belle Époque period, and was a reaction against the academicism, eclecticism and historicism of 19th century architecture and decorative art. One major objective of Art Nouveau was to break down the traditional distinction between fine arts (especially painting and sculpture) and applied arts. It was most widely used in interior design, graphic arts, furniture, glass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
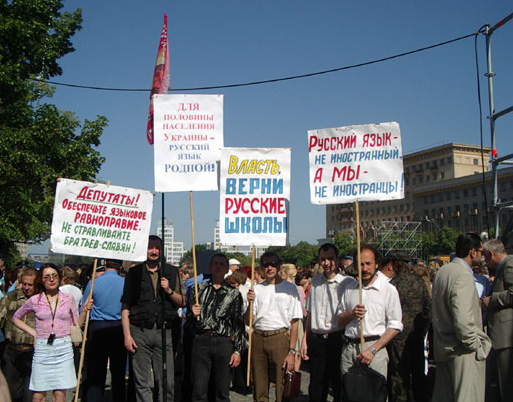
Russian Language In Ukraine
Russian language, Russian is the most common first language in the Donbas and Crimea regions of Ukraine and the city of Kharkiv, and the predominant language in large cities in the East Ukraine, eastern and South Ukraine, southern portions of the country. The usage and status of the language is the subject of political disputes. Ukrainian language, Ukrainian is the country's sole state language since the adoption of the Constitution of Ukraine, 1996 Constitution, which prohibits an official bilingual system at state level but also guarantees the free development, use and protection of Russian and other languages of national minorities. In 2017 a new ''Law on Education'' was passed which restricted the use of Russian as a language of instruction. Nevertheless, Russian remains a widely used language in Ukraine in pop culture and in informal and commerce, business communication. History of the Russian language in Ukraine The East Slavic languages originated in the language spoken ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrainian Language
Ukrainian (, ) is an East Slavic languages, East Slavic language, spoken primarily in Ukraine. It is the first language, first (native) language of a large majority of Ukrainians. Written Ukrainian uses the Ukrainian alphabet, a variant of the Cyrillic script. The standard language is studied by the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine and Potebnia Institute of Linguistics. Comparisons are often made between Ukrainian and Russian language, Russian, another East Slavic language, yet there is more mutual intelligibility with Belarusian language, Belarusian,Alexander M. Schenker. 1993. "Proto-Slavonic", ''The Slavonic Languages''. (Routledge). pp. 60–121. p. 60: "[The] distinction between dialect and language being blurred, there can be no unanimity on this issue in all instances..."C.F. Voegelin and F.M. Voegelin. 1977. ''Classification and Index of the World's Languages'' (Elsevier). p. 311, "In terms of immediate mutual intelligibility, the East Slavic zone is a sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elizabeth Of Russia
Elizabeth or Elizaveta Petrovna (; ) was Empress of Russia from 1741 until her death in 1762. She remains one of the most popular List of Russian rulers, Russian monarchs because of her decision not to execute a single person during her reign, her numerous construction projects, and her strong opposition to Prussian policies. She was the last person on the agnatic line of the Romanovs as Peter III of Russia, her nephew ascended, thus creating the house of Holstein-Gottorp-Romanov. The second-eldest daughter of Tsar Peter the Great (), Elizabeth lived through the confused successions of her father's descendants following her half-brother Alexei Petrovich, Tsarevich of Russia, Alexei's death in 1718. The throne first passed to her mother Catherine I of Russia (), then to her nephew Peter II of Russia, Peter II, who died in 1730 and was succeeded by Elizabeth's first cousin Anna of Russia, Anna (). After the brief rule of Anna's infant great-nephew, Ivan VI of Russia, Ivan VI, Eliz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empress Of Russia
The emperor and autocrat of all Russia (, ), also translated as emperor and autocrat of all the Russias, was the official title of the Russian monarch from 1721 to 1917. The title originated in connection with Russia's victory in the Great Northern War (17001721) and appeared as an adaptation of the tsar's title under the accepted system of titling in Europe. The title was transformed from the previous title of tsar and grand prince of all Russia. The old title ''tsar'' (or ''tsaritsa'') continued to be popularly used to refer to the emperor (or empress) until the monarchy was abolished in 1917. Title Article 1 of the '' Fundamental Laws of the Russian Empire'' stated that "the Emperor of All Russia is an autocratic and unrestricted monarch. To obey his supreme authority, not only out of fear but out of conscience as well, God himself commands". The full title of the emperor in the 20th century (Art. 37 of the Fundamental Laws) was: Tsarist autocracy History Peter I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirill Razumovski
Count Kirill Grigoryevich Razumovsky or Razumovski (also known as ''Cyril Razumovski''; ; ;Oleksander Ohloblyn. Rozumovsky, Kyrylo'. Encyclopedia of Ukraine – ) was a Russian statesman of Ukrainian Cossack origin who served as the last hetman of the Zaporozhian Host on both sides of the Dnieper (from 1750 to 1764) and then as a General field marshal in the Imperial Russian Army. Razumovsky was also the president of the St. Petersburg Imperial Academy of Sciences from 1746 to 1798. Biography Kirill Rozum was born into the Razumovsky family, at that time low-rank family of Cossack Grigory (Hryhoriy) Rozum in the settlement of Lemeshi in the (now in Chernihiv Raion, Chernihiv Oblast, Ukraine) on 18 March 1728.Putro, O. Kyrylo Rozumovsky (РОЗУМОВСЬКИЙ КИРИЛО ГРИГОРОВИЧ)'. Encyclopedia of History of Ukraine. From 1743 to 1744, Kirill Razumovsky incognito attended the University of Göttingen. Razumovsky's adjutant in his journey to Germany ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hetman Of The Zaporizhian Host
The Hetman of the Zaporozhian Host (, ) was the head of state of the Cossack Hetmanate. The office was abolished by the Russian government in 1764. Brief history The position was established by Bohdan Khmelnytsky during the Cossack Hetmanate in the mid 17th century. During that period the office was electoral. All elections, except for the first one, took place in the Senior Council in Chyhyryn which, until 1669, served as the capital of the Hetmanate. After the Pereiaslav Agreement of 1654, several senior cossacks sided with the Tsardom of Russia and, in 1663, they convened the Black Council of 1663 in Nizhyn which elected Ivan Briukhovetsky as an alternative hetman. Since the defeat of Petro Doroshenko in 1669, the title hetman was adapted by pro-Russian elected hetmans who resided in Baturyn. In the course of the Great Northern War one of them, Ivan Mazepa, decided to revolt against Russian rule in 1708, which later drew terrible consequences for the Cossack Hetmanate as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yad Vashem
Yad Vashem (; ) is Israel's official memorial institution to the victims of Holocaust, the Holocaust known in Hebrew language, Hebrew as the (). It is dedicated to preserving the memory of the Jews who were murdered; echoing the stories of the survivors; honoring Jews who fought against their Nazi oppressors and gentiles who selflessly aided Jews in need; and researching the phenomenon of the Holocaust in particular and genocide in general, with the aim of avoiding such events in the future. Yad Vashem's vision, as stated on its website, is: "To lead the documentation, research, education and commemoration of the Holocaust, and to convey the chronicles of this singular Jewish and human event to every person in Israel, to the Jewish people, and to every significant and relevant audience worldwide." Established in 1953, Yad Vashem is located on the Mount of Remembrance, on the western slope of Mount Herzl, a height in western Jerusalem, Above mean sea level, above sea level and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Institute Of Ukrainian Studies
The University of Alberta (also known as U of A or UAlberta, ) is a public research university located in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. It was founded in 1908 by Alexander Cameron Rutherford, the first premier of Alberta, and Henry Marshall Tory, the university's first president. It was enabled through the ''Post-secondary Learning Act.'' The university is considered a "comprehensive academic and research university" (CARU), which means that it offers a range of academic and professional programs that generally lead to undergraduate and graduate level credentials. The university comprises four campuses in Edmonton, an Augustana Campus in Camrose, and a staff centre in downtown Calgary. The original north campus consists of 150 buildings covering 50 city blocks on the south rim of the North Saskatchewan River valley, across and west from downtown Edmonton. About 37,000 students from Canada and 150 other countries participate in 400 programs in 18 faculties. The university is a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Encyclopedia Of Ukraine
The ''Encyclopedia of Ukraine'' (), published from 1984 to 2001, is a fundamental work of Ukrainian Studies. Development The work was created under the auspices of the Shevchenko Scientific Society in Europe (Sarcelles, near Paris). As the ''Encyclopedia of Ukrainian Studies'' it conditionally consists of two parts, the first being a general part that consists of a three volume reference work divided in to subjects or themes. The second part is a 10 volume encyclopedia with entries arranged alphabetically. The editor-in-chief of Volumes I and II (published in 1984 and 1988 respectively) was Volodymyr Kubijovyč. The concluding three volumes, with Danylo Husar Struk as editor-in-chief, appeared in 1993. The encyclopedia set came with a 30-page ''Map & Gazetteer of Ukraine'' compiled by Kubijovyč and Arkadii Zhukovsky. It contained a detailed fold-out map (scale 1:2,000,000). A final volume, ''Encyclopedia of Ukraine: Index and Errata'', containing only the index and a list ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |