|
Zenith Plateau
The Zenith Plateau is a large bathymetric high in the Indian Ocean, located about west-northwest of the Wallaby Plateau, west-northwest of Carnarvon, Western Australia, and north-west of Perth, Western Australia. The summit of the Zenith Plateau lies below sea level and its base is at about below sea level. It is about long and wide. In the east, the Zenith Plateau is separated from the Wallaby (Cuvier) Plateau by a wide, north to northeast-trending bathymetric trough.British Oceanographic Data Centre, 2003, ''GEBCO Digital Atlas.'' British Oceanographic Data Centre, National Environment Research Council, United Kingdom. The Zenith Plateau lies outside of the Australian Exclusive Economic Zone.Sayers, J., I. Borissova, D. Ramsay and P. A. Symonds. 2002, ''Geological framework of the Wallaby Plateau and adjacent areas.'' Record no. 2002/21. Petroleum & Marine Division, Geoscience Australia, Canberra, West Australia. As discussed by AmosAmos, J., 2014''Malaysia Airlines MH370 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bathymetry
Bathymetry (; ) is the study of underwater depth of seabed, ocean floors (''seabed topography''), lake floors, or river floors. In other words, bathymetry is the underwater equivalent to hypsometry or topography. The first recorded evidence of water depth measurements are from Ancient Egypt over 3000 years ago. Bathymetric (or hydrography, hydrographic) charts are typically produced to support safety of surface or sub-surface navigation, and usually show seafloor relief or terrain as contour lines (called depth contours or isobaths) and selected depths (''Depth sounding, soundings''), and typically also provide surface navigational information. Bathymetric maps (a more general term where navigational safety is not a concern) may also use a Digital Terrain Model and artificial illumination techniques to illustrate the depths being portrayed. The global bathymetry is sometimes combined with topography data to yield a global relief model. Paleobathymetry is the study of past underwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Rock
Volcanic rock (often shortened to volcanics in scientific contexts) is a rock formed from lava erupted from a volcano. In other words, it differs from other igneous rock by being of volcanic origin. Like all rock types, the concept of volcanic rock is artificial, and in nature volcanic rocks grade into hypabyssal and metamorphic rocks and constitute an important element of some sediments and sedimentary rocks. For these reasons, in geology, volcanics and shallow hypabyssal rocks are not always treated as distinct. In the context of Precambrian shield geology, the term "volcanic" is often applied to what are strictly metavolcanic rocks. Volcanic rocks and sediment that form from magma erupted into the air are called "volcaniclastics," and these are technically sedimentary rocks. Volcanic rocks are among the most common rock types on Earth's surface, particularly in the oceans. On land, they are very common at plate boundaries and in flood basalt provinces. It has been est ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaysia Airlines Flight 370
Malaysia Airlines Flight 370 (MH370/MAS370) was an international passenger flight operated by Malaysia Airlines that disappeared on 8 March 2014 while flying from Kuala Lumpur International Airport in Malaysia to its planned destination, Beijing Capital International Airport. The crew of the Boeing 777-200ER registered as 9M-MRO, last communicated with air traffic control (ATC) around 38 minutes after takeoff when the flight was over the South China Sea. The aircraft was lost from ATC radar screens minutes later, but was tracked by military radar for another hour, deviating westward from its planned flight path, crossing the Malay Peninsula and Andaman Sea. It left radar range northwest of Penang Island in northwestern Peninsular Malaysia. With all 227 passengers and 12 crew aboard presumed dead, the disappearance of Flight 370 was the deadliest incident involving a Boeing 777 and the deadliest in Malaysia Airlines' history until it was surpassed i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiocarbon Dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon. The method was developed in the late 1940s at the University of Chicago by Willard Libby. It is based on the fact that radiocarbon () is constantly being created in the Earth's atmosphere by the interaction of cosmic rays with atmospheric nitrogen. The resulting combines with atmospheric oxygen to form radioactive carbon dioxide, which is incorporated into plants by photosynthesis; animals then acquire by eating the plants. When the animal or plant dies, it stops exchanging carbon with its environment, and thereafter the amount of it contains begins to decrease as the undergoes radioactive decay. Measuring the amount of in a sample from a dead plant or animal, such as a piece of wood or a fragment of bone, provides information that can be used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foraminifera
Foraminifera (; Latin for "hole bearers"; informally called "forams") are single-celled organisms, members of a phylum or class of amoeboid protists characterized by streaming granular ectoplasm for catching food and other uses; and commonly an external shell (called a "test") of diverse forms and materials. Tests of chitin (found in some simple genera, and Textularia in particular) are believed to be the most primitive type. Most foraminifera are marine, the majority of which live on or within the seafloor sediment (i.e., are benthic), while a smaller number float in the water column at various depths (i.e., are planktonic), which belong to the suborder Globigerinina. Fewer are known from freshwater or brackish conditions, and some very few (nonaquatic) soil species have been identified through molecular analysis of small subunit ribosomal DNA. Foraminifera typically produce a test, or shell, which can have either one or multiple chambers, some becoming quite elaborate in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
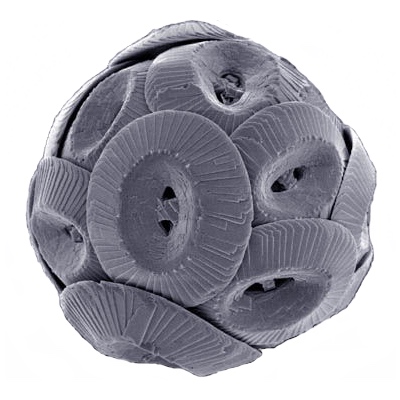
Coccolith
Coccoliths are individual plates or scales of calcium carbonate formed by coccolithophores (single-celled phytoplankton such as ''Emiliania huxleyi'') and cover the cell surface arranged in the form of a spherical shell, called a '' coccosphere''. Overview Coccolithophores are spherical cells about 5–100 micrometres across, enclosed by calcareous plates called coccoliths, which are about 2–25 micrometres across. Coccolithophores are an important group of about 200 marine phytoplankton species which cover themselves with a calcium carbonate shell called a "coccosphere". They are ecologically and biogeochemically important but the reason why they calcify remains elusive. One key function may be that the coccosphere offers protection against microzooplankton predation, which is one of the main causes of phytoplankton death in the ocean. Material was copied from this source, which is available under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License File:Cross section o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelite
A pelite (Greek: ''pelos'', "clay") or metapelite is a metamorphosed fine-grained sedimentary rock, i.e. mudstone or siltstone. The term was earlier used by geologists to describe a clay-rich, fine-grained clastic sediment or sedimentary rock, i.e. mud or a mudstone, the metamorphosed version of which would technically have been a ''metapelite''. It was equivalent to the now little-used Latin-derived term lutite.Potter, P.E., J.B. Maynard, and P.J. Depetris (2005) ''Muds and Mudstones.'' New York, New York, Springer. 279 pp. Neuendorf, K.K.E., J.P. Mehl, Jr., and J.A. Jackson, eds. (2005) ''Glossary of Geology'' (5th ed.). Alexandria, Virginia, American Geological Institute. 779 pp. A semipelite is defined in part as having similar chemical composition but being of a crystalloblastic nature. Pettijohn (1975) gives the following descriptive terms based on grain size, avoiding the use of terms such as clay or argillaceous which carry an implication of chemical composition. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelagic Sediment
Pelagic sediment or pelagite is a fine-grained sediment that accumulates as the result of the settling of particles to the floor of the open ocean, far from land. These particles consist primarily of either the microscopic, calcareous or siliceous shells of phytoplankton or zooplankton; clay-size siliciclastic sediment; or some mixture of these. Trace amounts of meteoric dust and variable amounts of volcanic ash also occur within pelagic sediments. Based upon the composition of the ooze, there are three main types of pelagic sediments: siliceous oozes, calcareous oozes, and red clays.Rothwell, R.G., (2005) ''Deep Ocean Pelagic Oozes'', Vol. 5. of Selley, Richard C., L. Robin McCocks, and Ian R. Plimer, Encyclopedia of Geology, Oxford: Elsevier Limited. HüNeke, H., and T. Mulder (2011) ''Deep-Sea Sediments''. Developments in Sedimentology, vol. 63. Elsiever, New York. 849 pp. The composition of pelagic sediments is controlled by three main factors. The first factor is the dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand and silt can be carried in suspension in river water and on reaching the sea bed deposited by sedimentation; if buried, they may eventually become sandstone and siltstone (sedimentary rocks) through lithification. Sediments are most often transported by water ( fluvial processes), but also wind ( aeolian processes) and glaciers. Beach sands and river channel deposits are examples of fluvial transport and deposition, though sediment also often settles out of slow-moving or standing water in lakes and oceans. Desert sand dunes and loess are examples of aeolian transport and deposition. Glacial moraine deposits and till are ice-transported sediments. Classification Sediment can be classified based on its grain size, grain sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
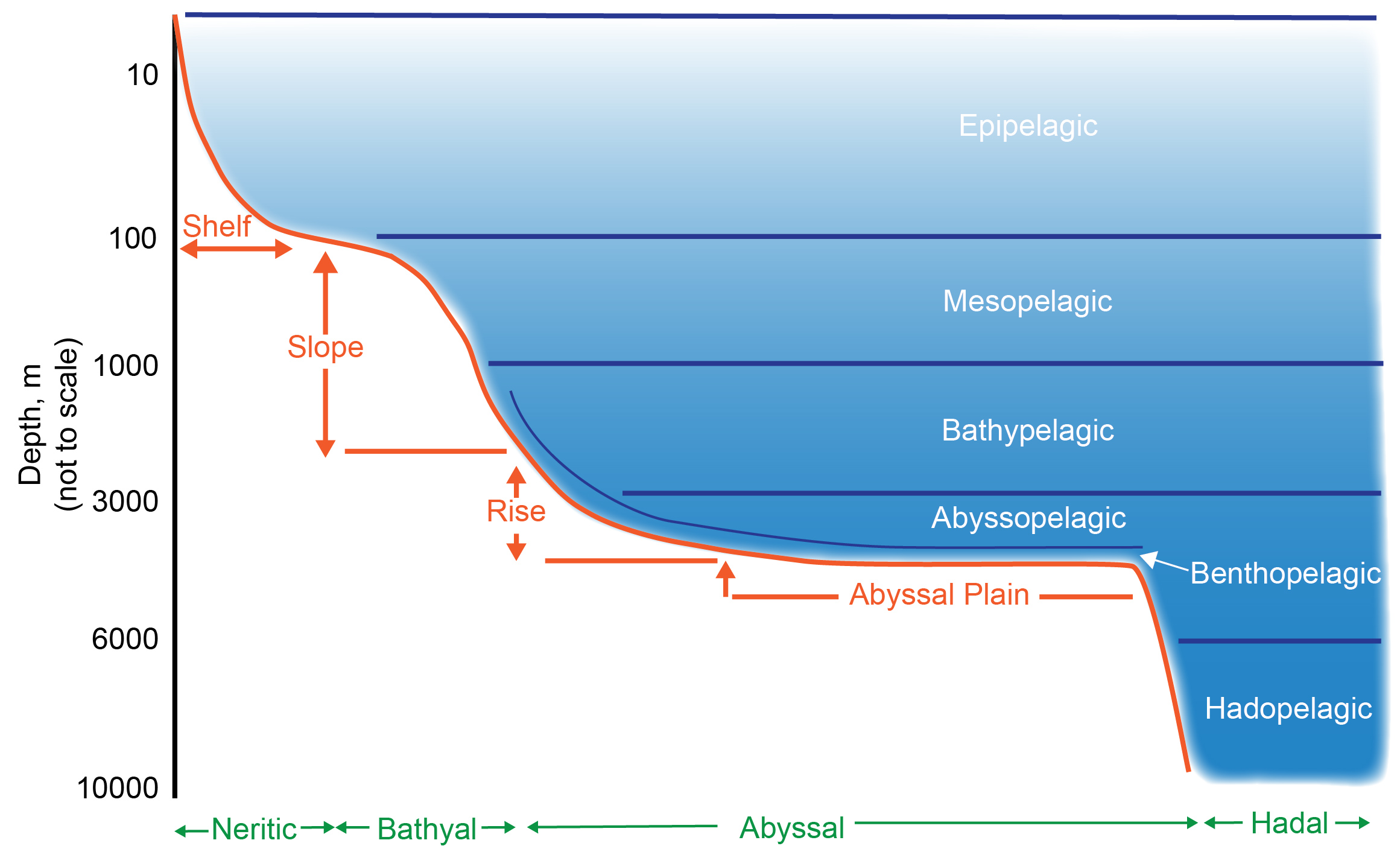
Deep Sea
The deep sea is broadly defined as the ocean depth where light begins to fade, at an approximate depth of 200 metres (656 feet) or the point of transition from continental shelves to continental slopes. Conditions within the deep sea are a combination of low temperatures, darkness and high pressure The deep sea is considered the least explored Earth biome, with the extreme conditions making the environment difficult to access and explore. Organisms living within the deep sea have a variety of adaptations to survive in these conditions. Organisms can survive in the deep sea through a number of feeding methods including scavenging, predation and filtration, with a number of organisms surviving by feeding on marine snow. Marine snow is organic material that has fallen from upper waters into the deep sea. In 1960, the bathyscaphe '' Trieste'' descended to the bottom of the Mariana Trench near Guam, at , the deepest known spot in any ocean. If Mount Everest () were submerged there, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configuration of continents. It is the latest of three geological eras since complex life evolved, preceded by the Mesozoic and Paleozoic. It started with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, when many species, including the non-avian dinosaurs, became extinct in an event attributed by most experts to the impact of a large asteroid or other celestial body, the Chicxulub impactor. The Cenozoic is also known as the Age of Mammals because the terrestrial animals that dominated both hemispheres were mammalsthe eutherians (placentals) in the northern hemisphere and the metatherians (marsupials, now mainly restricted to Australia) in the southern hemisphere. The extinction of many groups allowed mammals and birds to greatly diversify so tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |