|
Zenta-class Cruiser
The ''Zenta'' class was a group of three protected cruisers built for the Austro-Hungarian Navy in the 1890s. Design In January 1895, the senior officers of the Austro-Hungarian Navy decided to build two types of modern cruisers: large armored cruisers of around and smaller vessels of around . The latter were intended to screen the battleships of the main fleet, scouting for enemy vessels and protecting them from torpedo boat attacks; they would also serve abroad on foreign stations. In a preliminary meeting on 22 January, the naval command issued a set of basic specifications for the projected small cruiser; the length was to be , and the ship should carry an armament of eight guns and sixteen guns. The chief constructor, Josef Kuchinka, prepared the initial design based on specifications that had been issued by the naval command, and his proposal featured a top speed of and a cruising range of at a speed of . Since the speed of the new cruisers was the highest priority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pula
Pula (; also known as Pola, it, Pola , hu, Pòla, Venetian; ''Pola''; Istriot: ''Puola'', Slovene: ''Pulj'') is the largest city in Istria County, Croatia, and the seventh-largest city in the country, situated at the southern tip of the Istrian peninsula, with a population of 52,411 in 2021. It is known for its multitude of ancient Roman buildings, the most famous of which is the Pula Arena, one of the best preserved Roman amphitheaters. The city has a long tradition of wine making, fishing, shipbuilding, and tourism. It was the administrative centre of Istria from ancient Roman times until superseded by Pazin in 1991. History Pre-history Evidence of the presence of '' Homo erectus'' one million years ago has been found in the cave of Šandalja near Pula. Pottery from the Neolithic period (6000–2000 BC), indicating human settlement, has been found around Pula. In the Bronze Age (1800–1000 BC), a new type of settlement appeared in Istria, called 'gradine', or Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armored Cruiser
The armored cruiser was a type of warship of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It was designed like other types of cruisers to operate as a long-range, independent warship, capable of defeating any ship apart from a battleship and fast enough to outrun any battleship it encountered. For many decades, naval technology had not advanced far enough for designers to produce a cruiser which combined an armored belt with the long range and high speed required to fulfill its mission. For this reason, beginning in the 1880s and 1890s, many navies preferred to build protected cruisers, which only relied on a light armored deck to protect the vital parts of the ship. However, by the late 1880s, the development of modern rapid-fire breech-loading cannon and high-explosive shells made the reintroduction of side armor a necessity. The invention of face-hardened armor in the mid-1890s offered effective protection with less weight than previously. Varying in size, the armored cruiser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
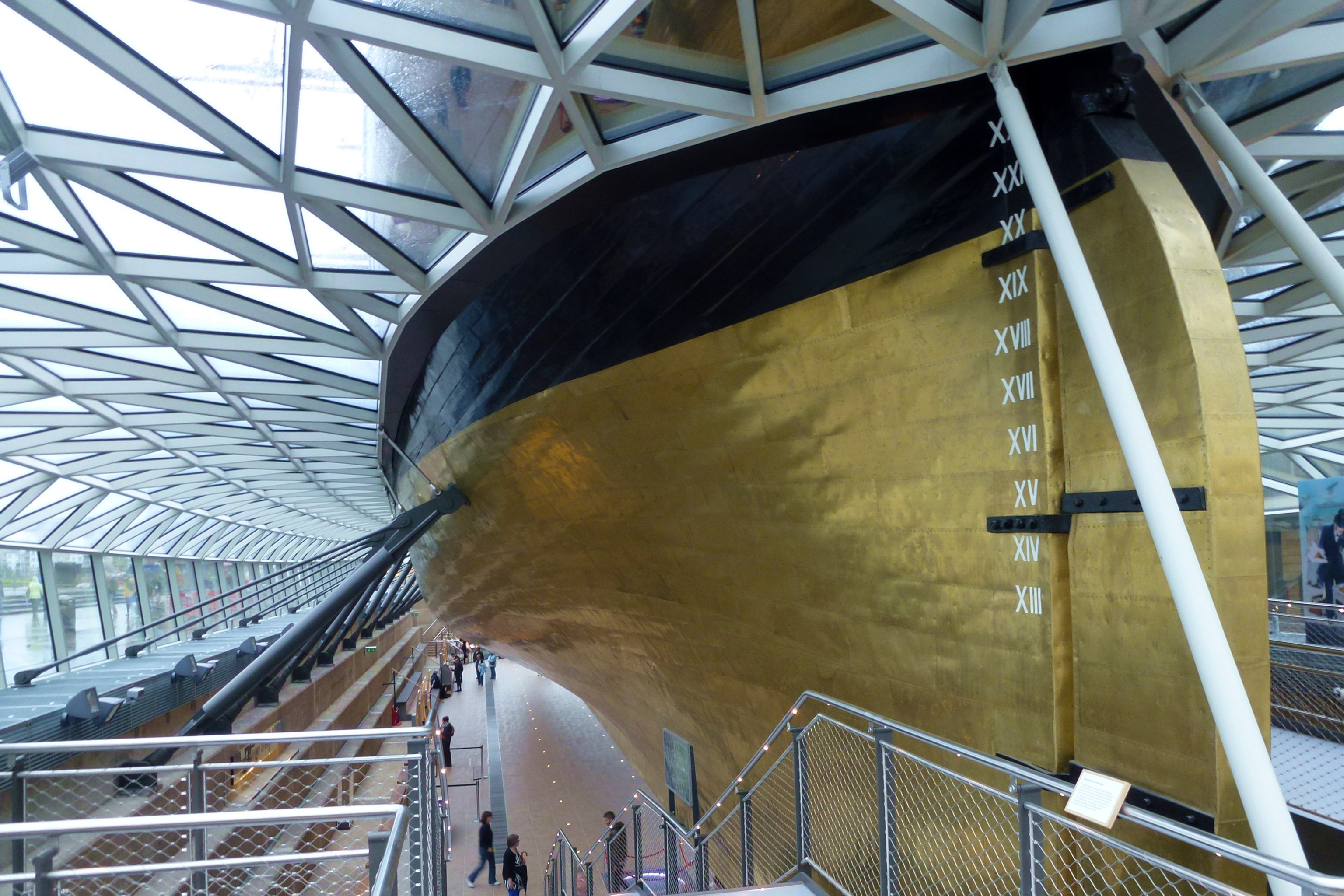
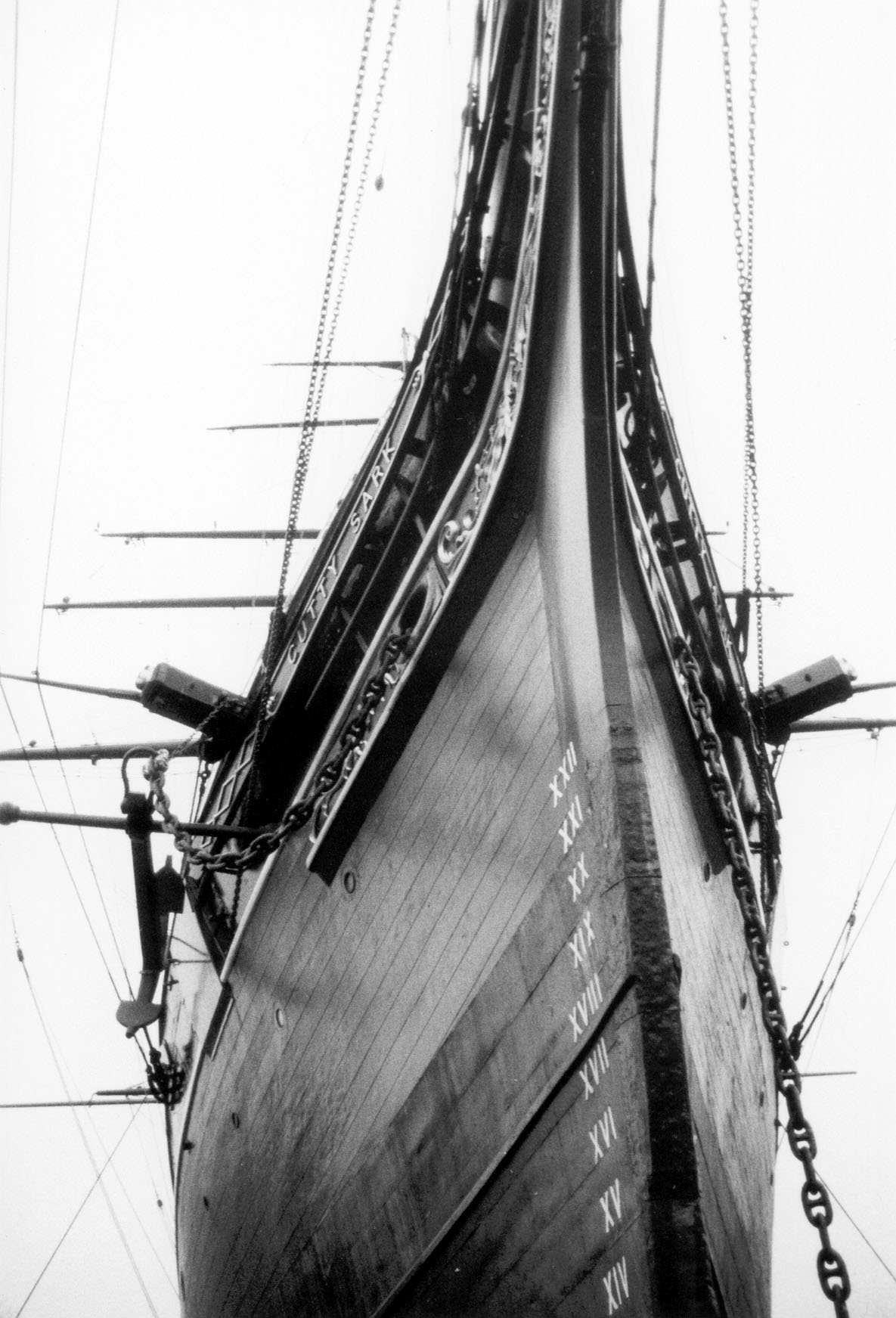
Copper Sheathing
Copper sheathing is the practice of protecting the under-water hull of a ship or boat from the corrosive effects of salt water and biofouling through the use of copper plates affixed to the outside of the hull. It was pioneered and developed by the Royal Navy during the 18th century. In antiquity, ancient Greeks used lead plates to protect the underwater hull. Development Deterioration of the hull of a wooden ship was a significant problem during the Age of Sail. Ships' hulls were under continuous attack by shipworm, barnacles and various marine weeds, all of which had some adverse effect on the ship, be it structurally, in the case of the worm, or affecting speed and handling in the case of the weeds. The most common methods of dealing with these problems were through the use of wood, and sometimes lead, sheathing. Expendable wood sheathing effectively provided a non-structural skin to the hull for the worm to attack, and could be easily replaced in dry dock at regular inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teak
Teak (''Tectona grandis'') is a tropical hardwood tree species in the family Lamiaceae. It is a large, deciduous tree that occurs in mixed hardwood forests. ''Tectona grandis'' has small, fragrant white flowers arranged in dense clusters (panicles) at the end of the branches. These flowers contain both types of reproductive organs (perfect flowers). The large, papery leaves of teak trees are often hairy on the lower surface. Teak wood has a leather-like smell when it is freshly milled and is particularly valued for its durability and water resistance. The wood is used for boat building, exterior construction, veneer, furniture, carving, turnings, and other small wood projects. ''Tectona grandis'' is native to south and southeast Asia, mainly Bangladesh, India, Indonesia, Malaysia, Myanmar, Thailand and Sri Lanka, but is naturalised and cultivated in many countries in Africa and the Caribbean. Myanmar's teak forests account for nearly half of the world's naturally occurring t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muntz Metal
Muntz metal (also known as yellow metal) is an alpha-beta brass alloy composed of approximately 60% copper, 40% zinc and a trace of iron. It is named after George Fredrick Muntz, a metal-roller of Birmingham, England, who commercialised the alloy following his patent of 1832. The alloy must be worked hot and is used today for corrosion-resistant machine parts. Alpha-beta (also called duplex) metals contain both the α and β phases. The α phase refers to a crystal structure that is face-centered cubic, while the β phase is body-centered cubic. Its original application was as a replacement for copper sheathing on the bottom of boats, as it maintained the anti-fouling abilities of the pure copper at around two thirds of the price. It became the material of choice for this application and Muntz made his fortune. It was found that copper would gradually leach from the alloy in sea water, poisoning any organism that attempted to attach itself to a hull sheathed in the metal. Thus, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
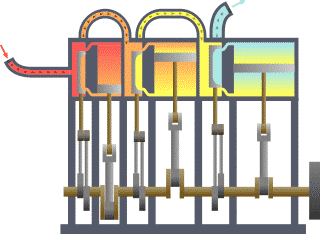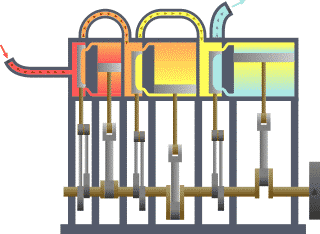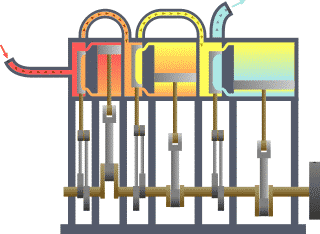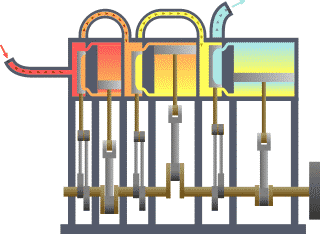
Triple-expansion Steam Engine
A compound steam engine unit is a type of steam engine where steam is expanded in two or more stages. A typical arrangement for a compound engine is that the steam is first expanded in a high-pressure ''(HP)'' cylinder, then having given up heat and losing pressure, it exhausts directly into one or more larger-volume low-pressure ''(LP)'' cylinders. Multiple-expansion engines employ additional cylinders, of progressively lower pressure, to extract further energy from the steam. Invented in 1781, this technique was first employed on a Cornish beam engine in 1804. Around 1850, compound engines were first introduced into Lancashire textile mills. Compound systems There are many compound systems and configurations, but there are two basic types, according to how HP and LP piston strokes are phased and hence whether the HP exhaust is able to pass directly from HP to LP ( Woolf compounds) or whether pressure fluctuation necessitates an intermediate "buffer" space in the form of a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waterline
The waterline is the line where the hull of a ship meets the surface of the water. Specifically, it is also the name of a special marking, also known as an international load line, Plimsoll line and water line (positioned amidships), that indicates the draft of the ship and the legal limit to which a ship may be loaded for specific water types and temperatures in order to safely maintain buoyancy, particularly with regard to the hazard of waves that may arise. Varying water temperatures will affect a ship's draft, because warm water is less dense than cold water, providing less buoyancy. In the same way, fresh water is less dense than salinated or seawater with a similar lessening effect upon buoyancy. For vessels with displacement hulls, the hull speed is defined by, among other things, the waterline length. In a sailing boat, the waterline length can change significantly as the boat heels, and can dynamically affect the speed of the boat. A waterline can also refer to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hull (watercraft)
A hull is the watertight body of a ship, boat, or flying boat. The hull may open at the top (such as a dinghy), or it may be fully or partially covered with a deck. Atop the deck may be a deckhouse and other superstructures, such as a funnel, derrick, or mast. The line where the hull meets the water surface is called the waterline. General features There is a wide variety of hull types that are chosen for suitability for different usages, the hull shape being dependent upon the needs of the design. Shapes range from a nearly perfect box in the case of scow barges to a needle-sharp surface of revolution in the case of a racing multihull sailboat. The shape is chosen to strike a balance between cost, hydrostatic considerations (accommodation, load carrying, and stability), hydrodynamics (speed, power requirements, and motion and behavior in a seaway) and special considerations for the ship's role, such as the rounded bow of an icebreaker or the flat bottom of a landing craft. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
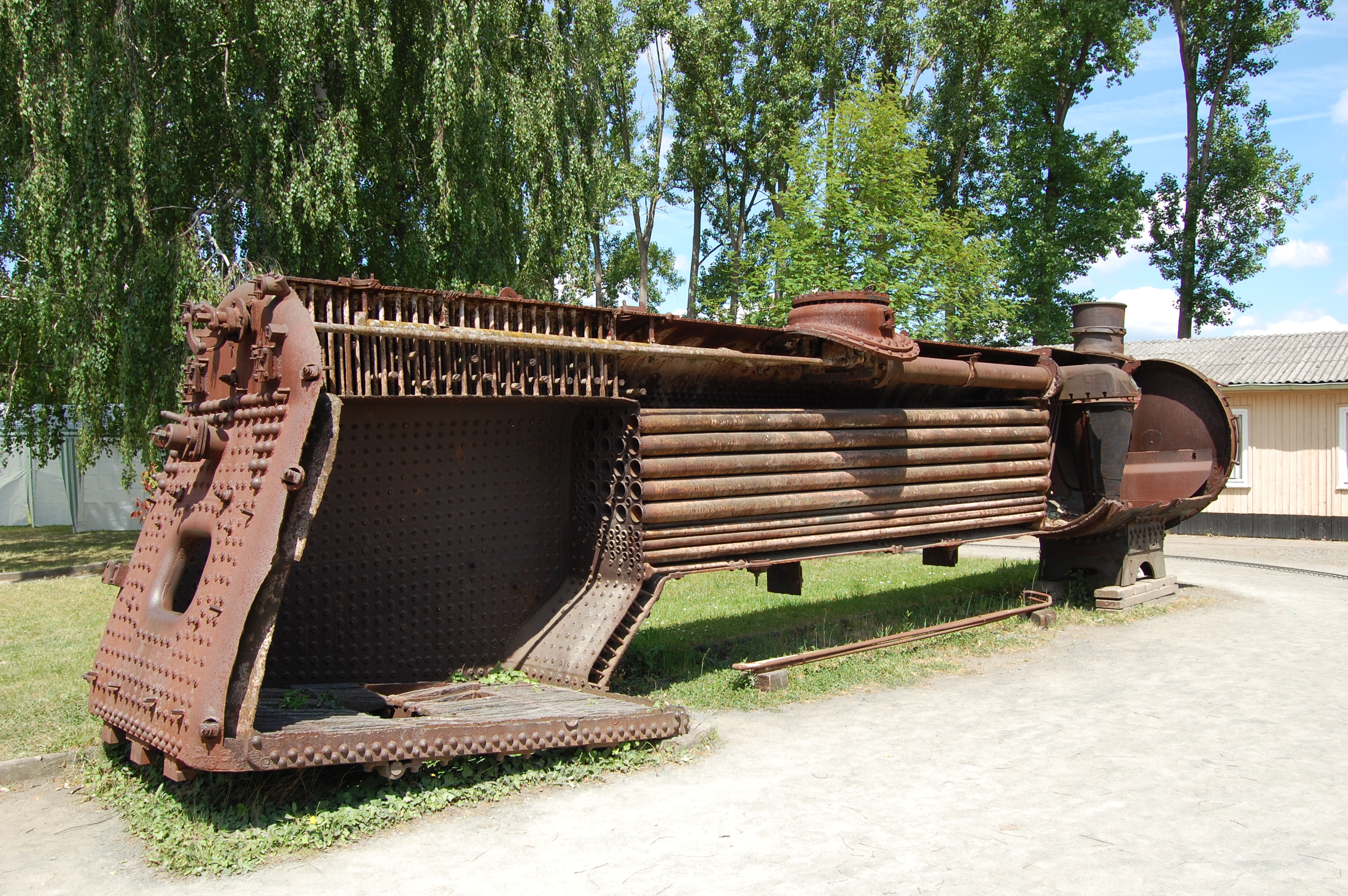
Locomotive Boiler
A fire-tube boiler is a type of boiler in which hot gases pass from a fire through one or more tubes running through a sealed container of water. The heat of the gases is transferred through the walls of the tubes by thermal conduction, heating the water and ultimately creating steam. The fire-tube boiler developed as the third of the four major historical types of boilers: low-pressure tank or " haystack" boilers, flued boilers with one or two large flues, fire-tube boilers with many small tubes, and high-pressure water-tube boilers. Their advantage over flued boilers with a single large flue is that the many small tubes offer far greater heating surface area for the same overall boiler volume. The general construction is as a tank of water penetrated by tubes that carry the hot flue gases from the fire. The tank is usually cylindrical for the most part—being the strongest practical shape for a pressurized container—and this cylindrical tank may be either horizontal or ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thornycroft Boiler
Three-drum boilers are a class of water-tube boiler used to generate steam, typically to power ships. They are compact and of high evaporative power, factors that encourage this use. Other boiler designs may be more efficient, although bulkier, and so the three-drum pattern was rare as a land-based stationary boiler. The fundamental characteristic of the "three-drum" design is the arrangement of a steam drum above two water drums, in a triangular layout. Water tubes fill in the two sides of this triangle between the drums, and the furnace is in the centre. The whole assembly is then enclosed in a casing, leading to the exhaust flue. Firing can be by either coal or oil. Many coal-fired boilers used multiple firedoors and teams of stokers, often from both ends. Development Development of the three-drum boiler began in the late 19th century, with the demand from naval ships that required high power and a compact boiler. The move to water-tube boilers had already begun, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boiler
A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid (generally water) is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, central heating, boiler-based power generation, cooking, and sanitation. Heat sources In a fossil fuel power plant using a steam cycle for power generation, the primary heat source will be combustion of coal, oil, or natural gas. In some cases byproduct fuel such as the carbon monoxide rich offgasses of a coke battery can be burned to heat a boiler; biofuels such as bagasse, where economically available, can also be used. In a nuclear power plant, boilers called steam generators are heated by the heat produced by nuclear fission. Where a large volume of hot gas is available from some process, a heat recovery steam generator or recovery boiler can use the heat to produce steam, with little or no extra fuel consumed; such a configuration i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |